
Common Affiliate Payment Agreements: PPS, PPL, PPC & More
Discover the most common affiliate payment agreements including PPS, PPL, and PPC. Learn how each model works and which is best for you.
Discover the different types of affiliate campaigns including PPC, PPL, PPS, and other commission models. Learn which model works best for your business with PostAffiliatePro.
The different types of affiliate campaigns include pay-per-click (PPC), pay-per-lead (PPL), and pay-per-sale (PPS). Additional models include pay-per-action (PPA), cost-per-impression (CPM), recurring commissions, tiered commissions, two-tier programs, and hybrid models. Each model compensates affiliates differently based on specific user actions or outcomes.
Affiliate marketing has become one of the most effective performance-based marketing strategies for businesses looking to expand their reach and drive revenue growth. The foundation of any successful affiliate program lies in choosing the right compensation model that aligns with your business objectives, profit margins, and target audience. Understanding the different types of affiliate campaigns is essential for both merchants and affiliates, as each model offers distinct advantages and challenges that directly impact earning potential and return on investment.
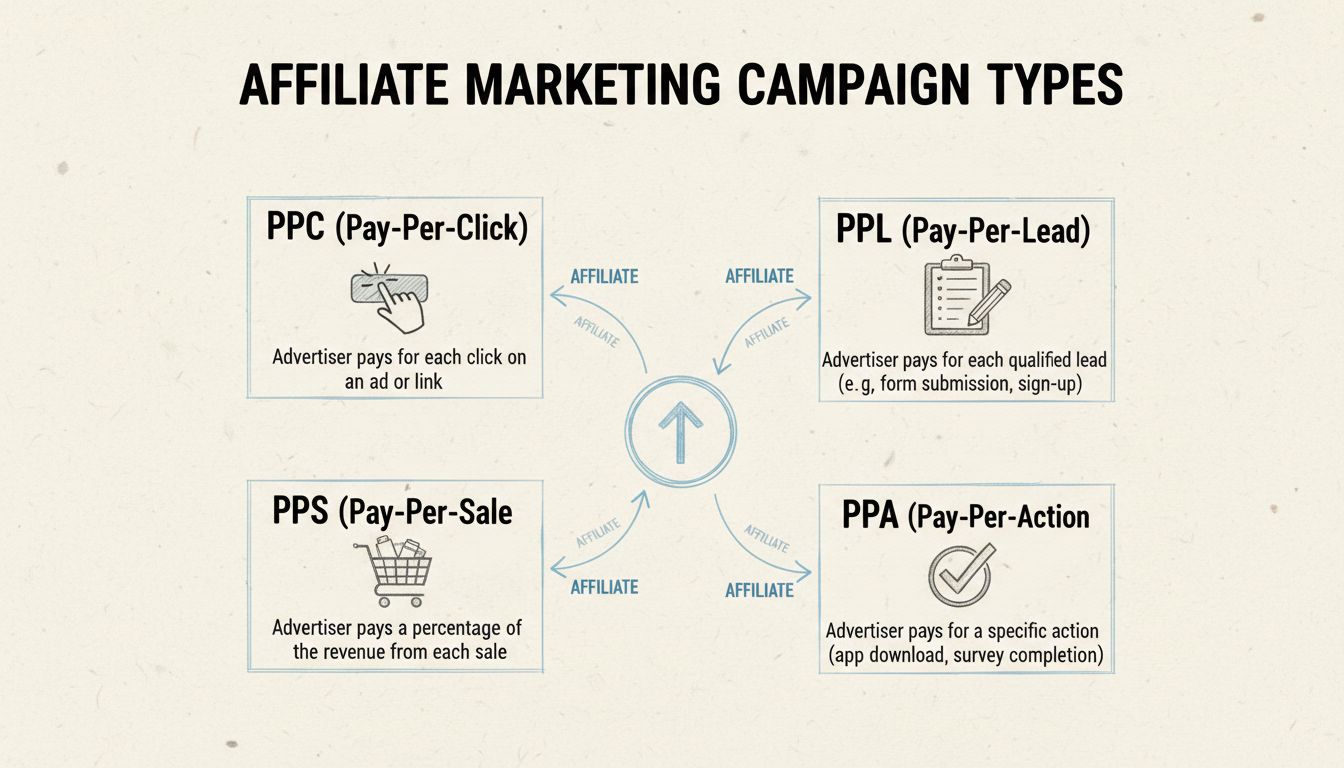
Pay-Per-Click represents one of the most accessible entry points for affiliate marketers and is widely used across digital advertising platforms. In this model, affiliates earn a commission every time a user clicks on their unique affiliate link, regardless of whether that click results in a purchase, lead, or any other conversion. The affiliate receives payment based purely on traffic generation, making it an excellent option for those focused on driving brand awareness and website visibility.
