Nowadays, businesses have many ways to reach their audiences. Digital and affiliate marketing are two of the top methods. Both aim to boost growth and visibility, but they work differently and have unique effects. Knowing the differences between affiliate marketing and digital marketing is key to creating a strategy that maximizes your brand’s potential and gets real results.
This article gives you clear explanations of both concepts, highlighting their differences and similarities. For a full understanding, you’ll find real-life examples at the end. Ready? Let’s explore digital and affiliate marketing!
Table of Contents
What is digital marketing?
Let’s start with the basics. Digital marketing refers to using online channels, platforms, and technologies to promote products, services, or brands to consumers. You may also encounter it under the name of online marketing or internet marketing.
This form of marketing covers many activities, like SEO/search engine optimization, content marketing, social media marketing, email marketing, online ads (such as Google Ads or social media ads), and affiliate marketing. In short, digital marketing uses the internet and electronic devices to reach potential customers where they spend much of their time: online.
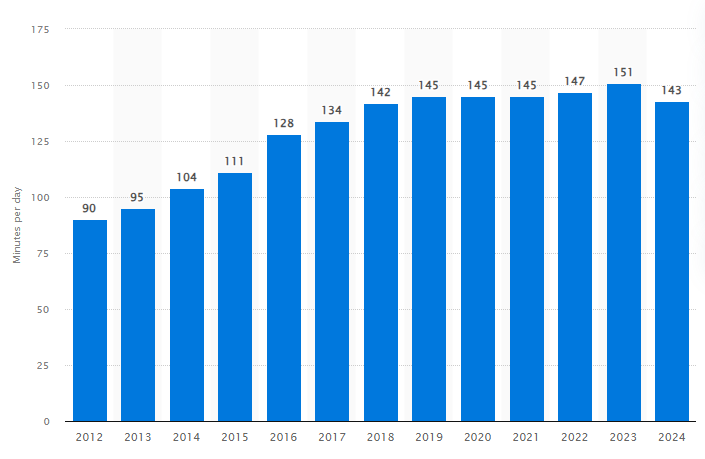
Did you know that by 2024, global digital ad spending is expected to hit
$740.3 billion? Plus, the average person spends almost 2.5 hours a day on social networks and messaging apps.
The core of digital marketing lies in personalization. To succeed, companies can target specific audiences with tailored messages, measure their campaigns’ success through data analytics, and adjust their strategies in real-time to maximize ROI.
What is affiliate marketing?
Affiliate marketing is an online marketing strategy where a third party, known as an affiliate, drives traffic or sales to a website. It’s often considered one of the best ways to earn passive income. As mentioned earlier, affiliate marketing is a part of digital marketing. Wondering how it works? Let’s break it down.
In affiliate marketing, you’ll come across these key terms:
- The merchant is the business that sells products or services and wants to boost online sales. They are the product owner.
- The affiliate (or affiliate marketer) is the person or company that promotes the merchant’s products through channels like blogs, social media, or email newsletters.
- The end user is the consumer who clicks on the affiliate’s content and makes a purchase on the merchant’s website.
Here’s how the process works:
- The affiliate joins the merchant’s affiliate program.
- The merchant gives the affiliate unique tracking links or codes for promotion.
- The affiliate promotes the merchant’s products using these links across various channels.
- A consumer clicks the affiliate link and is taken to the merchant’s website. If they make a purchase, the transaction is tracked via the unique link.
- The affiliate earns a commission, either a percentage of the sale or a fixed fee, as agreed upon with the merchant.
For businesses managing multiple affiliate programs and networks, tracking activities, or creating materials for affiliates, the right software is essential. Post Affiliate Pro can be a game-changer here, helping with every step of the affiliate journey.
