Crawlers and Their Role in Search Engine Ranking
Crawlers accumulate data and information from the internet by visiting websites and reading the pages. Find out more about them.
Learn what Google Spider (Googlebot) is, how it crawls and indexes websites, and why it’s essential for SEO. Discover how to optimize your site for better crawling.
The Google Spider, formally known as Googlebot, is an automated program that crawls websites to discover, index, and store content in Google's database. It follows links to find new or updated pages, which are then processed and added to Google's search index, enabling the search engine to provide relevant results to users.
The Google Spider, more formally known as Googlebot, is an automated software program that systematically crawls the internet to discover, analyze, and index web content. It is the primary tool Google uses to explore websites, collect information, and build its massive search index. Without Googlebot, Google would be unable to discover new pages, detect updates to existing content, or provide relevant search results to billions of users worldwide. The spider operates continuously, visiting millions of websites every day to ensure Google’s index remains current and comprehensive.
Googlebot is essentially a sophisticated web crawler that follows a complex algorithmic process to determine which sites to visit, how frequently to crawl them, and how many pages to fetch from each domain. The crawler reads the HTML code, text content, and metadata on each page it visits, then stores this information in Google’s central database. This indexing process is fundamental to how search engines function and directly impacts your website’s visibility in search results.
The Google Spider operates through a well-defined crawling process that begins with a seed list of known web pages. This initial list is generated from previous crawl processes and is continuously augmented with sitemap data provided by webmasters through Google Search Console. When Googlebot visits a website, it doesn’t simply read the content—it performs a comprehensive analysis of the page structure, follows internal and external links, and identifies any changes or new content that may have been added since the last visit.
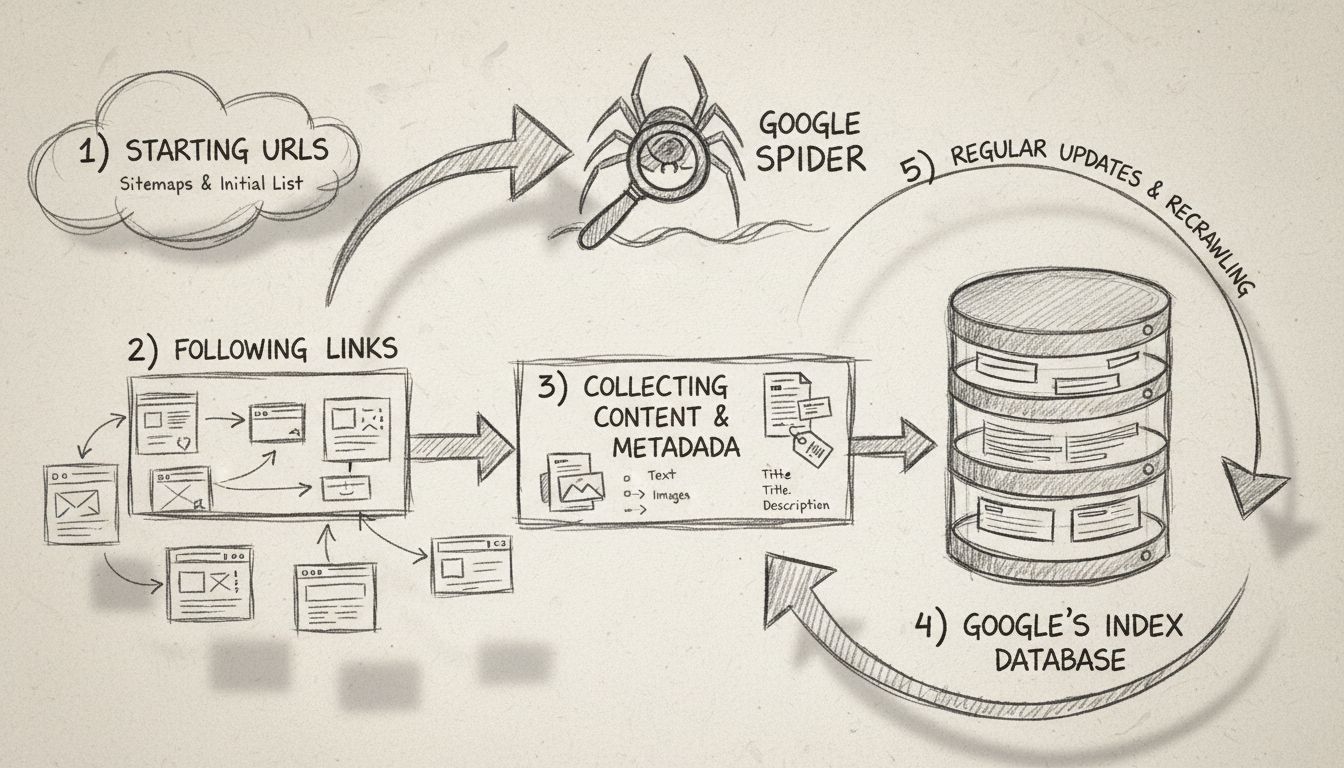
The crawling process follows these key steps: First, Googlebot starts with a list of webpage URLs from previous crawls and sitemaps. Second, it navigates through websites by following links (both SRC and HREF attributes) on each page to discover new content. Third, the crawler fetches and analyzes the content of each page, including text, HTML structure, metadata, and other relevant information. Fourth, this collected data is sent to Google’s servers for processing and storage in the search index. Finally, Googlebot revisits websites at regular intervals to check for new content, updates, or changes to existing pages.