The mechanics of PPC campaigns are straightforward and transparent. When an affiliate promotes a product or service through banner ads, text links, or display advertisements, each click is tracked through a unique URL parameter or cookie-based system. The advertiser pays a predetermined amount per click, which can vary significantly depending on factors such as keyword competitiveness, industry niche, and overall market demand. For example, a technology affiliate might earn $0.50 to $2.00 per click, while finance-related clicks could command premium rates of $5.00 or higher.
PPC campaigns work exceptionally well for startups and businesses seeking rapid brand exposure without immediate sales pressure. The model eliminates the need for affiliates to master complex sales techniques or conversion optimization strategies. However, the primary drawback is the relatively low earnings per click, which means affiliates must generate substantial traffic volumes to achieve meaningful income. Additionally, businesses face the risk of click fraud, where malicious actors generate fake clicks to inflate affiliate earnings without delivering genuine traffic.
Pay-Per-Lead campaigns shift the focus from traffic generation to lead quality and customer interest validation. In this model, affiliates earn commissions when they successfully drive a potential customer to complete a specific action that qualifies as a lead. These qualifying actions typically include filling out contact forms, signing up for newsletters, requesting product demos, completing surveys, registering for free trials, or providing email addresses for further communication.
The PPL model operates on the principle that a lead represents genuine customer interest and has higher conversion potential than a random click. Advertisers are willing to pay more per lead than per click because leads represent pre-qualified prospects who have demonstrated explicit interest in the product or service. Lead validation is a critical component of PPL campaigns, as advertisers often implement quality checks to ensure that submitted information is accurate and that leads meet specific criteria such as geographic location, income level, or industry qualification.
PPL campaigns are particularly popular in industries with longer sales cycles and higher customer acquisition costs, such as insurance, real estate, financial services, education, and B2B software solutions. For instance, an insurance company might pay $15 to $50 per qualified lead, while an online education platform could offer $20 to $100 per student inquiry. The advantage for affiliates is that lead generation typically requires less effort than driving sales, making it more achievable for newer marketers. However, the disadvantage is that lead payouts are generally lower than sales commissions, requiring affiliates to generate high volumes of leads to build substantial income.
Pay-Per-Sale, also known as Cost-Per-Action (CPA) or Pay-Per-Conversion, represents the most performance-driven affiliate model and is the most widely adopted across e-commerce and digital product industries. In PPS campaigns, affiliates only earn commissions when a referred customer completes a purchase through their unique affiliate link. The commission is typically calculated as a percentage of the sale amount or as a flat fee per transaction.
PPS campaigns create perfect alignment between affiliate efforts and business results, as both parties benefit directly from actual revenue generation. An affiliate promoting a $100 product with a 10% commission would earn $10 per sale, while promoting a $500 service with a 15% commission would generate $75 per sale. This model is highly attractive to merchants because they only pay for measurable results and can easily calculate return on investment. The commission structure can be customized to account for product margins, customer lifetime value, and competitive positioning within the industry.
The primary advantage of PPS campaigns is the highest ROI potential for businesses and the highest earning potential for top-performing affiliates. However, the model requires affiliates to possess strong marketing and conversion optimization skills, as they must not only drive traffic but also convince visitors to make purchases. This higher barrier to entry makes PPS campaigns more challenging for beginners but extremely rewarding for experienced marketers who understand sales psychology and conversion rate optimization.