Affiliate marketing vs digital marketing: differences from A to Z
Let us show and explain to you the most significant differences to fully understand both models. Digital marketing and affiliate marketing differ when it comes to:
Participants & control
In digital marketing, the main players are the brand or company promoting its products, the marketing teams or agencies running the campaigns, and the digital platforms like Google, Facebook, and Instagram where these campaigns are hosted. The brand controls its messaging, while the marketing team or agency manages strategies to reach the audience.
In affiliate marketing, three parties are involved: merchants, affiliates, and consumers. Unlike digital marketing, affiliates act as independent promoters, using their own methods and channels to drive traffic or sales to the brand’s website.
Dependency on platforms
Digital marketing depends heavily on specific platforms, such as search engines (Google, Bing), social media (Facebook, Instagram), and email services. Brands must adapt their strategies to the rules and algorithms of each platform to succeed. Changes in these algorithms can significantly impact campaign results.
Affiliate marketing, on the other hand, is less dependent on any single platform. Affiliates choose how and where to promote the brand, using various platforms, websites, blogs, and social media channels. This spread reduces the brand’s reliance on a single platform’s success or policies.
Resources
Running a digital marketing campaign usually requires significant resources, including a skilled marketing team, creative professionals like designers and writers, and technical support for SEO and analytics. The brand handles all aspects of the campaign, from planning to execution, which can be resource-heavy.
In affiliate marketing, the brand provides initial resources like banners, links, and guidelines, but the affiliates handle most of the promotional work. This allows the brand to tap into the affiliates’ resources and creativity, reducing the need for a large in-house team and focusing on managing affiliate relationships.
Budget flexibility
Digital marketing campaigns need a flexible budget, as costs can vary widely depending on the goals, platforms, and strategies used. Paid advertising often requires significant upfront investment, and brands must adjust their spending based on campaign performance and analytics.
Affiliate marketing is generally more budget-friendly and offers greater flexibility. The brand pays commissions only on successful conversions, so there are minimal upfront costs. This approach allows brands to scale their spending based on the program’s success, making budget management easier.
Content creation
Quality content is crucial for a successful marketing campaign. In digital marketing, the brand is responsible for creating all the content, including ads, blog posts, social media updates, videos, and emails. This requires ongoing effort to produce high-quality content that resonates with the target audience. Consistency is key, as digital marketers typically follow certain styles and formats aligned with the brand’s voice and goals.
In affiliate marketing, affiliates create their own content to promote the brand’s products. This content varies based on the affiliate’s style and audience, allowing for more personalized and authentic promotion. However, it also means the brand has less control over the content and how it represents the brand.
When considering content for your audience, think about these key questions:
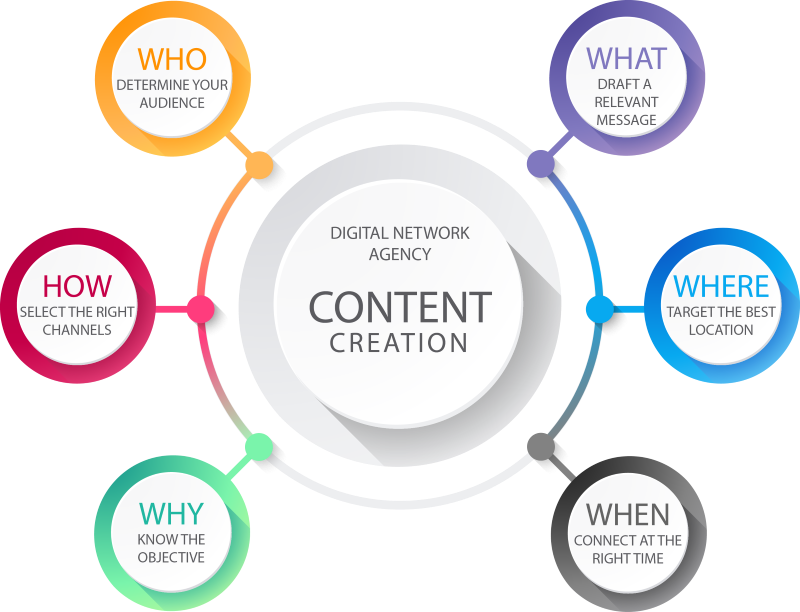
Types of promotional materials
In digital marketing, common promotional materials include videos, infographics, banners, social media posts, email newsletters, blog posts, and interactive content. The brand usually creates these materials in-house or through agencies to ensure they align with overall marketing tactics and brand guidelines.