Google operates multiple specialized crawler variants, each designed for specific purposes and identified by unique user-agent strings. Understanding these different types helps website owners optimize their sites for the appropriate crawler. The main Googlebot variants include the desktop crawler, mobile crawler, video crawler, image crawler, and news crawler, each serving distinct functions in Google’s indexing ecosystem.
| Googlebot Type | User-Agent String | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Googlebot (Desktop) | Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html) | Crawls desktop versions of websites for general search index |
| Googlebot (Mobile) | Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 6.0.1; Nexus 5X Build/MMB29P) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/W.X.Y.Z Mobile Safari/537.36 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html) | Crawls mobile-optimized versions of websites |
| Googlebot-Video | Googlebot-Video/1.0 | Indexes video content embedded on web pages |
| Googlebot-Image | Googlebot-Image/1.0 | Crawls and indexes images for Google Images search |
| Googlebot-News | Googlebot-News | Crawls news content for Google News aggregation |
Beyond these primary crawlers, Google also operates specialized bots for other purposes. AdSense Bot checks ad quality and compliance, while Mobile Apps Android crawler indexes content from Android applications. Each bot has a distinct user-agent identifier that allows website administrators to track which specific crawler is accessing their site through server logs. This distinction is important because different crawlers may have different crawl budgets and priorities, affecting how frequently they visit your site.
The Google Spider is absolutely critical for search engine optimization because it determines whether your website’s content gets discovered, indexed, and ranked in search results. If Googlebot cannot crawl your site effectively, your pages will not appear in Google’s index, making them invisible to potential visitors searching for your products or services. This is why technical SEO—ensuring your site is crawler-friendly—is one of the most important foundations of any successful SEO strategy.
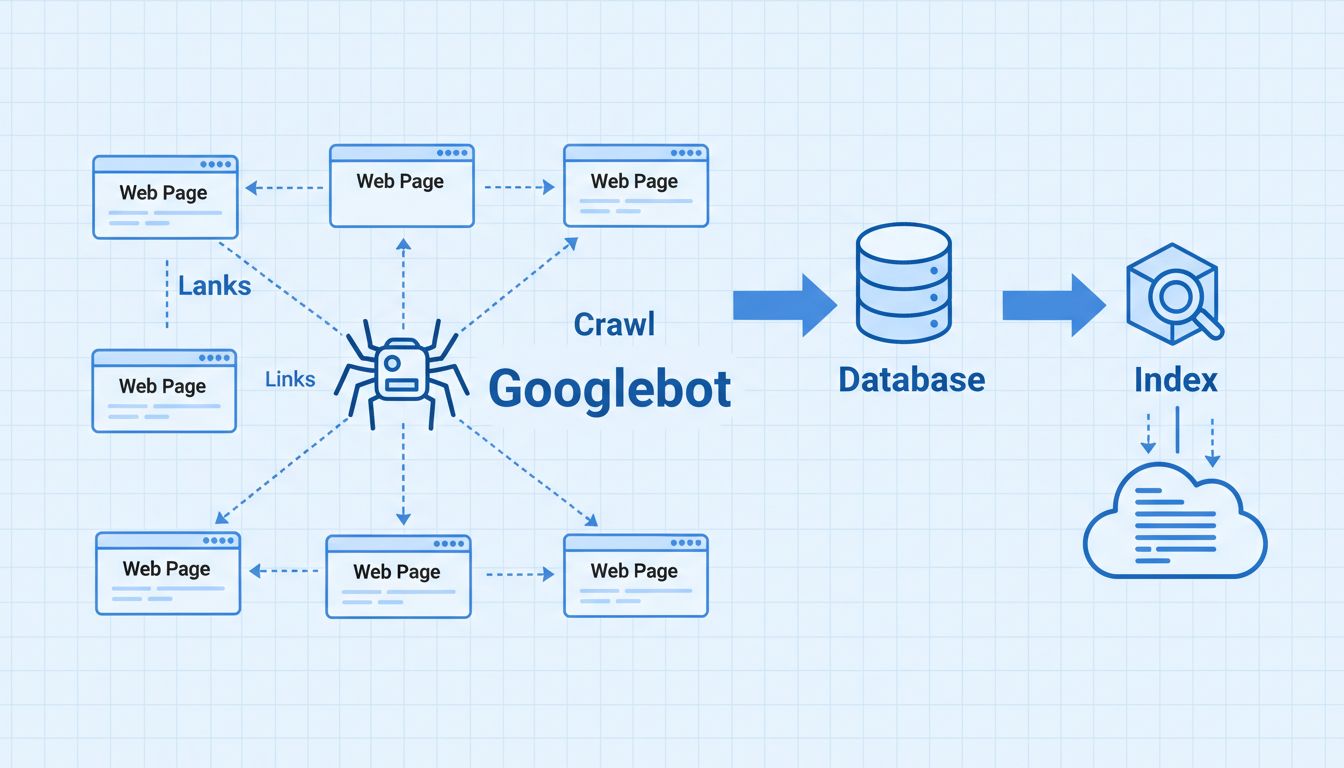
When Googlebot crawls your website, it compiles a massive index of all the words it finds and their locations on each page, along with HTML information such as title tags, meta descriptions, and heading structures. This indexed information is stored in Google’s database and used by search algorithms to rank pages and determine how valuable your content is for specific search queries. The more efficiently Googlebot can crawl your site, the more frequently it will return, and the faster new content will be indexed and potentially ranked in search results.
