Indexing (Indexed)
Indexing is a process when a certain webpage is found by crawlers. Key signals are noticed and all data is tracked in the index.
Learn what SEO indexing means, how it works, and why it’s critical for your website’s search visibility. Discover best practices to ensure your pages get indexed by Google.
Indexing is the process of adding a website or individual web page to a search engine's database. It's how search engines organize and store information about web pages so they can be retrieved and displayed in search results when users perform relevant searches.
Indexing is one of the most critical yet often misunderstood concepts in search engine optimization. While many website owners focus on keywords and backlinks, they overlook the fundamental requirement for search visibility: their pages must first be indexed by search engines. Without indexing, even the most perfectly optimized content will never appear in search results, regardless of its quality or relevance. This comprehensive guide explains what indexing means, how it works, and why it’s essential for your online success.
Indexing is the process by which search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo discover, analyze, and store information about web pages in their massive databases called indexes. Think of a search engine’s index as a giant library catalog—instead of cataloging books, it catalogs web pages. When a user enters a search query, the search engine searches through its index to find relevant pages and displays them in the search results. Without an index, search engines would need to crawl the entire internet every single time someone performed a search, which would be impossibly slow and inefficient. The index allows search engines to instantly retrieve relevant results from billions of indexed pages, providing users with the fast, accurate search experience they expect.
The indexing process is fundamentally different from crawling, though the two are closely related. Crawling is when search engine bots discover and access web pages by following links across the internet. Indexing is what happens after crawling—the search engine analyzes the content it found and stores it in its database. A page can be crawled but not indexed, which is a common problem that affects many websites. Understanding this distinction is crucial for diagnosing and fixing indexing issues on your site.
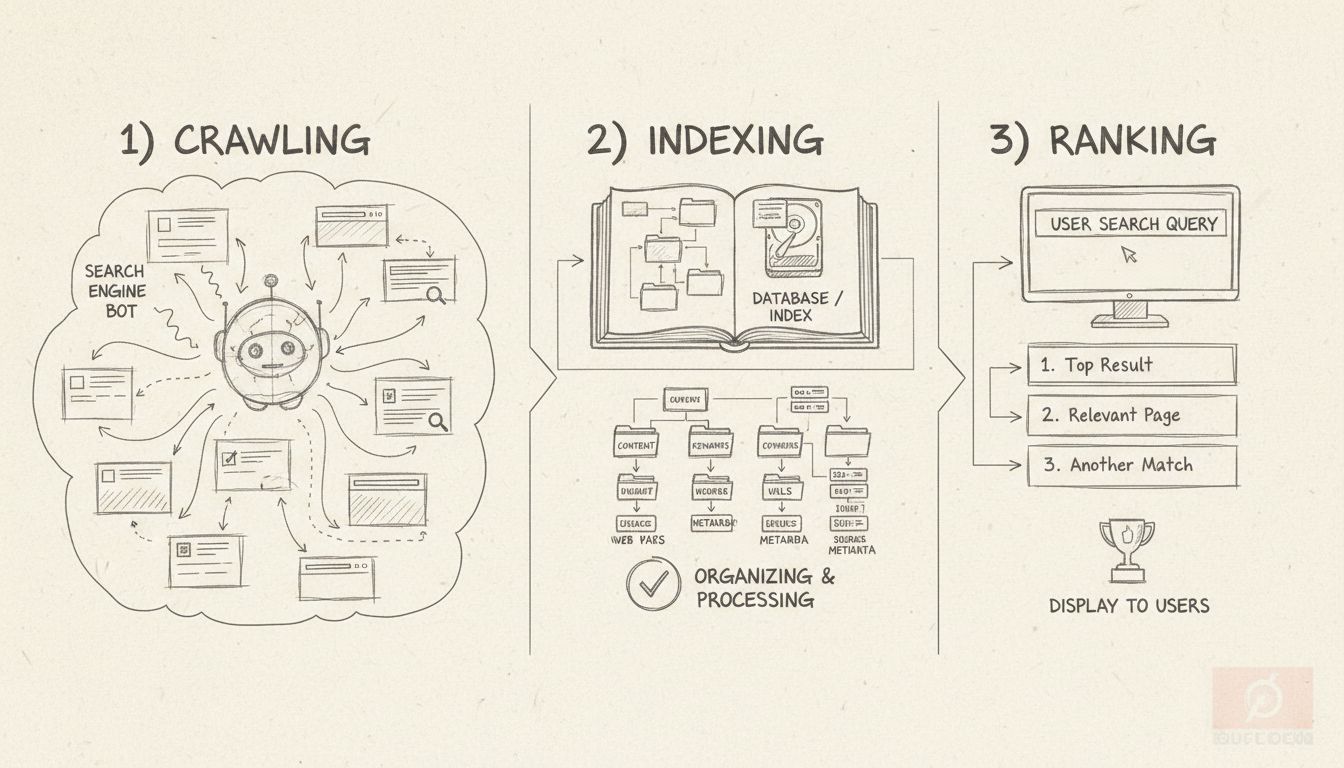
Search engines follow a three-stage process to make content available to users. Understanding these stages helps you optimize your website for better visibility and ensures your content reaches your target audience effectively.