Pay-Per-Action campaigns extend beyond simple clicks and leads to encompass more complex user behaviors that demonstrate higher commitment levels. These actions might include starting a free trial, downloading software, subscribing to a service, creating an account, or completing a multi-step registration process. PPA campaigns are particularly effective for SaaS companies, subscription services, and digital platforms where the goal is to acquire active users rather than passive leads.
The distinction between PPL and PPA lies in the complexity and value of the required action. While a lead might simply be an email address, an action typically requires more user engagement and commitment. For example, a project management software company might pay $25 for a lead (email signup) but $75 for an action (completed account setup with project creation). This model incentivizes affiliates to drive higher-quality traffic that is more likely to engage with the platform and potentially convert to paying customers.
Cost-Per-Impression campaigns, also known as Pay-Per-Impression, compensate affiliates based on the number of times their advertisements are displayed to users, regardless of clicks or conversions. Advertisers pay a fixed amount for every thousand impressions (CPM), typically ranging from $0.50 to $10.00 depending on audience quality and industry. This model is ideal for brand awareness campaigns where the primary goal is visibility and repeated exposure rather than immediate conversions.
CPM campaigns work exceptionally well for luxury brands, premium services, and products that benefit from repeated brand exposure. The model is particularly effective on display advertising networks, social media platforms, and high-traffic websites where impressions can be generated at scale. However, CPM campaigns typically generate the lowest earnings per impression, requiring massive traffic volumes to generate meaningful affiliate income.
Recurring Commission models are specifically designed for subscription-based businesses and services with recurring revenue streams. In this model, affiliates earn commissions not just on the initial sale but on every subsequent billing cycle as long as the referred customer maintains their subscription. This creates a passive income stream for affiliates and provides strong incentive for promoting high-quality, retention-focused products.
For example, a SaaS company offering a $99 monthly subscription with a 20% recurring commission would pay an affiliate $19.80 every month for each customer they referred, as long as that customer remains subscribed. Over a year, a single customer referral could generate $237.60 in affiliate earnings. This model is particularly popular in the software, membership site, and digital service industries, where customer lifetime value is a critical metric.
Tiered Commission structures implement performance-based incentives that reward affiliates for achieving higher sales or lead generation volumes. Commission rates increase as affiliates reach predetermined milestones, creating a motivational framework that encourages continuous improvement and higher performance. A typical tiered structure might look like: 0-50 sales at 10% commission, 51-100 sales at 15% commission, and 100+ sales at 20% commission.
Tiered commissions are highly effective for recruiting and retaining top-performing affiliates, as they provide clear visibility into earning potential and create achievable goals. The model works particularly well for high-ticket products and services where individual sales have significant value. However, tiered structures can be complex to manage and communicate, requiring clear documentation and transparent tracking systems.
Two-Tier affiliate programs create a multi-level structure where affiliates earn commissions not only on their direct sales or leads but also on the sales generated by other affiliates they recruit. This creates a secondary income stream and incentivizes affiliates to build their own affiliate networks. For example, an affiliate might earn 10% on their direct sales and 2% on the sales of any affiliates they recruit.
Two-tier programs are particularly effective for building large-scale affiliate networks and creating long-term partnerships. However, they require careful management to avoid resembling pyramid schemes and must include clear ethical guidelines and performance requirements for recruited affiliates.
