What Is a URL? Easy and Understandable Definition
A uniform resource locator (URL) defines an address of a web page. It consists of three parts: protocol, hostname, and file name.
Learn exactly where URLs are located in web browsers. Discover the address bar, its functions, security features, and how to use it effectively for safe web navigation in 2025.
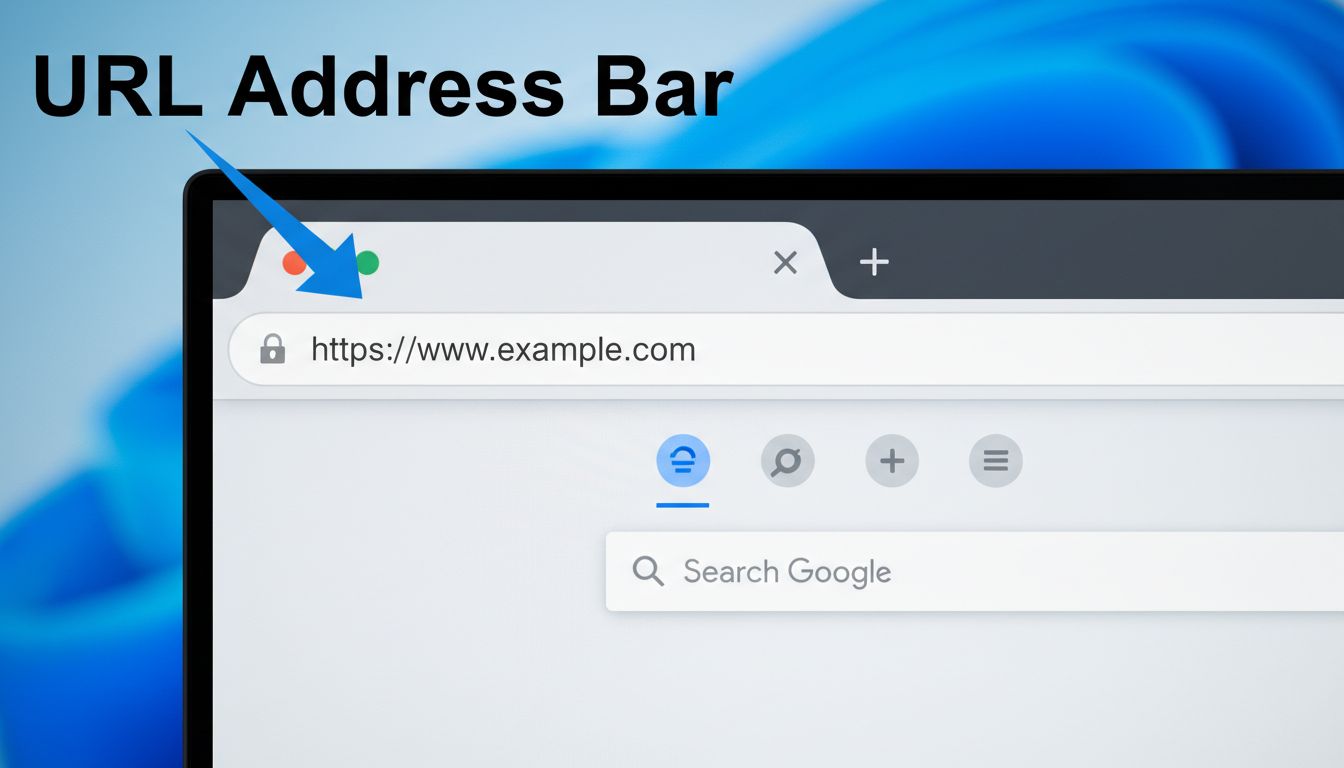
The URL is located in the address bar at the top of your web browser. This rectangular input field displays the web address of the current page and allows you to type new addresses to navigate to different websites.