| Stage | Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Crawling | Search engine bots discover and access web pages by following links | Identify new and updated content on the web |
| Indexing | Search engines analyze and store page content in their database | Organize information for quick retrieval during searches |
| Ranking | Search engines determine which pages are most relevant to a query | Display results in order of relevance and authority |
All three stages must occur for your content to appear in search results. If your page isn’t crawled, it won’t be indexed. If it isn’t indexed, it can’t be ranked or displayed to users. This interconnected process means that problems at any stage can prevent your content from reaching your audience. PostAffiliatePro users benefit from understanding this process because it directly impacts how effectively your affiliate marketing content reaches potential customers and drives conversions.
The indexing process involves several sophisticated steps that search engines execute to organize and evaluate web pages. When Googlebot or another search engine crawler visits your page, it doesn’t immediately add it to the index. Instead, the search engine performs a complex analysis to determine whether the page deserves to be indexed and how it should be categorized. This process includes rendering the page to see how it appears to users, extracting text and media content, identifying keywords and topics, and evaluating the page’s quality and relevance. The search engine also checks for technical issues like broken links, slow loading times, or security problems that might prevent indexing.
During the indexing phase, search engines use advanced algorithms to understand what your page is about and how it relates to other pages on the web. They analyze factors like page structure, meta tags, headings, content quality, and internal linking patterns. The search engine also checks whether your page is a duplicate of another page or contains thin content that doesn’t provide value to users. If the search engine determines that your page meets its quality standards and isn’t a duplicate, it adds the page to the index. However, if the page has issues—such as being blocked by robots.txt, having a noindex tag, or containing low-quality content—the search engine may skip indexing it entirely.
Indexing is absolutely essential for your website’s search visibility and organic traffic. No matter how well-optimized your content is, how many backlinks you have, or how perfect your technical SEO is, if your pages aren’t indexed, they won’t appear in search results. Research shows that an average of 16% of valuable, indexable pages on well-known websites aren’t indexed, representing a significant loss of potential traffic and revenue. This problem affects websites of all sizes—from small blogs to major retailers like Walmart, which has 45% of its product pages unindexed. The impact is particularly severe for eCommerce sites, large websites with thousands of pages, and JavaScript-heavy websites, but even small websites can suffer from indexing issues due to technical problems or poor site structure.
Indexing is important because it enables search engines to retrieve relevant results quickly when users perform searches. When your pages are properly indexed, they have the opportunity to rank for relevant keywords and appear in search results. This visibility drives organic traffic to your website, which is often the most valuable source of traffic because it represents users actively searching for what you offer. Without indexing, your content is invisible to search engines and your target audience. For affiliate marketers using PostAffiliatePro, ensuring your content is indexed is the first step toward driving conversions and earning commissions. Every day that your content remains unindexed is a day you’re losing potential revenue.
Understanding why pages fail to get indexed is crucial for fixing indexing problems on your website. Technical issues are the most common culprits, but there are many other reasons search engines might skip your pages. Pages with noindex meta tags or X-Robots tags explicitly tell search engines not to index them, which is sometimes intentional but often accidental. Pages blocked by robots.txt directives can’t be crawled and therefore can’t be indexed. Pages with canonical tags pointing to other pages won’t be indexed because the search engine treats them as duplicates. Soft 404 errors, where a page returns a 200 status code but contains little or no useful content, signal to search engines that the page isn’t worth indexing. Duplicate content, whether on your own site or copied from other websites, often gets filtered out during indexing because search engines prefer to index unique, original content.
