
Why Small and Medium Businesses Are Targeted by Hackers
why SMBs are the primary targets for cybercriminals, the vulnerabilities they face, and how to protect your business from cyber threats with proven security
Discover why regular backups are essential for business security. Learn how cloud and offsite backups protect against cyberattacks, ransomware, data loss, and ensure business continuity with PostAffiliatePro’s comprehensive guide.
Regular backups to the cloud and offsite locations enable quick recovery and minimize business disruption in the event of a cyberattack or data loss. They protect against ransomware, hardware failures, human error, and natural disasters while ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
In today’s digital landscape, data represents one of the most valuable assets any business possesses. From customer information and financial records to operational data and proprietary research, the information stored across your systems directly impacts your ability to operate, serve customers, and maintain competitive advantage. However, the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, combined with the fragility of digital infrastructure, means that data loss is no longer a question of “if” but “when.” This reality makes regular backups not just a best practice, but an absolute necessity for business security and continuity.
The statistics surrounding data loss are sobering and should serve as a wake-up call for any business leader. According to recent research, up to 94% of companies that experience severe data loss never fully recover, with half closing within two years and 43% never reopening at all. For smaller businesses, the situation is even more dire—almost 70% close within a year of losing a large amount of data. These aren’t theoretical scenarios; they represent real businesses that failed to implement adequate backup strategies and paid the ultimate price. The average cost of a data breach in the UK reached approximately $4.53 million (£3.6 million) in 2024, a figure that encompasses not only recovery costs but also regulatory fines, legal fees, and reputational damage.
The consequences of inadequate backup strategies extend far beyond financial losses. When critical data becomes inaccessible or corrupted, business operations grind to a halt. Employees cannot access essential files, customers cannot be served, transactions cannot be processed, and revenue generation stops entirely. This downtime creates a cascading effect of problems: lost productivity, damaged customer relationships, missed business opportunities, and erosion of trust that can take years to rebuild.
Ransomware has emerged as one of the most dangerous threats facing businesses today. According to Verizon’s 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report, ransomware was involved in 44% of the breaches they investigated. In a typical ransomware attack, cybercriminals encrypt an organization’s data and demand payment for the decryption key. Without reliable backups, businesses face an impossible choice: pay the ransom with no guarantee of data recovery, or lose access to critical information permanently.
Regular backups fundamentally change this equation. When you maintain secure, up-to-date backups stored separately from your primary systems, you can restore your data without capitulating to criminal demands. This capability transforms ransomware from an existential threat into a manageable incident. Organizations with robust backup strategies can isolate infected systems, restore clean versions of their data from backups, and resume operations within hours rather than days or weeks. This rapid recovery capability is what separates businesses that survive cyberattacks from those that don’t.
Beyond ransomware, backups protect against other malicious threats including data breaches, malware infections, and phishing attacks that result in data corruption or unauthorized access. By maintaining multiple backup copies, you ensure that even if one backup is compromised, you have clean, untainted versions available for restoration.
Security experts and disaster recovery professionals universally recommend following the 3-2-1 backup rule as the foundation of any comprehensive backup strategy. This rule specifies that organizations should maintain three copies of important data, stored on two different types of storage media, with one copy kept offsite away from the primary business location.
| Backup Component | Details | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 3 Copies | Original data + 2 backup copies | Ensures redundancy and recovery options |
| 2 Storage Types | Local storage (hard drive/NAS) + Cloud storage | Protects against single point of failure |
| 1 Offsite Copy | Cloud backup or remote facility | Protects against physical disasters |
This approach provides multiple layers of protection. The local backup enables rapid recovery for everyday incidents like accidental file deletion or minor system failures. The cloud backup provides geographic redundancy and protection against physical disasters like fires, floods, or theft. By distributing backups across different storage types and locations, you ensure that no single failure—whether technical, environmental, or malicious—can result in complete data loss.