The address bar, also known as the location bar or URL bar, is a fundamental component of every web browser that serves as the primary interface for web navigation. Located at the very top of your browser window, this rectangular input field displays the complete web address (URL) of the current webpage you are viewing. The address bar is positioned prominently above the main content area, making it immediately visible and accessible to users. Whether you are using Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Safari, or Opera, every modern browser features this essential navigation tool in a similar position and with comparable functionality.
The address bar’s primary function is to show users exactly where they are on the internet by displaying the full Uniform Resource Locator (URL) of the active webpage. This transparency is crucial for understanding web navigation and maintaining awareness of which websites you are visiting. Beyond simply displaying the current URL, the address bar also serves as an input field where users can type new web addresses to navigate to different websites. This dual functionality—displaying current location while enabling new navigation—makes the address bar one of the most important elements of the browser interface.
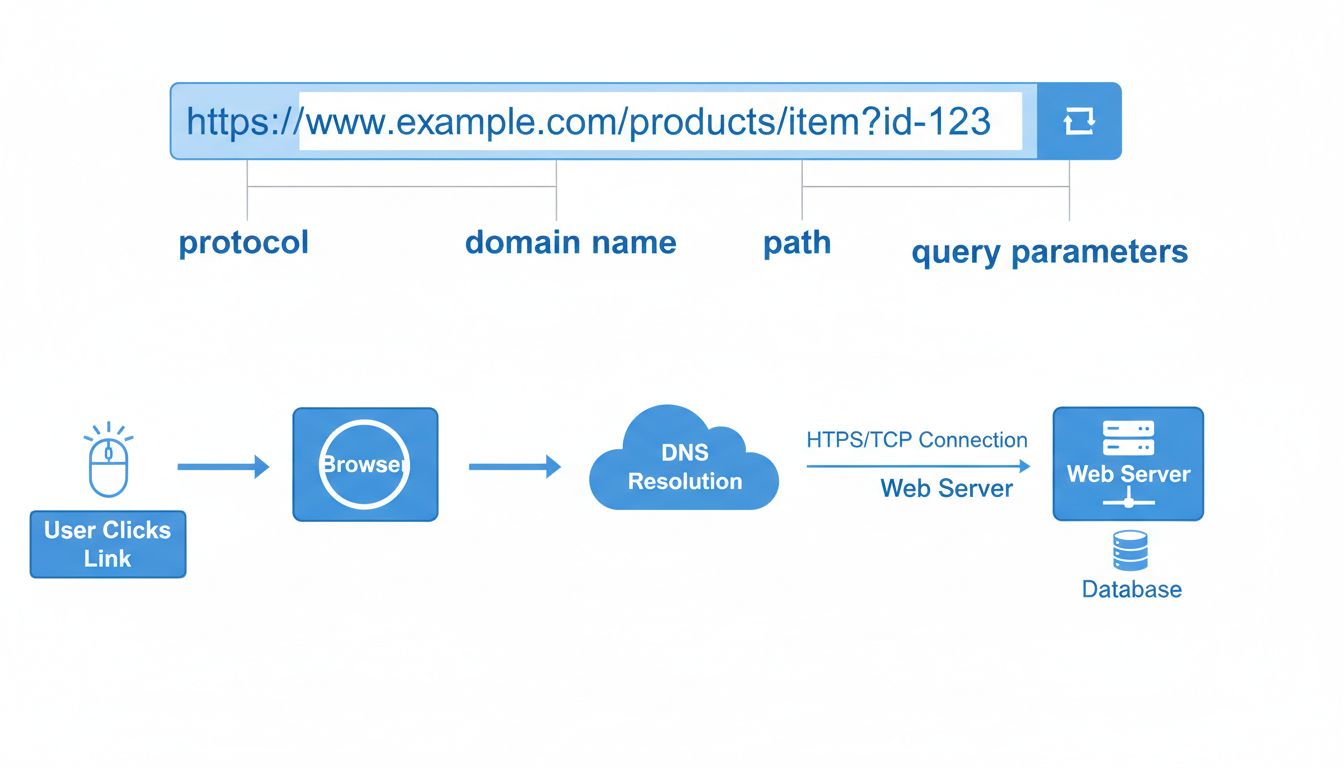
When you look at the address bar, you will see a complete URL that contains several distinct components working together to identify and locate a specific resource on the internet. Understanding these components helps you recognize legitimate websites and identify potential security threats. The first component is the protocol, which typically appears as either “http://” or “https://” at the beginning of the URL. The protocol determines how data is transmitted between your browser and the web server—HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) transmits data without encryption, while HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts the data using SSL/TLS technology, providing a secure connection for sensitive information like passwords and credit card numbers.