Technical SEO issues also prevent indexing. Pages that load slowly may be crawled less frequently, and if they’re not crawled, they can’t be indexed. Pages with poor mobile optimization may not be indexed because Google now uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it crawls and indexes the mobile version of your site first. Pages with broken internal links or poor site architecture may not be discovered by search engines at all. Server errors like 500 Internal Server Errors or 502 Bad Gateway errors prevent crawling and indexing. Pages hidden behind login forms, paywalls, or search forms can’t be indexed because search engine bots can’t access the content. Additionally, pages with thin content—pages that provide little value to users—are often not indexed because search engines prioritize quality content that serves user intent.
Ensuring your pages are indexed requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses technical, structural, and content-related factors. First, make sure your pages are indexable by removing any barriers to indexing. Don’t use noindex tags on pages you want indexed, don’t block important pages with robots.txt, and don’t use canonical tags pointing to other pages unless you specifically want to consolidate duplicate content. Create an XML sitemap that includes all your important pages and submit it to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools. An XML sitemap helps search engines discover your pages more efficiently, especially on large websites with thousands of pages. Update your sitemap whenever you add, modify, or delete pages so search engines always have current information about your site structure.
Optimize your site’s internal linking structure to help search engines discover and crawl your pages more effectively. Every important page should be reachable through internal links from other pages on your site. Avoid orphan pages—pages that exist in your sitemap but aren’t linked to from anywhere else on your site—because search engines may not discover them through normal crawling. Use descriptive anchor text in your internal links to help search engines understand what your pages are about. Ensure your site loads quickly because page speed affects crawl frequency and indexing. Optimize your images, minimize CSS and JavaScript, enable browser caching, and use a content delivery network to improve performance. Fix any technical errors that prevent crawling, such as broken links, redirect chains, and server errors. Use Google Search Console to monitor your indexing status and identify any issues preventing your pages from being indexed.
Many people confuse indexing with ranking, but they’re two distinct processes. Indexing is when a search engine adds your page to its database. Ranking is when the search engine determines where your page should appear in search results for specific keywords. A page can be indexed but not rank for any keywords, which means it appears in the search engine’s database but doesn’t show up in search results for any searches. Conversely, a page can’t rank if it isn’t indexed first. Indexing is a prerequisite for ranking, but indexing alone doesn’t guarantee rankings. To rank well, your page needs to be indexed, but it also needs to be relevant to search queries, have high-quality content, have authority through backlinks, and meet all of Google’s ranking factors.
This distinction is important because it means you need to focus on two separate optimization efforts. First, ensure all your important pages are indexed by addressing technical issues and following indexing best practices. Second, optimize those indexed pages for ranking by creating high-quality content, building backlinks, and optimizing on-page SEO factors. Many website owners waste time trying to rank pages that aren’t even indexed, which is futile. PostAffiliatePro users should prioritize indexing first, then focus on ranking and conversion optimization to maximize their affiliate marketing ROI.
Indexing speed varies significantly depending on your website’s authority, age, content freshness, and crawl budget. Research shows that Google indexes only about 56% of indexable URLs within one day of publication, and it takes approximately two weeks for 87% of URLs to be indexed. This means that even if you publish new content today, there’s a good chance it won’t be indexed for several days or even weeks. The delay is particularly frustrating for time-sensitive content like news articles or product launches, where immediate visibility is important. However, there are ways to speed up indexing. Using Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool to request indexing can help, though it’s not guaranteed to work immediately. Using the IndexNow protocol, which is supported by Google, Bing, and Yandex, can notify search engines about new or updated content more quickly than traditional methods.
Your website’s crawl budget affects indexing speed. Crawl budget is the number of pages a search engine will crawl on your site within a specific timeframe. If your site has a large number of URLs but a limited crawl budget, search engines may not crawl all your pages, which means some pages won’t be indexed. You can improve your crawl budget by improving site speed, fixing technical errors, and ensuring your site structure is efficient. Removing low-quality pages and consolidating duplicate content also helps because it means search engines can spend more of their crawl budget on your valuable pages. For large websites, this is particularly important because search engines may only crawl a fraction of your pages if your crawl budget is limited.