Organizations should implement a combination of backup methods to optimize both recovery speed and storage efficiency. Full backups create complete copies of all data but consume significant storage space and take considerable time to complete. Incremental backups only capture data that has changed since the last backup, dramatically reducing storage requirements and backup duration. Differential backups capture changes since the last full backup, offering a middle ground between speed and storage efficiency.
Most modern backup solutions employ automated scheduling to ensure backups occur consistently without manual intervention. This automation is critical because manual backups are prone to human error and frequently skipped due to time constraints or oversight. Automated backups running daily or even multiple times per day ensure that your recovery point objective (RPO)—the maximum acceptable amount of data loss—remains minimal. For mission-critical systems, some organizations implement continuous data protection that captures changes in near-real-time.
Recovery time objective (RTO) represents how quickly you can restore systems and resume operations. Organizations should establish RTOs based on business impact analysis, recognizing that different systems have different criticality levels. Customer-facing systems might require RTOs measured in minutes, while less critical systems might tolerate RTOs of several hours. Your backup strategy should be designed to meet these RTOs, with regular testing to verify that recovery can actually be achieved within the specified timeframe.
Data protection regulations have become increasingly stringent across industries and jurisdictions. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in healthcare, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for payment processing, and numerous other regulations mandate specific data retention and protection requirements. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in substantial fines—GDPR violations can result in penalties up to €20 million or 4% of annual global revenue, whichever is higher.
Regular backups are essential for demonstrating compliance with these regulations. They provide documented evidence that your organization takes data protection seriously and has implemented reasonable safeguards. In the event of an audit or investigation, the availability of reliable backups significantly strengthens your compliance posture. Additionally, many insurance providers now require businesses to maintain documented backup and disaster recovery procedures as a condition of coverage, making backups not just a security best practice but a business requirement.
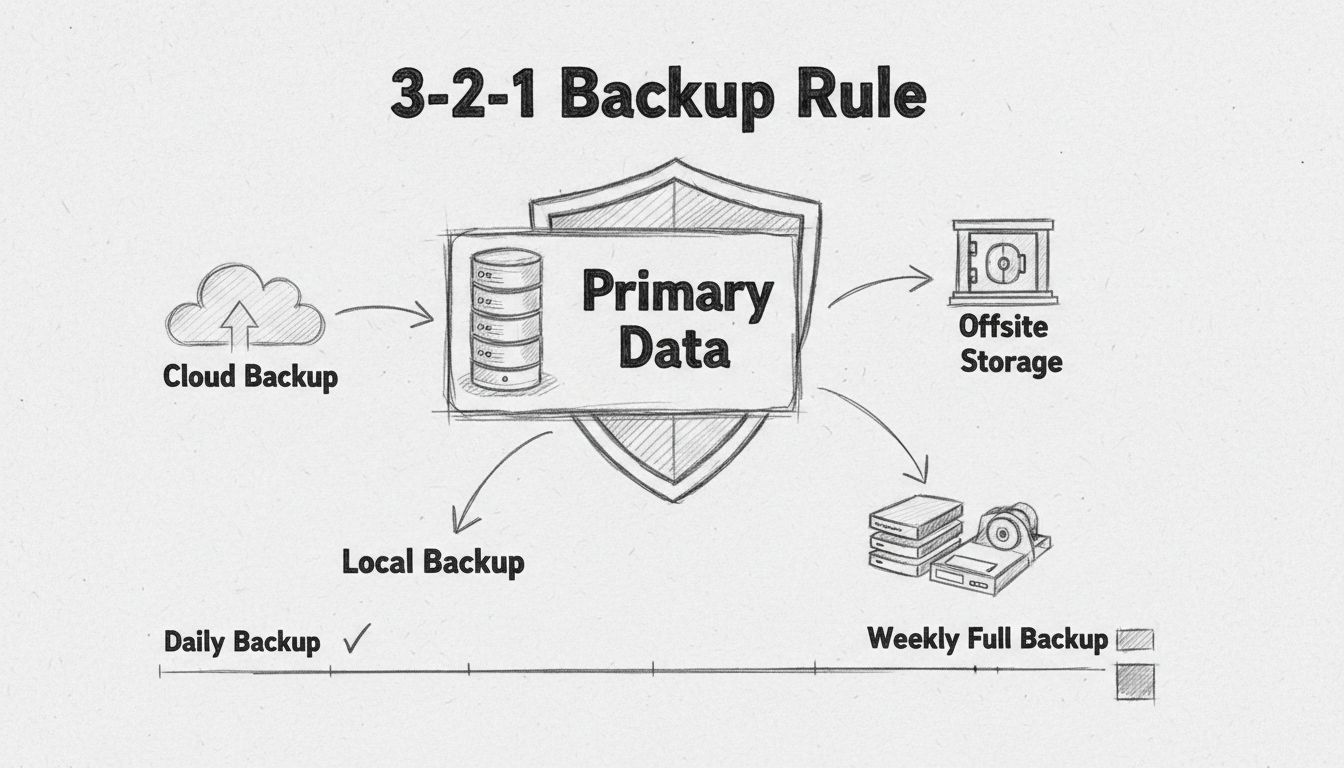
Natural disasters, infrastructure failures, and other catastrophic events can destroy physical data centers and on-premises infrastructure within minutes. Fires, floods, earthquakes, and severe weather events pose genuine threats to businesses in vulnerable locations. Without offsite backups, such events would result in permanent data loss and business failure. Cloud-based backups and offsite storage facilities provide a critical lifeline, ensuring that your business can continue operations even if your primary physical location is destroyed.