To ensure Googlebot can crawl your website effectively and efficiently, you need to implement several technical best practices. First, maintain a clear and logical site structure with proper navigation that makes it easy for the crawler to discover all important pages. Internal linking should be strategic and relevant, using descriptive anchor text that helps both users and crawlers understand the context of linked pages. Your website should load quickly, as page speed is a factor that influences crawl efficiency and how much of your site Googlebot will crawl within its allocated crawl budget.
Create and submit an XML sitemap to Google Search Console, which provides Googlebot with a comprehensive list of all pages you want indexed. This is particularly important for large websites or sites with pages that may not be easily discoverable through internal linking alone. Additionally, ensure your robots.txt file is properly configured to allow Googlebot to access the pages you want indexed while blocking access to sensitive areas or duplicate content. However, be careful not to accidentally block important pages, as this will prevent them from being indexed entirely.
Google Search Console is an essential tool for monitoring how Googlebot interacts with your website and identifying any crawling issues that may prevent proper indexing. The Crawl Stats section provides detailed information about how many pages Googlebot crawled, how much time it spent crawling your site, and how many errors it encountered. You can see the average response time of your server, which directly impacts how efficiently Googlebot can crawl your pages—slower servers mean fewer pages crawled within the same time period.
The Coverage report in Google Search Console shows which pages have been successfully indexed, which pages have errors preventing indexing, and which pages are excluded from the index. This information is invaluable for identifying technical issues like broken links, server errors, or pages blocked by robots.txt that you may not have intended to block. You can also use the URL Inspection tool to test how Googlebot sees a specific page, including whether it can render JavaScript content and access all resources needed to display the page properly.
Every website has a “crawl budget”—the number of pages Googlebot will crawl on your site within a given time period. For most websites, crawl budget is not a limiting factor, but for very large sites with thousands or millions of pages, optimizing crawl budget becomes important. Google allocates crawl budget based on two factors: crawl capacity (how much your server can handle) and crawl demand (how important Google considers your site to be). Improving your site’s speed and fixing crawl errors increases crawl capacity, while creating high-quality, frequently updated content increases crawl demand.
To optimize your crawl budget, eliminate duplicate content that wastes crawling resources, fix broken links and redirect chains, and remove pages that don’t provide value to users. Avoid blocking important pages with robots.txt or noindex tags, and ensure your site structure makes it easy for Googlebot to discover all important pages within a few clicks from the homepage. Regularly updating your XML sitemap and removing outdated pages helps Googlebot focus its crawling efforts on content that matters most to your business.
Website owners often encounter various issues that prevent Googlebot from crawling their sites effectively. Server errors (5xx status codes) indicate that your server is having problems responding to requests, which can prevent pages from being indexed. Redirect chains—where one page redirects to another, which redirects to a third page—waste crawl budget and slow down the indexing process. Blocked resources, such as CSS files or JavaScript files that are blocked by robots.txt, can prevent Googlebot from properly rendering and understanding your pages.
Soft 404 errors occur when a page returns a 200 status code (success) but contains little or no actual content, confusing Googlebot about whether the page should be indexed. Noindex tags accidentally applied to important pages prevent them from appearing in search results. Slow page load times reduce the number of pages Googlebot can crawl within its allocated budget. To address these issues, regularly audit your website using Google Search Console, monitor server logs for crawl errors, and use tools like Screaming Frog to identify technical issues before they impact your search visibility.
