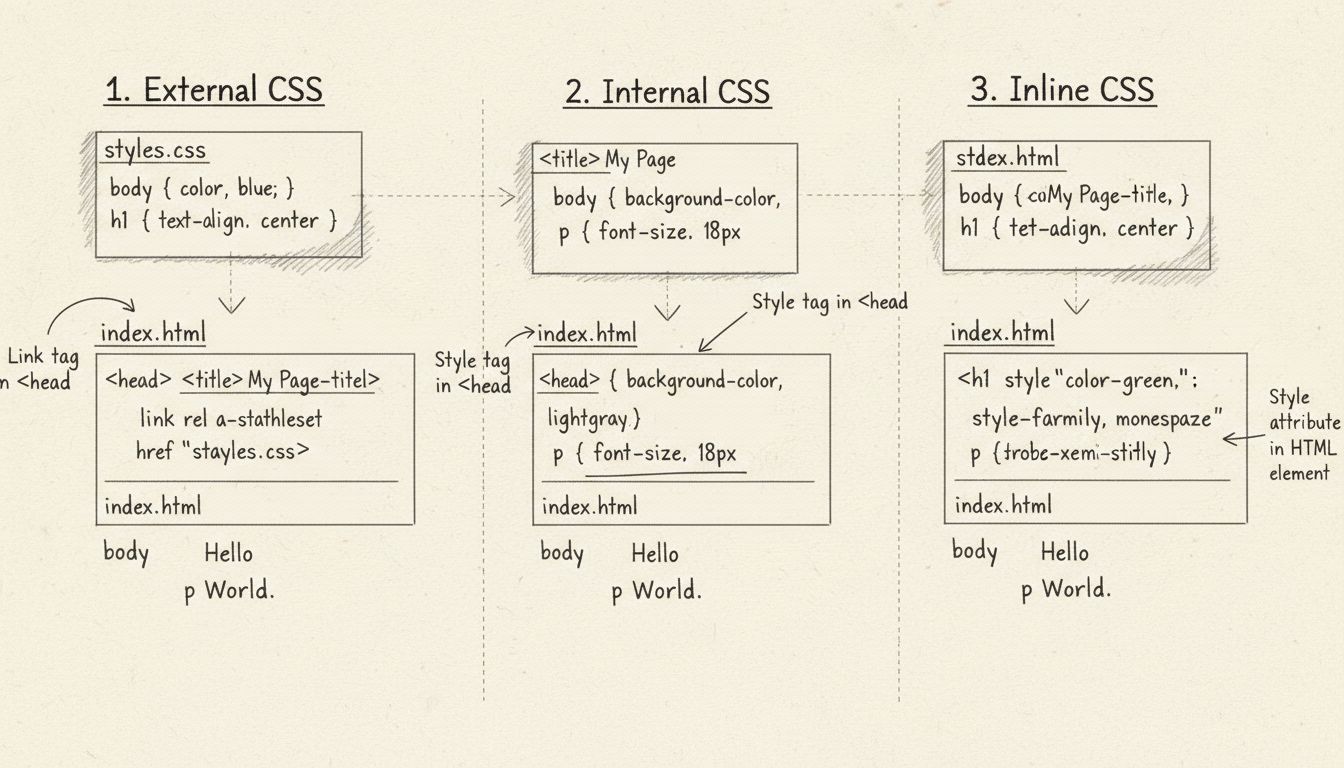
How to Add CSS to HTML
Learn three proven methods to add CSS to HTML: external stylesheets, internal styles, and inline CSS. Discover best practices, cascading order, and when to use ...
Learn how to change fonts in HTML using CSS font-family property, style attributes, and web fonts. Master font stacks, Google Fonts, and best practices for web typography.
To change the font in HTML, use the CSS font-family property within a style attribute or CSS rule. You can apply fonts inline using style="font-family: Arial, sans-serif;" or through external CSS stylesheets. Always include fallback fonts in a font stack to ensure proper rendering across browsers.
