Why Are Micro Conversions Important?
Discover why micro conversions matter for your business. Learn how small user actions drive engagement, build trust, and lead to higher macro conversions with P...
Learn how to track micro conversions effectively using Google Analytics, conversion pixels, UTM parameters, and advanced tools. Discover best practices for monitoring user engagement and optimizing your conversion funnel with PostAffiliatePro.
Track micro conversions using data analytics tools like Google Analytics to set up event tracking for specific user actions, implement conversion tracking pixels (Facebook Pixel, Google Ads tag), create conversion funnels to visualize user journeys, and use heatmaps and session recordings to understand user behavior patterns.
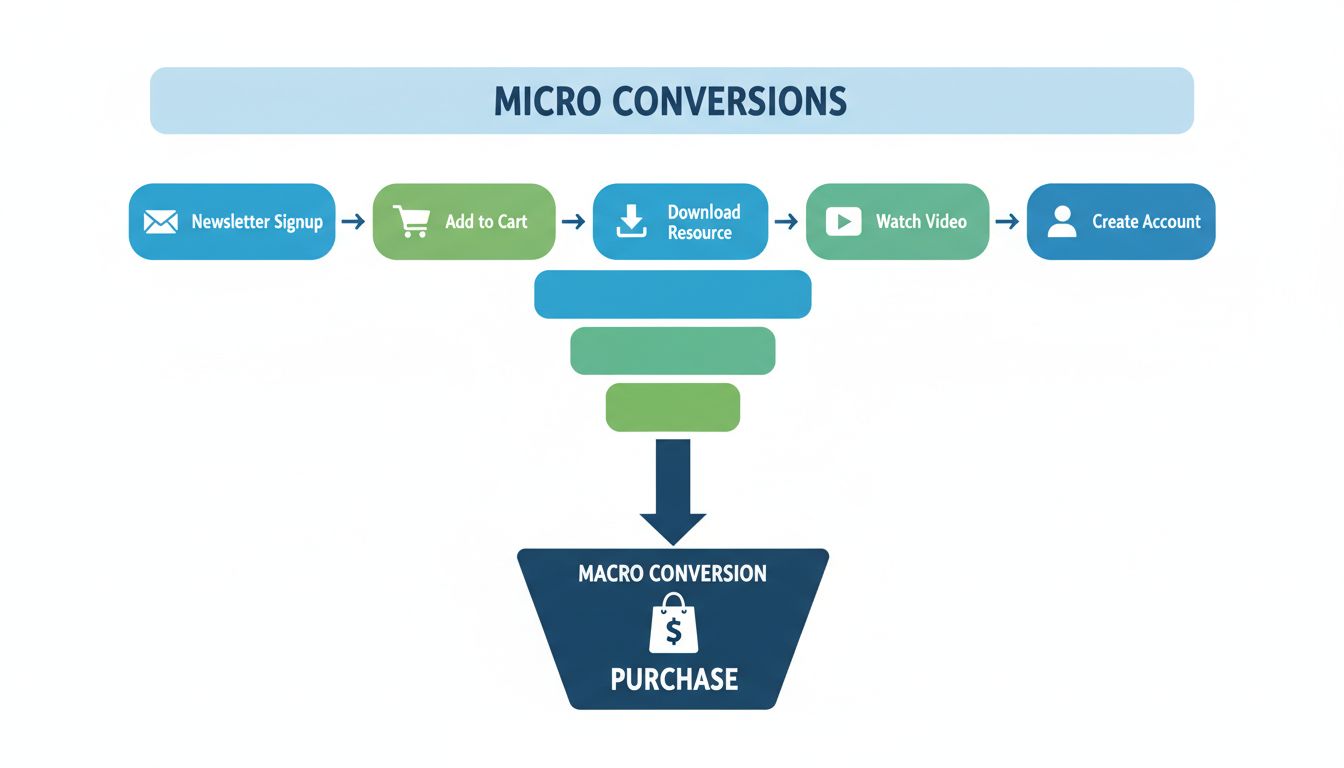
Micro conversions are smaller, measurable actions that users take on your website before completing a primary conversion goal (macro conversion). These intermediate steps—such as newsletter signups, product page views, video plays, adding items to cart, or downloading resources—provide invaluable insights into user behavior and engagement patterns. Unlike macro conversions (purchases or major commitments), micro conversions represent the stepping stones that guide users through your conversion funnel. Understanding and tracking these actions is essential for modern digital marketing because they reveal where users engage most, where friction exists, and how to optimize the entire customer journey for better results. By monitoring micro conversions, you gain early warning signals about potential issues in your conversion process before they impact your bottom line.