Following the protocol is the domain name or hostname, which identifies the specific website you are visiting. For example, in the URL “https://www.postaffiliatepro.com/pricing/" , the domain name is “postaffiliatepro.com” and “www” is a subdomain. The domain name is registered with domain registrars and points to specific IP addresses that host the website’s content. After the domain name comes the path, which specifies the exact location of a resource on that website. In the example above, “/pricing/” is the path that directs you to the pricing page specifically. Some URLs also include query parameters (indicated by a question mark followed by key-value pairs) that pass additional information to the server, such as search terms or filter options.
| URL Component | Example | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | https:// | Determines data transmission method and security level |
| Domain Name | postaffiliatepro.com | Identifies the specific website |
| Subdomain | www | Organizes website sections or services |
| Path | /pricing/ | Specifies the exact page or resource location |
| Query Parameters | ?id=123&sort=price | Passes additional data to the server |
| Fragment | #features | Jumps to specific sections within a page |
Accessing the address bar is straightforward and can be accomplished through multiple methods depending on your browser and personal preference. The most direct method is to simply click on the address bar with your mouse, which will activate the field and allow you to type a new URL or edit the existing one. Most browsers also provide keyboard shortcuts for quick access to the address bar without using a mouse. In Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge, pressing Ctrl+L (or Cmd+L on Mac) will immediately select the entire URL in the address bar, highlighting it and preparing it for replacement with a new address. This keyboard shortcut is particularly useful for power users who prefer keyboard navigation over mouse interaction.
Once you have accessed the address bar, you can type a new web address to navigate to a different website. Modern browsers have implemented intelligent autocomplete features that suggest previously visited websites and bookmarked pages as you type. These suggestions appear in a dropdown menu below the address bar, allowing you to quickly select a frequently visited site without typing the complete URL. Additionally, many browsers now allow you to use the address bar as a search engine by simply typing keywords instead of a full URL. If you type “affiliate marketing software” into the address bar, your browser will automatically search for that term using your default search engine, demonstrating the multifunctional nature of this interface element.
The address bar plays a critical role in web security by providing visual indicators that help you identify whether a website is secure and legitimate. The most important security indicator is the presence of “https://” at the beginning of the URL, which indicates that the connection is encrypted and secure. Secure websites also display a padlock icon next to the URL in the address bar, providing additional visual confirmation that your data is protected. When you click on this padlock icon, your browser displays detailed information about the website’s SSL certificate, including the organization name and certificate validity period. This information helps you verify that you are visiting the legitimate website and not a fraudulent imposter.
Conversely, websites using “http://” (without the “s”) transmit data without encryption, making them vulnerable to interception by malicious actors. Modern browsers now display warning messages when you attempt to enter sensitive information on non-secure websites, alerting you to the potential security risk. Phishing attacks often exploit user inattention to the address bar by creating URLs that closely resemble legitimate websites through typo squatting or domain spoofing techniques. For example, a malicious actor might register a domain like “postaffiliatepro-official.com” or “postaffiliatepro.net” to deceive users into visiting their fraudulent site. By carefully examining the address bar before entering any personal information, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to phishing attacks or other online fraud schemes.