Changing fonts in HTML is one of the most fundamental aspects of web design and typography. Unlike older HTML approaches that relied on deprecated <font> tags, modern web development uses CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) to control font styling. The primary method involves the font-family property, which allows you to specify which typeface should be displayed for text elements. This approach provides better control, consistency, and maintainability across your entire website. Understanding how to properly implement font changes is essential for creating professional-looking websites that maintain brand identity and improve user experience.
The font-family property is the cornerstone of font styling in modern HTML. This CSS property accepts a comma-separated list of font names, allowing you to create what’s called a font stack. A font stack is a prioritized list of fonts where the browser attempts to use the first font listed, and if that font isn’t available on the user’s system, it falls back to the next font in the list. This fallback mechanism is crucial because not all fonts are installed on every user’s computer. The syntax is straightforward: you specify the font name followed by a generic font family as a final fallback. Generic font families include serif, sans-serif, monospace, cursive, and fantasy, which represent broad categories of fonts that every browser can render.
The simplest way to change a font for a specific HTML element is using the inline style attribute. This method applies CSS directly to individual elements without requiring separate stylesheets. For example, you can write <p style="font-family: Arial, sans-serif;">This text uses Arial font</p> to apply Arial font to a paragraph. The inline method is useful for quick styling or testing, but it’s not recommended for large-scale projects because it mixes content with presentation and makes maintenance difficult. When using inline styles, always include at least one fallback font family. In the Arial example, sans-serif serves as the generic fallback, ensuring that if Arial isn’t available, the browser will use any available sans-serif font instead of defaulting to its standard font.
{{< lazyimg src="/images/faq/CSS_font-family_in_HTML_che_mostrano_diversi_metodi_di_stilizzazione_dei_caratteri_lazyimg0_src.webp?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Credential=AKIAWO5JVUDXIZCF3DUO%2F20251128%2Feu-central-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20251128T101422Z&X-Amz-Expires=604800&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&X-Amz-Signature=e2634c3f0959c21d174603820fb2d476cfdc07f99fb133e3ea18e0399d4afd01" alt=“HTML font-family CSS property examples showing different font styling methods” class=“rounded-lg shadow-md” >}}
For better organization and maintainability, use internal CSS within <style> tags in the HTML <head> section or external CSS files linked to your HTML document. Internal CSS allows you to define styles for multiple elements without cluttering your HTML with inline styles. For instance, you can write a rule like p { font-family: Georgia, serif; } to apply Georgia font to all paragraph elements. External CSS files are even more powerful because they can be linked to multiple HTML pages, ensuring consistent styling across your entire website. This approach separates content from presentation, making your code cleaner and easier to maintain. When using external stylesheets, you link them in the HTML head with <link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">, and then define your font rules in the separate CSS file.
Creating effective font stacks is essential for reliable font rendering across different browsers and devices. A well-constructed font stack typically includes three to four fonts, starting with your preferred font and ending with a generic font family. For example, font-family: "Trebuchet MS", Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; creates a stack where the browser tries Trebuchet MS first, then Verdana, then Arial, and finally any sans-serif font if none of the others are available. Font names with spaces must be enclosed in quotation marks, such as "Times New Roman" or "Courier New". The generic font families serve as ultimate fallbacks and are crucial for ensuring that text remains readable even if none of your preferred fonts are installed. Different font stacks work better for different purposes: serif fonts like Georgia or Times New Roman are often used for body text in formal documents, while sans-serif fonts like Arial, Helvetica, and Verdana are popular for web content due to their clean, modern appearance.