As of March 2021, all websites are subject to mobile-first indexing, which means Google crawls, indexes, and ranks based on the mobile version of your site rather than the desktop version. This is a significant shift from the past when Google primarily used the desktop version for indexing and ranking. If your mobile site is significantly different from your desktop site, or if your mobile site has technical issues, your indexing and rankings may suffer. Ensure your mobile site has the same content and functionality as your desktop site. Make sure all important pages are accessible on mobile, that internal links work properly, and that your mobile site loads quickly. Test your mobile site regularly using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to identify any issues that might prevent indexing or hurt your rankings.
Regularly monitoring your indexing status helps you identify and fix problems before they significantly impact your traffic. Google Search Console provides detailed information about your indexing status through the Pages report. You can see how many pages are indexed, how many are discovered but not indexed, and why pages aren’t indexed. The report shows common issues like soft 404 errors, duplicate content, crawl errors, and pages blocked by robots.txt. Click on any issue to see which pages are affected and get recommendations for fixing the problem. You can also use the URL Inspection tool to check the indexing status of individual pages. For large websites, you can export your indexing data to analyze trends and identify patterns in indexing issues. Monitoring your indexing status regularly ensures you catch and fix problems quickly, minimizing the impact on your organic traffic and revenue.
PostAffiliatePro helps you track and optimize your affiliate marketing performance with advanced analytics and real-time monitoring. Ensure your content reaches the right audience and drives conversions with our comprehensive affiliate management platform.
Indexing is a process when a certain webpage is found by crawlers. Key signals are noticed and all data is tracked in the index.
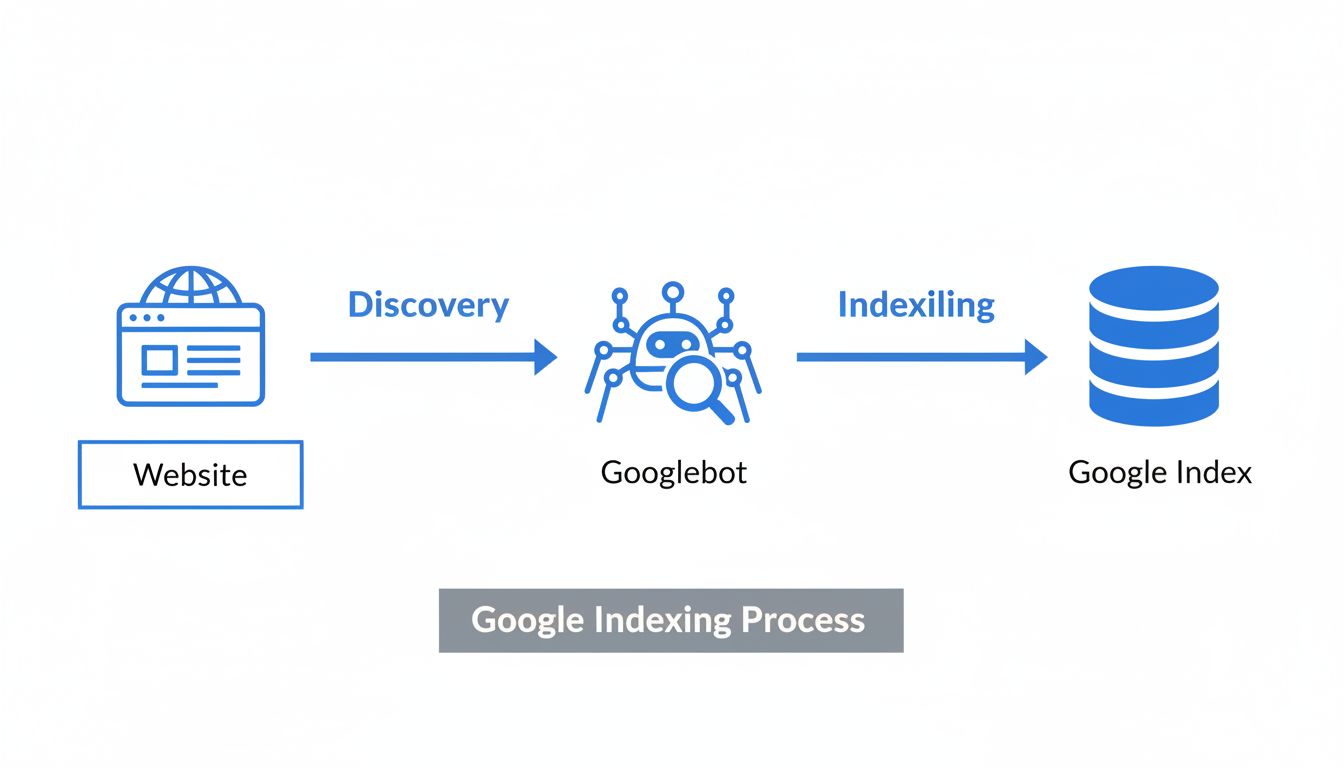
Learn 7 proven methods to check if your website is indexed by Google. Use Google Search Console, site operators, URL inspection tools, and more to verify indexi...