Affiliates often use banners, text links, product reviews, and personalized recommendations. While the brand may provide some basic materials, affiliates typically customize them to suit their platform and audience, resulting in a more targeted promotional approach.
Ad placement options
In digital marketing, brands have control over where and when ads appear, allowing for precise targeting and optimization. Marketers place ads on specific platforms like Google, Facebook, Instagram, or YouTube, targeting certain demographics and audiences.
In affiliate marketing, affiliates decide where and how to place ads. The brand relies on the affiliate’s understanding of their audience and platform to achieve optimal results.
Effort
Digital marketing requires continuous effort from the brand, including planning campaigns, creating content, placing ads, and monitoring and optimizing results. Consistent effort is essential for maintaining a strong online presence and achieving marketing goals.
In affiliate marketing, much of the promotional work is done by affiliates. Once the program is set up and affiliates are onboarded, the brand’s main tasks are managing relationships, providing support, and tracking performance. This reduces the direct workload on the brand, allowing it to focus on other aspects of the online business.
Audience reach
In digital marketing, audience reach depends on the brand’s efforts, budget, and chosen platforms. Through targeted ads, SEO, and social media campaigns, brands can reach wide or specific audiences. However, this reach is often limited by budget and the effectiveness of the strategies used.
Affiliates, on the other hand, often have established relationships with niche audiences. This allows brands to tap into these markets more effectively, expanding their reach into areas that may be difficult to access through traditional digital marketing methods.
Brand visibility
Brand visibility in digital marketing is driven by the brand’s consistent efforts across various channels. By regularly creating and sharing content, running ads, and engaging with audiences, brands can stay top of mind and ensure exposure across multiple platforms.
In affiliate marketing, brand visibility is enhanced through the efforts of affiliates, who introduce the brand to their followers and audiences. This can lead to increased exposure, particularly in niche markets, and often feels more organic and trusted since it comes from a third-party recommendation.
Tracking and analytics
In digital marketing, tracking and analytics involve using tools like Google Analytics, social media insights, and ad platform dashboards to monitor campaign performance. Metrics such as impressions, clicks, conversions, and engagement are tracked to optimize campaigns and understand consumer behavior.
In affiliate marketing, tracking and analytics focus on affiliate performance. Software like Post Affiliate Pro is often used to manage and track affiliate activities, monitor referrals, track conversions, manage payouts, and generate detailed reports, ensuring the affiliate program operates smoothly and effectively.