Modern web development has revolutionized font usage through web fonts, which are hosted on servers and downloaded by browsers when needed. This eliminates the dependency on fonts being installed on users’ computers. Google Fonts is the most popular free web font service, offering hundreds of high-quality fonts that can be easily integrated into your website. To use Google Fonts, you include a link tag in your HTML head, such as <link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Roboto&display=swap" rel="stylesheet">, and then reference the font in your CSS with font-family: 'Roboto', sans-serif;. The display=swap parameter ensures that text remains visible while the font loads, improving user experience. Other web font services include Adobe Fonts, Typekit, and self-hosted font files using the @font-face CSS rule. Web fonts provide unlimited design possibilities and ensure that your website displays exactly as intended, regardless of what fonts users have installed on their systems.
| Method | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inline Styles | Quick to implement, no separate files needed | Hard to maintain, mixes content with presentation | Quick testing, single elements |
| Internal CSS | Centralized styling, cleaner HTML | Styles only apply to one page | Single-page websites, specific page styling |
| External CSS | Reusable across multiple pages, easy maintenance | Requires additional HTTP request | Large websites, consistent branding |
| Web Fonts (Google Fonts) | Unlimited design options, professional appearance | Requires internet connection, slight performance impact | Modern websites, custom typography |
| System Fonts | Fast loading, no external dependencies | Limited design options, less control | Performance-critical applications |
When implementing font changes in HTML, follow these essential best practices to ensure optimal results. Always include fallback fonts in your font stacks to guarantee readability even if your preferred fonts fail to load. Limit the number of different fonts on your website to maintain visual consistency and improve loading performance; typically, two to three fonts are sufficient for most websites. Consider font size, line height, and letter spacing in conjunction with font choice to create readable, professional-looking text. Test your fonts across different browsers and devices to ensure consistent rendering, as font appearance can vary slightly depending on the operating system and browser. Use web-safe fonts or web fonts for critical content to ensure consistent display across all users’ devices. Pay attention to font licensing, especially when using commercial fonts, and always respect the terms of service for web font providers. For affiliate marketing websites like those using PostAffiliatePro, maintaining professional typography is crucial for building trust and credibility with your audience.
Professional web design relies on proven font combinations that work reliably across all browsers and devices. For body text, the stack "Georgia", "Times New Roman", serif provides excellent readability with a classic, professional appearance. For headings and modern designs, use "Helvetica Neue", "Arial", sans-serif or "Trebuchet MS", "Verdana", sans-serif for a clean, contemporary look. For monospace text (code, technical content), use "Courier New", "Courier", monospace to maintain proper character alignment. For elegant, serif designs, try "Garamond", "Georgia", serif to create a sophisticated appearance. Modern websites increasingly use web fonts like Google Fonts to achieve unique typography while maintaining reliability. PostAffiliatePro users can leverage these font stacks to create professional affiliate marketing websites that stand out from competitors and effectively communicate their value proposition to potential partners and customers.
If fonts aren’t displaying as expected, several factors could be responsible. First, verify that font names are spelled correctly and that multi-word font names are properly quoted in your CSS. Check that your CSS file is properly linked in the HTML head section and that there are no syntax errors in your font-family declarations. If using web fonts, ensure that the font link is correct and that the font service is accessible. Browser caching can sometimes cause outdated fonts to display; try clearing your browser cache or using a hard refresh (Ctrl+Shift+R or Cmd+Shift+R). Different browsers may render fonts slightly differently due to anti-aliasing and rendering engines, which is normal and expected. If a font appears too small or too large, adjust the font-size property in addition to the font-family. For affiliate websites, consistent font rendering is important for maintaining brand identity, so testing across multiple browsers and devices is essential before launching your site.
PostAffiliatePro provides powerful tools to manage your affiliate program with professional design and functionality. Create stunning web pages with proper typography and styling to maximize conversions.

Learn three proven methods to add CSS to HTML: external stylesheets, internal styles, and inline CSS. Discover best practices, cascading order, and when to use ...
HTML, also known as hypertext markup language, determines how text and images will appear on a website. See the article for more information.
Discover how HTML empowers affiliate marketers with SEO optimization, mobile responsiveness, conversion tracking, and enhanced user experience to drive higher s...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.