Google Analytics remains one of the most powerful and accessible tools for tracking micro conversions. To begin, you need to configure specific events that correspond to the micro-conversion actions you want to monitor. Start by accessing your Google Analytics 4 property and navigating to the Events section. Define clear event names that describe the action (for example, “newsletter_signup,” “video_play,” or “add_to_cart”). Each event should have associated parameters that provide context—such as the page URL, user ID, or product category. You can implement these events directly through your website code or use Google Tag Manager for easier management without requiring developer intervention. The key is to be consistent with your naming conventions and ensure that events fire correctly when users perform the desired actions. Once configured, these events will populate your Analytics dashboard, allowing you to create custom reports and analyze conversion paths. Advanced users can set up conversion events that automatically track specific user actions, while beginners can use pre-built event templates provided by Google.
Conversion tracking pixels are small snippets of code that monitor specific user actions and send data back to advertising platforms or analytics services. The most commonly used pixels include the Google Ads conversion tag, Facebook Pixel, LinkedIn Insight Tag, and X Pixel. To implement the Google Ads conversion tag, log into your Google Ads account, navigate to Tools & Settings, select Conversions under Measurement, and create a new conversion action. Choose “Website” as your conversion source and specify details like conversion name, value, and count settings. Google will provide you with a conversion tag (gtag.js) that you place in the header of your website, plus event snippets for specific conversion pages. For Facebook Pixel, install the base code on all pages of your website and configure standard events like ViewContent, AddToCart, and Purchase. These pixels work by placing cookies on user browsers, allowing platforms to track users across devices and attribute conversions to specific campaigns. Proper pixel implementation is crucial because it enables accurate measurement of campaign performance and provides data for retargeting campaigns. Many marketers use Google Tag Manager to simplify pixel deployment across multiple platforms without manual code editing.
| Tracking Method | Best For | Implementation Complexity | Data Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Analytics Events | Comprehensive user behavior analysis | Medium | High |
| Google Ads Conversion Tag | PPC campaign optimization | Low | High |
| Facebook Pixel | Social media campaign tracking | Low | Medium-High |
| UTM Parameters | Campaign source identification | Low | Medium |
| Heatmaps & Session Recordings | User interaction visualization | Medium | High |
| CRM Integration | Lead scoring and nurturing | High | High |
A conversion funnel visualizes the step-by-step journey users take toward completing a desired action. In Google Analytics, you can create funnels by defining sequential steps that represent your conversion path. For an eCommerce site, this might include: Product Page View → Add to Cart → Checkout Initiated → Payment Completed. For a SaaS platform, it could be: Landing Page View → Free Trial Signup → Feature Exploration → Upgrade to Paid Plan. By analyzing where users drop off in your funnel, you identify friction points that need optimization. If you notice that 80% of users view products but only 20% add items to cart, this indicates a problem with product presentation or pricing clarity. Conversion funnels also help you understand which marketing channels deliver users most likely to progress through your funnel. Some channels may drive high traffic but low-quality visitors who abandon early, while others drive fewer visitors but with higher conversion potential. This insight allows you to allocate marketing budgets more effectively. Understanding your funnel structure enables you to make data-driven decisions about where to invest optimization efforts for maximum impact.
Heatmaps and session recordings provide qualitative data that complements quantitative analytics. Heatmaps show where users click, scroll, and spend time on your pages, revealing which elements attract attention and which are ignored. Session recordings allow you to watch actual user interactions, understanding their frustrations, confusion points, and decision-making process. Tools like Hotjar, Crazy Egg, and LiveSession offer these capabilities. When analyzing heatmaps, look for patterns: Are users clicking on non-clickable elements? Are they scrolling past important CTAs? Do they spend time reading specific sections? Session recordings are particularly valuable for understanding why users abandon carts or don’t complete forms. You might discover that users are confused by unclear instructions, distracted by pop-ups, or unable to find required information. These insights often reveal micro-conversion optimization opportunities that pure analytics data cannot show. Combining heatmap data with conversion metrics creates a comprehensive understanding of user behavior that drives meaningful improvements.
UTM (Urchin Tracking Module) parameters are tags you add to URLs to track specific campaigns and their performance. They consist of five parameters: utm_source (where traffic comes from), utm_medium (type of marketing), utm_campaign (specific campaign name), utm_content (specific link or content), and utm_term (keywords for paid search). For example, a Facebook ad might use: https://yoursite.com?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=summer_sale&utm_content=banner_ad. UTM parameters allow you to see not just that users converted, but which specific campaigns, channels, and content drove those conversions. This is particularly valuable for tracking micro-conversions across different marketing initiatives. You can create custom reports in Google Analytics that show which UTM combinations generate the highest engagement rates, newsletter signups, or other micro-conversions. Consistent UTM naming conventions across your organization ensure data accuracy and make analysis easier. Many marketers use UTM builders to generate properly formatted URLs, reducing errors and ensuring consistency across campaigns.