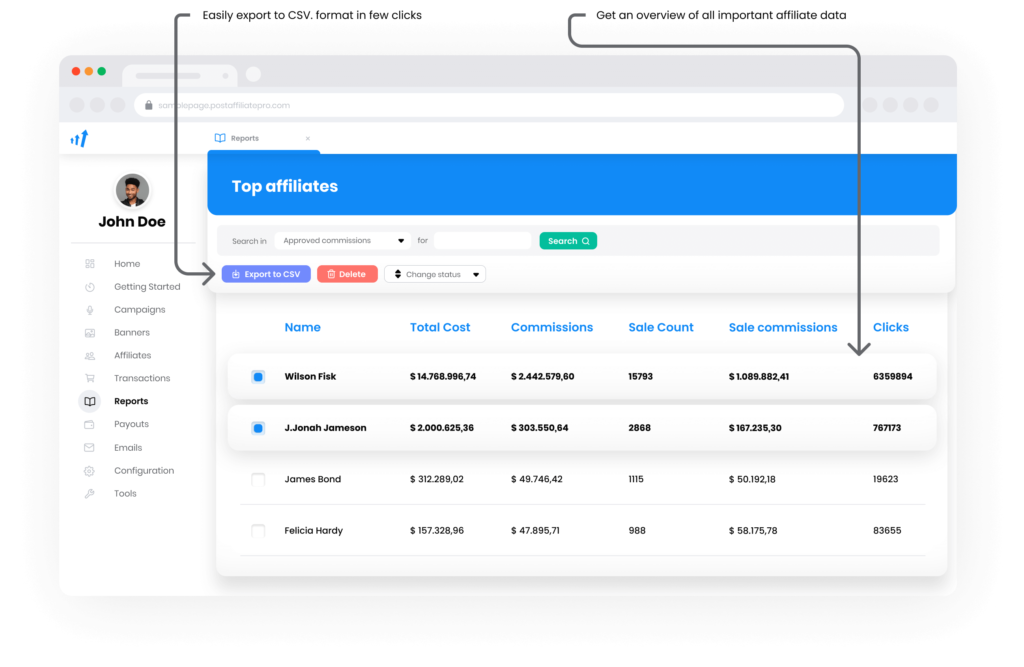
ROI measurement
Measuring ROI in digital marketing involves analyzing the return on investment across multiple platforms and campaigns. This can be complex, as it requires tracking and attributing revenue to specific marketing efforts. Brands need to consider factors like ad spend, content creation costs, and overall campaign performance to calculate ROI accurately.
In affiliate marketing, ROI measurement is simpler. It directly ties to the commissions paid to affiliates for successful conversions. Since affiliates are paid only when a sale or lead is generated, measuring ROI is more straightforward. This performance based marketing strategy ensures that the marketing budget is used effectively, often leading to a higher overall ROI.
Revenue model
In digital marketing, the revenue model is direct. Sales are generated through various campaigns, and the brand invests in ads, content, and other efforts to drive traffic and convert visitors into customers. The revenue generated is then compared to the campaign costs to assess profitability.
Affiliate marketing operates on a commission-based revenue model. Affiliates earn a percentage of the sales they generate for the brand. This model lowers financial risk for the brand, as it only pays for actual sales or leads, making it a cost-effective way to drive revenue with minimal upfront investment.
Relationship dynamics
The primary relationship in digital marketing is between the brand and its consumers. The brand communicates directly with its audience through various digital channels, building relationships over time through consistent engagement and value delivery.
In affiliate marketing, the relationship dynamics involve the brand, affiliates, and consumers. The brand needs to build strong relationships with affiliates, providing them with the tools and incentives needed to promote effectively. Affiliates, in turn, act as intermediaries, influencing consumers’ purchasing decisions through their promotions.
Payment structure
In digital marketing, payment often involves upfront costs for ad placements, content creation, and platform usage. Brands may pay for clicks, impressions, or ad placements, depending on the advertising model used (CPC, CPM, etc.). These costs are incurred regardless of the campaign’s success.
In affiliate marketing, the payment structure is performance-based. Brands pay affiliates a commission only when a sale or lead is generated through the affiliate’s efforts. This reduces financial risk, as payments are directly tied to the results achieved by the affiliates.
Risk
Digital marketing involves higher risk due to upfront costs and the potential for campaigns to underperform. If a campaign doesn’t deliver the expected results, the brand may face significant losses, especially with heavy investments in paid advertising.
Affiliate marketing carries lower financial risk since the brand only pays for successful conversions. The performance-based model ensures that marketing spend is closely tied to revenue generation, reducing the risk of wasted resources.
Reward
The rewards in digital marketing can be substantial if campaigns are well-targeted and executed. Successful campaigns can lead to increased sales, enhanced brand awareness, and stronger customer relationships. However, achieving these rewards often requires significant investment and continuous optimization.
The rewards in affiliate marketing include expanded reach, higher conversion rates, and cost-effective marketing. By leveraging affiliates’ existing audiences and marketing efforts, brands can achieve significant results with lower upfront costs.