Modern web browsers have evolved the address bar beyond its basic function of displaying and inputting URLs, incorporating numerous advanced features that enhance productivity and user experience. Many browsers now support bookmarking functionality directly from the address bar, allowing you to save frequently visited websites for quick access later. In Google Chrome, for example, you can click a star icon in the address bar to bookmark the current page, and these bookmarks appear as suggestions when you type in the address bar. This feature significantly reduces the time required to navigate to your most important websites, as you no longer need to remember or type their complete URLs.
Another powerful feature available in modern address bars is the ability to search within specific websites without leaving your current page. This functionality, known as site-specific search, allows you to type a website name followed by your search query directly into the address bar. For instance, typing “site:postaffiliatepro.com affiliate tracking” would search for pages about affiliate tracking specifically on the PostAffiliatePro website. Additionally, many browsers allow customization of address bar behavior through settings and extensions. You can configure which search engine the address bar uses, whether it displays suggestions from your browsing history, and what types of data it stores for autocomplete functionality. Privacy-conscious users can disable history-based suggestions entirely, while others may prefer to enable all suggestions for maximum convenience.
Mastering keyboard shortcuts related to the address bar can dramatically improve your web browsing efficiency and productivity. Beyond the basic Ctrl+L shortcut for accessing the address bar, several other useful shortcuts exist across different browsers. Pressing Ctrl+Enter in most browsers automatically adds “www.” to the beginning and “.com” to the end of whatever text you type in the address bar, allowing you to quickly navigate to common websites. For example, typing “postaffiliatepro” and pressing Ctrl+Enter would navigate directly to “www.postaffiliatepro.com ” without requiring you to type the full URL. This shortcut saves considerable time when navigating to well-known websites with standard domain structures.
Another valuable technique involves using the address bar to navigate through your browsing history. Pressing the down arrow key after clicking in the address bar displays a list of recently visited websites, allowing you to quickly return to a site you visited earlier without searching for it. Similarly, pressing Alt+Left Arrow navigates to the previous page in your browsing history, while Alt+Right Arrow moves forward through your history. These navigation shortcuts work seamlessly with the address bar to create a fluid browsing experience. For users managing multiple websites or affiliate programs, these shortcuts become invaluable tools for quickly switching between different platforms and resources without losing productivity.
While the fundamental purpose of the address bar remains consistent across all web browsers, each browser implements this feature with slight variations in appearance, functionality, and available features. Google Chrome combines the address bar with the search bar into a single unified field called the “Omnibox,” which intelligently determines whether your input is a URL or a search query. Chrome’s address bar displays a green padlock icon for secure HTTPS connections and provides detailed security information when you click the padlock. The browser also shows page load progress directly in the address bar, giving users visual feedback about page loading status.
Mozilla Firefox maintains a more traditional separation between the address bar and search bar, though both can be used interchangeably for navigation and searching. Firefox’s address bar displays a shield icon when enhanced tracking protection is active, indicating that the browser is blocking trackers on the current website. Microsoft Edge, built on the Chromium engine like Chrome, features a similar unified address bar design with integrated search functionality. Safari on macOS and iOS displays the address bar at the top of the browser window with a clean, minimalist design that emphasizes the current URL. Regardless of which browser you use, the address bar remains the central navigation interface, and understanding its location and functionality is essential for effective web browsing.
Just as the address bar is essential for web navigation, PostAffiliatePro is essential for managing your affiliate program. Track URLs, monitor affiliate performance, and optimize your commission structure all in one powerful platform.
A uniform resource locator (URL) defines an address of a web page. It consists of three parts: protocol, hostname, and file name.
Learn how website links work, understand URL structure, DNS resolution, and the technical process behind web navigation. Expert guide for 2025.

Discover proven methods to get a free domain name in 2025. Learn about web hosting bundles, website builders, free registrars, and promotional offers. Compare o...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.