A/B testing (split testing) involves creating two versions of a page or element and measuring which performs better for micro-conversions. You might test different CTA button colors, form field lengths, headline copy, or page layouts. Tools like Google Optimize, Optimizely, and VWO make this process straightforward. When setting up A/B tests, ensure you have sufficient traffic and time to reach statistical significance—typically requiring at least 100-200 conversions per variation. Test one element at a time to isolate the impact of specific changes. For example, if you’re testing a CTA button, keep everything else identical and only change the button color or text. Track micro-conversions throughout your test, not just the final macro conversion. You might discover that a particular button color increases newsletter signups (a micro-conversion) even if it doesn’t immediately impact purchases. These insights compound over time, with each successful test incrementally improving your conversion rates. Document all tests and results to build institutional knowledge about what works for your audience.
Email marketing platforms like Mailchimp, Klaviyo, and HubSpot provide built-in tracking for email-related micro-conversions. These include email opens, link clicks, and landing page visits from email campaigns. By tracking these metrics, you understand which email content resonates with your audience and drives engagement. Set up email click tracking to see which links users interact with most, then use this data to refine future campaigns. Many platforms allow you to segment users based on their email engagement, creating targeted follow-up campaigns for users who clicked specific links. For SMS marketing, track similar metrics: delivery rates, click-through rates, and conversions from SMS links. Integration between your email platform and Google Analytics allows you to see the complete journey: which email campaigns drive traffic, which landing pages those users visit, and whether they complete micro-conversions like form submissions or video views. This end-to-end tracking reveals the true value of email marketing beyond immediate sales and helps justify marketing spend to stakeholders.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems like HubSpot, Salesforce, and Zoho provide sophisticated micro-conversion tracking capabilities. These platforms track every interaction a prospect has with your company: email opens, website visits, form submissions, chat conversations, and phone calls. By integrating your CRM with your website analytics, you create a unified view of each prospect’s journey. Lead scoring features automatically assign points based on micro-conversions, helping sales teams prioritize high-intent prospects. For example, a prospect who downloads a whitepaper, attends a webinar, and visits your pricing page receives higher scores than someone who only visited your blog. This scoring system ensures your sales team focuses on prospects most likely to convert. CRM integration also enables personalization: you can show different content to prospects based on their previous interactions and engagement level. A prospect who has already downloaded multiple resources might see different CTAs than a first-time visitor, creating a more relevant experience.
Cross-device tracking reveals how users interact with your brand across smartphones, tablets, and desktops. Many users begin their journey on mobile, continue on desktop, and complete actions on another device. Without cross-device tracking, you might attribute a conversion to the wrong channel or device. Google Analytics 4 provides cross-device reporting when users are signed into their Google accounts. For more comprehensive cross-device tracking, implement user ID tracking by having users log into your website or app. This allows you to track the same user across devices and attribute conversions accurately. Understanding device-specific behavior is crucial: mobile users might engage with different content than desktop users, and conversion rates often vary significantly by device. You might discover that mobile users frequently add products to carts but rarely complete purchases, indicating a mobile checkout optimization opportunity. By analyzing micro-conversions by device, you can optimize each experience appropriately and ensure consistent user experience across all touchpoints.
Before implementing tracking, establish baseline metrics for your current micro-conversions. Determine what percentage of visitors currently sign up for newsletters, download resources, or add items to carts. These baselines provide context for measuring improvement. Set specific, measurable goals for each micro-conversion: “Increase newsletter signups from 2% to 3% of visitors” or “Improve add-to-cart rate from 8% to 12%.” Goals should be ambitious but achievable, and they should align with your overall business objectives. Track progress toward these goals monthly or quarterly, adjusting your strategies based on results. Some micro-conversions are leading indicators of future macro-conversions—for example, users who download your product guide are significantly more likely to purchase within 30 days. By identifying these leading indicators, you can focus optimization efforts on the micro-conversions that matter most for your business and demonstrate clear ROI from your optimization efforts.
As you implement micro-conversion tracking, ensure compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and other data protection laws. Obtain explicit user consent before tracking personal data, and provide clear privacy policies explaining what data you collect and how you use it. Implement consent management platforms that allow users to opt out of tracking. Use first-party cookies and server-side tracking where possible, as these are more privacy-friendly than third-party cookies. Be transparent about your tracking practices: inform users that you’re tracking their interactions to improve their experience. Many users accept tracking when they understand the benefit (personalized recommendations, relevant content). Privacy-compliant tracking not only protects your users but also future-proofs your analytics as regulations continue to evolve. PostAffiliatePro prioritizes data privacy and compliance, ensuring your affiliate program tracking meets all regulatory requirements while providing comprehensive conversion insights.