What do digital and affiliate marketing share in common?
As we stated at the very beginning, affiliate marketing is often seen as a part of digital marketing. As a result, these two models share several key elements:
- Online presence: Both rely on the internet to reach audiences, promote products or services, and drive conversions. They use websites, social media platforms, and email as primary channels.
- Performance tracking: Both strategies use tools and software to monitor campaign effectiveness, track conversions, and measure ROI. Real-time tracking helps you fine-tune your strategy to improve results.
- Relationship building: Digital marketing focuses on creating long-term relationships with customers through engagement and personalized experiences. Affiliate marketing, on the other hand, builds strong ties with affiliates who can promote your brand effectively.
- Content marketing: Content is crucial for both. In digital marketing, you create content to engage and inform your audience. In affiliate marketing, affiliates often produce content to promote your products.
- Scalability: You can scale digital marketing campaigns up or down based on your budget and goals. Similarly, you can grow an affiliate marketing program by recruiting more affiliates.
Digital marketing vs. affiliate marketing: real-life examples
Now, let’s explore how these strategies work in real life. Look at companies that have used both digital and affiliate marketing to boost their performance.
Amazon
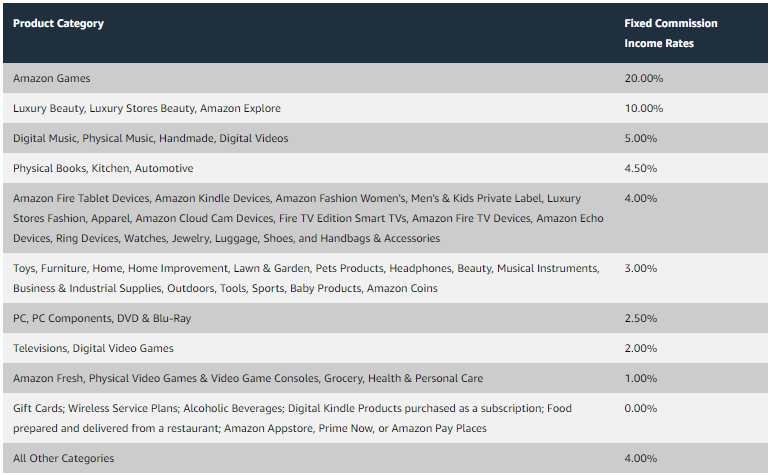
Amazon uses various digital marketing strategies, like search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, email marketing, and social media campaigns. It also runs one of the largest affiliate programs in the world, Amazon Associates.
This program allows website owners, bloggers, and influencers to earn commissions by promoting Amazon products. Through this affiliate program, Amazon has expanded its reach into niche markets and audiences that traditional digital marketing might not easily access.
Nike
Nike shines in digital marketing with strong social media campaigns, influencer partnerships, email marketing, and its own mobile app. These strategies help Nike connect with its global audience, launch new products, and maintain a strong online brand presence.
Nike also runs an affiliate program where partners can earn commissions by promoting Nike products on their websites, blogs, or social media. Affiliates can earn up to 15% on all valid U.S. sales, which is a substantial incentive. This program has allowed Nike to reach a wider audience, especially through niche fitness and lifestyle blogs.