| Campaign Type | Payment Trigger | Affiliate Earnings | Business Risk | Best For | Difficulty Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPC | Click on link | Low ($0.10-$2.00) | High (click fraud) | Brand awareness | Easy |
| PPL | Lead submission | Medium ($5-$100) | Medium (lead quality) | Lead generation | Moderate |
| PPS | Completed sale | High ($10-$500+) | Low (sales only) | E-commerce, products | Hard |
| PPA | Complex action | Medium-High ($20-$200) | Low-Medium | SaaS, subscriptions | Moderate-Hard |
| CPM | 1,000 impressions | Very Low ($0.50-$10) | Medium | Brand visibility | Easy |
| Recurring | Monthly subscription | Medium (ongoing) | Low | Subscription services | Moderate |
| Tiered | Performance milestone | Variable (10-30%) | Low | High-volume sales | Moderate |
| Two-Tier | Direct + recruited sales | Variable | Medium | Network building | Hard |
Choosing the optimal affiliate campaign model requires careful analysis of multiple business factors and strategic considerations. Your profit margins play a crucial role in determining sustainable commission rates—a product with 40% margins can support higher affiliate commissions than one with 15% margins. Customer lifetime value is equally important, as products with high CLV can justify higher upfront affiliate commissions, knowing that customers will generate additional revenue over time.
Market competition and industry standards significantly influence which models are viable and attractive to affiliates. In highly competitive niches, you may need to offer more generous commissions or multiple commission tiers to attract quality affiliates. Your sales cycle length is another critical factor—businesses with short sales cycles typically benefit from PPS models, while those with extended evaluation periods often find PPL or PPA models more effective.
Consider your target audience’s sophistication and marketing capabilities. If you’re recruiting beginner affiliates, PPC or PPL models with lower barriers to entry may be more appropriate. For established affiliate networks with experienced marketers, PPS or tiered commission models can drive higher performance. Your marketing infrastructure and tracking capabilities also matter—complex models like two-tier programs require robust affiliate software to manage accurately.
Transparency and Clear Communication form the foundation of successful affiliate programs. Clearly document all commission rates, payment schedules, terms and conditions, and any restrictions on promotional methods. Provide affiliates with detailed information about what qualifies as a valid conversion and what actions might result in commission denial.
Invest in Reliable Tracking Technology to ensure accurate attribution and prevent fraud. Modern affiliate software like PostAffiliatePro provides sophisticated tracking capabilities that handle multiple campaign types, prevent fraud, and generate detailed performance reports. Accurate tracking builds trust with affiliates and protects your business from fraudulent claims.
Provide Marketing Support and Resources to help affiliates succeed. Supply promotional materials, product information, landing pages, email templates, and creative assets that make it easier for affiliates to promote effectively. The easier you make it for affiliates to succeed, the better results you’ll achieve.
Monitor and Optimize Performance continuously. Track which affiliates drive the highest-quality traffic and conversions, and identify which campaign types generate the best ROI. Be prepared to adjust commission rates, add new campaign types, or modify terms based on performance data and market feedback.
Build Long-Term Relationships with top-performing affiliates. Recognize their contributions, provide exclusive opportunities, and consider offering performance bonuses or incentive programs. Long-term affiliate partnerships are more valuable than constantly recruiting new affiliates.
The diversity of affiliate campaign models available today allows businesses to design programs that perfectly align with their specific objectives, industry dynamics, and financial constraints. Whether you’re focused on brand awareness through PPC campaigns, lead generation via PPL models, or direct sales through PPS structures, each model offers distinct advantages when implemented strategically. The most successful affiliate programs often combine multiple campaign types to diversify their marketing approach and appeal to different affiliate skill levels and preferences.
PostAffiliatePro stands out as the leading affiliate management platform for implementing and managing all these campaign types effectively. With advanced tracking capabilities, flexible commission structures, comprehensive fraud prevention, and detailed reporting tools, PostAffiliatePro enables businesses to launch sophisticated affiliate programs that drive measurable results. Whether you’re just starting your affiliate program or looking to optimize an existing one, PostAffiliatePro provides the technology and support needed to succeed in today’s competitive affiliate marketing landscape.
PostAffiliatePro makes it easy to set up and manage any affiliate campaign type with advanced tracking, flexible commission structures, and comprehensive reporting tools.

Discover the most common affiliate payment agreements including PPS, PPL, and PPC. Learn how each model works and which is best for you.

Discover the different types of affiliates and affiliate marketing models. Learn about pay-per-sale, pay-per-click, pay-per-lead, and more. Find the best affili...

Discover the main types of affiliate programs including content, email marketing, loyalty, review sites, influencer, and more. Learn which model suits your busi...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.