A comprehensive disaster recovery plan built around regular backups enables organizations to maintain business continuity despite disruptions. Employees can access critical data from alternative locations, customers can continue receiving services, and revenue generation can resume quickly. This resilience is particularly important in today’s competitive landscape where customers have numerous alternatives and will quickly switch to competitors if service is interrupted.
While implementing and maintaining a comprehensive backup strategy requires investment in technology, infrastructure, and personnel, this cost is minimal compared to the potential losses from data loss. The direct costs of data recovery without backups can be astronomical—professional data recovery services can cost tens of thousands of dollars and are not always successful. Beyond recovery costs, organizations face lost revenue during downtime, potential regulatory fines, legal fees, and the immeasurable cost of reputational damage.
Consider a practical example: a mid-sized accounting firm losing its client database would face weeks of downtime attempting to rebuild records, potential loss of clients to competitors, regulatory penalties for failing to maintain required records, and possible lawsuits from clients. The total cost could easily exceed $1 million. In contrast, implementing a robust backup strategy costs a fraction of this amount and provides protection against this scenario and countless others.
Having backups is only half the equation; you must also verify that those backups actually work and can be restored when needed. Many organizations discover too late that their backup systems have failed silently, leaving them with no recovery option when disaster strikes. Regular testing of backup and recovery procedures is essential to identify and address problems before they become critical.
Organizations should conduct periodic recovery tests, ideally simulating realistic disaster scenarios. These tests should verify that data can be restored completely and accurately, that recovery times meet established RTOs, and that recovered systems function properly. Testing should also include verification that backups have not been compromised or corrupted, particularly important given the threat of ransomware that can affect backup systems as well as primary systems.
Regular backups represent one of the most cost-effective and impactful security investments any organization can make. They protect against the full spectrum of threats facing modern businesses—from ransomware and cyberattacks to hardware failures and natural disasters. By implementing a comprehensive backup strategy following industry best practices like the 3-2-1 rule, automating backup processes, and regularly testing recovery procedures, organizations can ensure that data loss becomes a manageable incident rather than an existential threat. In an era where data is increasingly central to business operations and value creation, regular backups are not optional—they are fundamental to business security and survival.