eBay
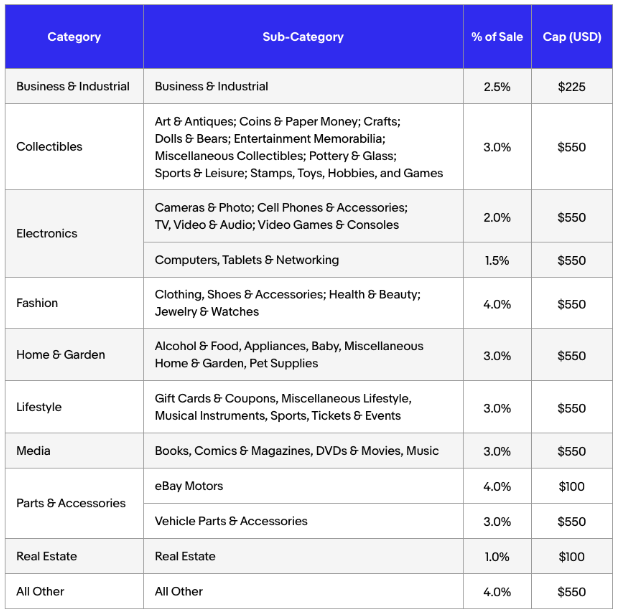
eBay effectively uses Google Ads, social media campaigns, email marketing, and SEO to drive traffic to its platform. These digital marketing strategies are key for attracting new users, engaging current customers, and promoting specific auctions or sales events.
eBay’s Partner Network, its affiliate marketing program, rewards affiliates for driving traffic and sales to eBay. Bloggers and website owners promote eBay listings and earn commissions on sales generated through their referrals.
Conclusion
Mastering both digital and affiliate marketing is a powerful tool for achieving your business objectives. In this article, we explained the key differences between these two strategies and highlighted their commonalities.
We also showed how companies like Amazon, Nike, and eBay use these strategies in practice. By understanding the differences between digital and affiliate marketing, you can strategically use both to maximize your reach and revenue. If you’re interested in seeing how affiliate marketing can boost your business, try Post Affiliate Pro’s 30-day free trial and experience the benefits yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can businesses use digital and affiliate marketing together?
Yes, combining digital and affiliate marketing can maximize reach and sales. Digital marketing enhances brand visibility and direct engagement, while affiliate marketing taps into niche audiences through third-party promoters, creating a powerful, complementary strategy.
How do businesses choose between digital and affiliate marketing in their overall strategy?
The choice depends on goals, resources, and target audience. Digital marketing is great for broad audience targeting and brand control, while affiliate marketing works well for performance-based models and reaching niche markets through third-party promoters.
How do the skills for digital marketing compare to those for affiliate marketing?
Digital marketing requires skills in content creation, data analytics, and platform management, focusing on direct consumer engagement. Affiliate marketing focuses on relationship management, negotiation, and tracking affiliate performance, emphasizing partnerships and performance-based promotion.
Which industries benefit more from digital marketing versus affiliate marketing?
Retail, technology, and consumer goods industries benefit from digital marketing for broad audience engagement and brand visibility. Niche markets, online service providers, and e-commerce often see better results with affiliate marketing, using specific influencers and targeted audiences to drive conversions.
Share this article
9 affiliate marketing tools that’ll help you run your affiliate program
Discover 9 essential tools to supercharge your affiliate marketing program! From visual content creation with Visme to comprehensive management with Post Affiliate Pro and audience insights via Smartlook, these tools will boost your sales and refine your strategy. Dive in to maximize your affiliate success!
Affiliate networks vs. affiliate tracking software
Explore the key differences between affiliate networks and affiliate tracking software to streamline your affiliate marketing operations. Discover which solution offers the best automation, control, and efficiency for your program. Make an informed choice to optimize your revenue strategy.
Discover the essential role of affiliate software in managing and optimizing your affiliate marketing programs. Learn how it streamlines link tracking, referral management, and commission payments, ensuring data security and fraud prevention. Unlock growth opportunities with efficient program management and boost your business's reach and ROI. Visit now to explore the benefits of investing in affiliate software!
The Evolution of Affiliate Marketing: What to Expect in 2025
Explore the future of affiliate marketing in 2025 with insights and trends to boost your strategy. Discover what's next!
Explore Post Affiliate Pro's comprehensive Affiliate Marketing Glossary to enhance your industry knowledge with easy-to-understand definitions of essential terms. Perfect for marketers seeking to understand the fundamentals and advanced concepts, this glossary helps you master the language of affiliate marketing. Visit now to boost your expertise!