In 2025, the Google Spider remains as important as ever, though its role has evolved to accommodate new technologies and content formats. Googlebot now handles JavaScript rendering, meaning it can crawl and index content generated dynamically by JavaScript frameworks. It also processes structured data markup (Schema.org) to better understand page content and provide rich snippets in search results. Mobile-first indexing means Googlebot prioritizes crawling and indexing the mobile version of your website, making mobile optimization essential for SEO success.
The spider also plays a crucial role in Google’s ability to detect and combat spam, identify hacked content, and ensure that search results remain relevant and trustworthy. As search engines continue to evolve with AI and machine learning technologies, Googlebot’s crawling and indexing capabilities become even more sophisticated, allowing Google to better understand user intent and deliver more accurate search results. Understanding how Googlebot works and optimizing your website accordingly remains one of the most fundamental aspects of SEO strategy.
Just like Google Spider crawls and indexes your content, PostAffiliatePro helps you track and optimize your affiliate marketing performance. Monitor every click, conversion, and commission with our industry-leading affiliate management platform.
Crawlers accumulate data and information from the internet by visiting websites and reading the pages. Find out more about them.
Spiders are bots created for spamming, which may cause your business a lot of problems. Learn more about them in the article.
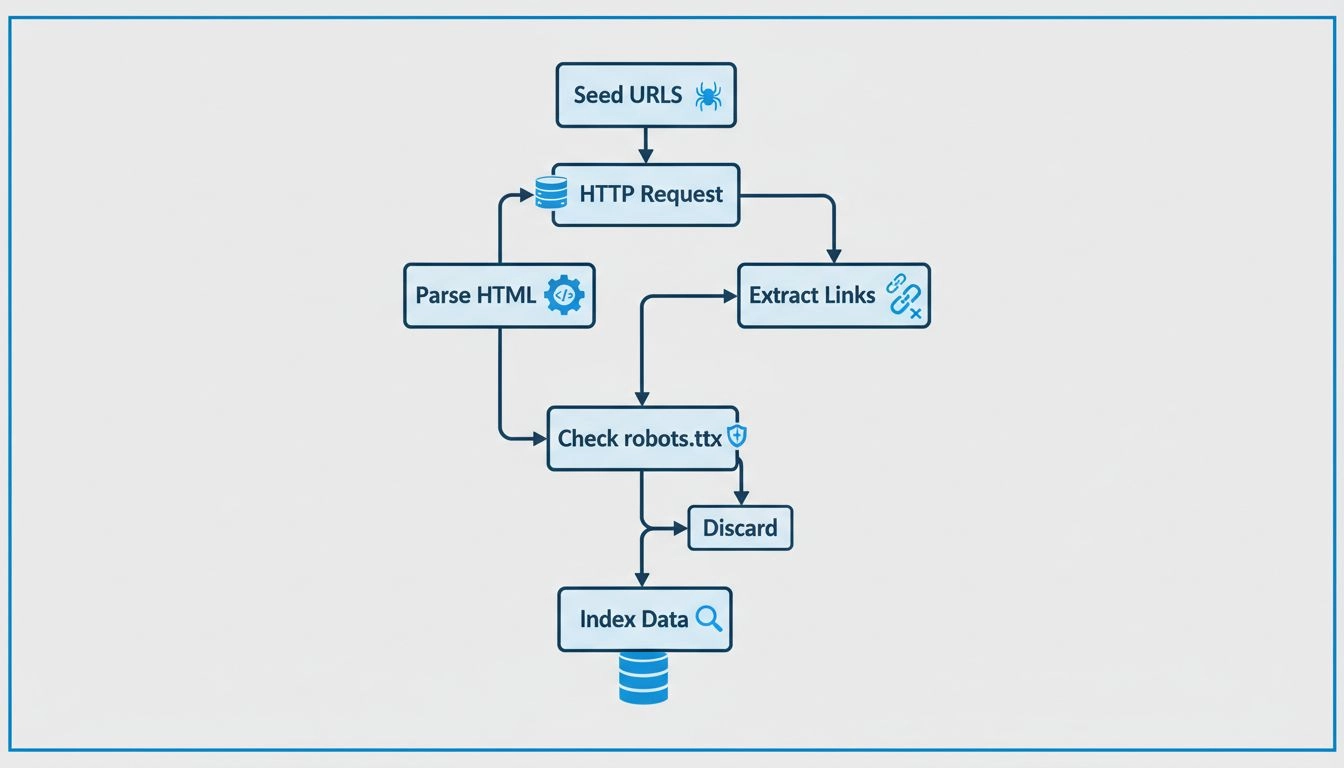
Learn how web crawlers work, from seed URLs to indexing. Understand the technical process, crawler types, robots.txt rules, and how crawlers impact SEO and affi...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.