Just as regular backups safeguard your business data, PostAffiliatePro safeguards your affiliate program with enterprise-grade security, automated tracking, and reliable infrastructure. Ensure your affiliate network is always protected and performing at peak efficiency.

why SMBs are the primary targets for cybercriminals, the vulnerabilities they face, and how to protect your business from cyber threats with proven security

Protect your small business from data breaches with 7 essential security tips: firewalls, password policies, backups, and more.
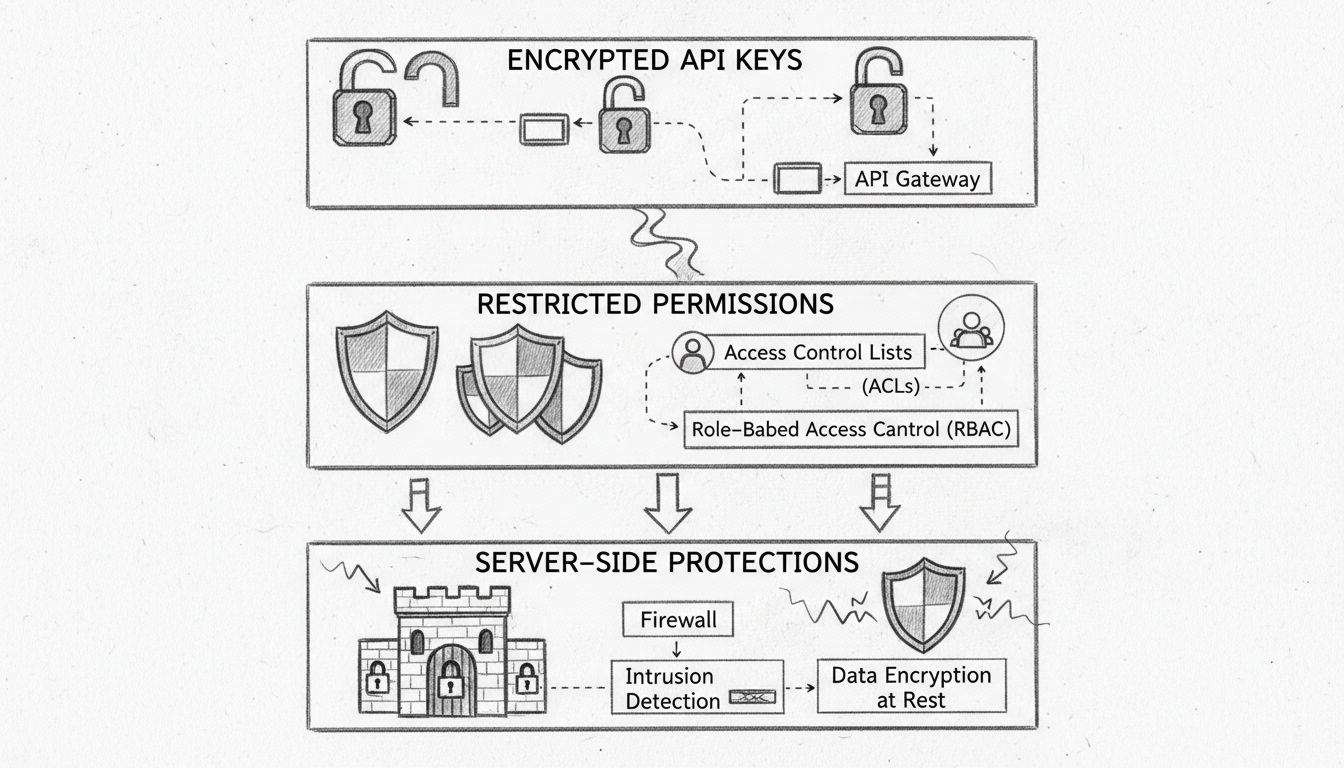
Learn how PostAffiliatePro protects your affiliate and customer data with encrypted API keys, restricted permissions, and server-side protections. Comprehensive...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.