Effective micro-conversion tracking is an ongoing process requiring continuous optimization. Regularly review your tracking data to identify trends, patterns, and opportunities. Look for seasonal variations in micro-conversions and adjust your strategies accordingly. Test new tracking methods and tools to find what works best for your specific business model. Share micro-conversion data across your organization—marketing, sales, product, and customer success teams all benefit from understanding user engagement patterns. Create dashboards that display key micro-conversion metrics in real-time, making data accessible to decision-makers. Use micro-conversion insights to inform product development, content strategy, and marketing campaigns. When you understand which actions indicate user interest and engagement, you can design experiences that naturally guide users toward these actions. This data-driven approach transforms micro-conversions from vanity metrics into actionable intelligence that drives business growth and improves customer experience significantly.
PostAffiliatePro provides comprehensive conversion tracking and affiliate management tools that help you monitor every step of your customer journey. Track micro conversions, optimize your funnel, and maximize your affiliate program performance with our advanced analytics platform.

Discover why micro conversions matter for your business. Learn how small user actions drive engagement, build trust, and lead to higher macro conversions with P...
Micro conversions are user actions that indicate a likelihood to convert. Discover what micro conversions are, why they matter in affiliate marketing, how to tr...
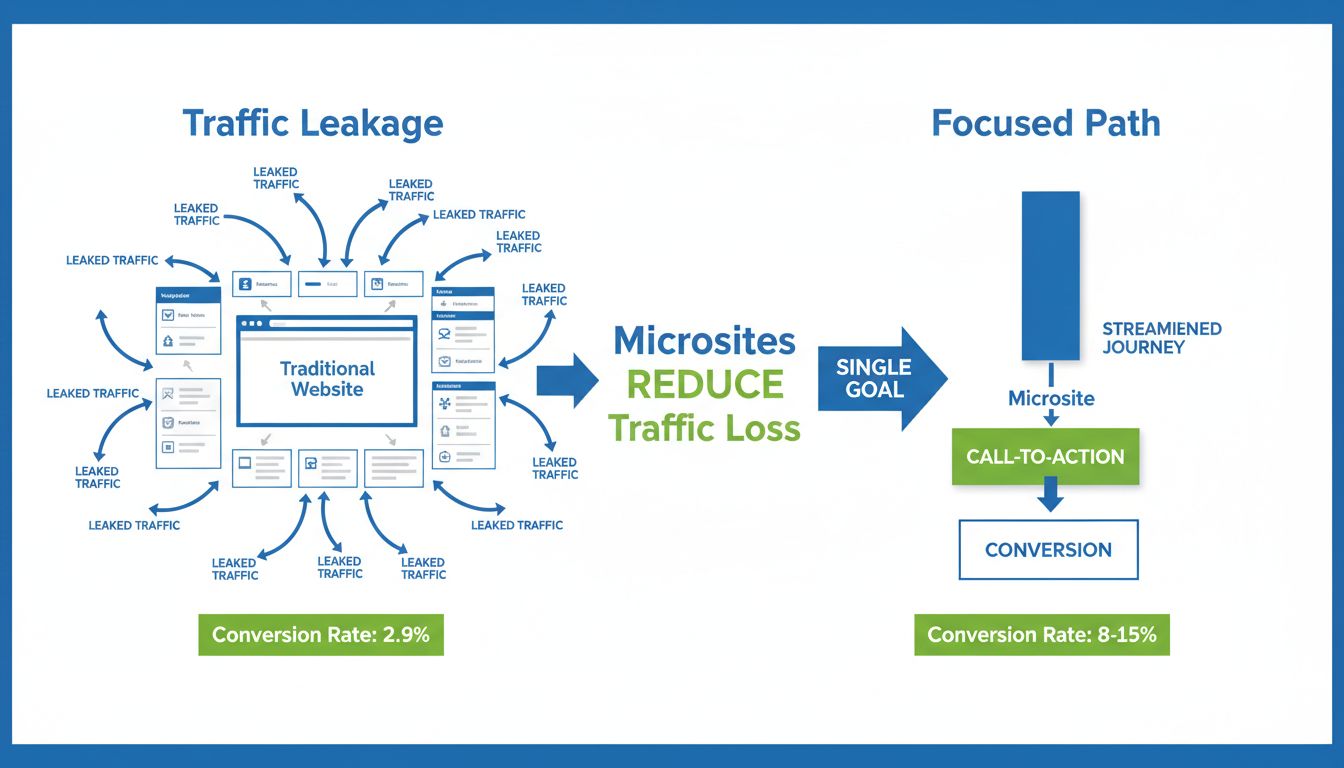
Discover how microsites reduce traffic leakage, boost conversion rates by 50-100%, and accelerate affiliate marketing success. Learn best practices and ROI metr...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.