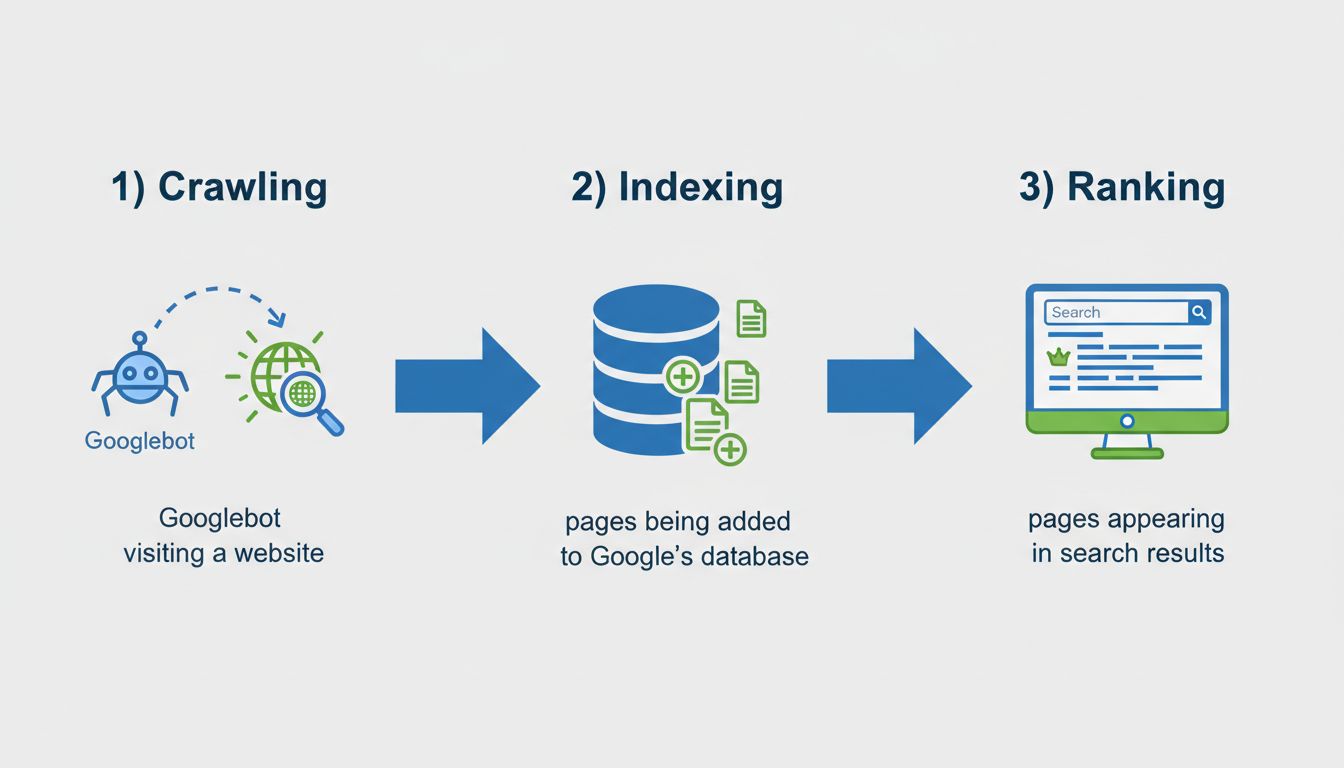
Learn what page indexing means, why pages aren't indexed by Google, and how to fix indexing issues. Discover technical solutions and best practices for 2025.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.