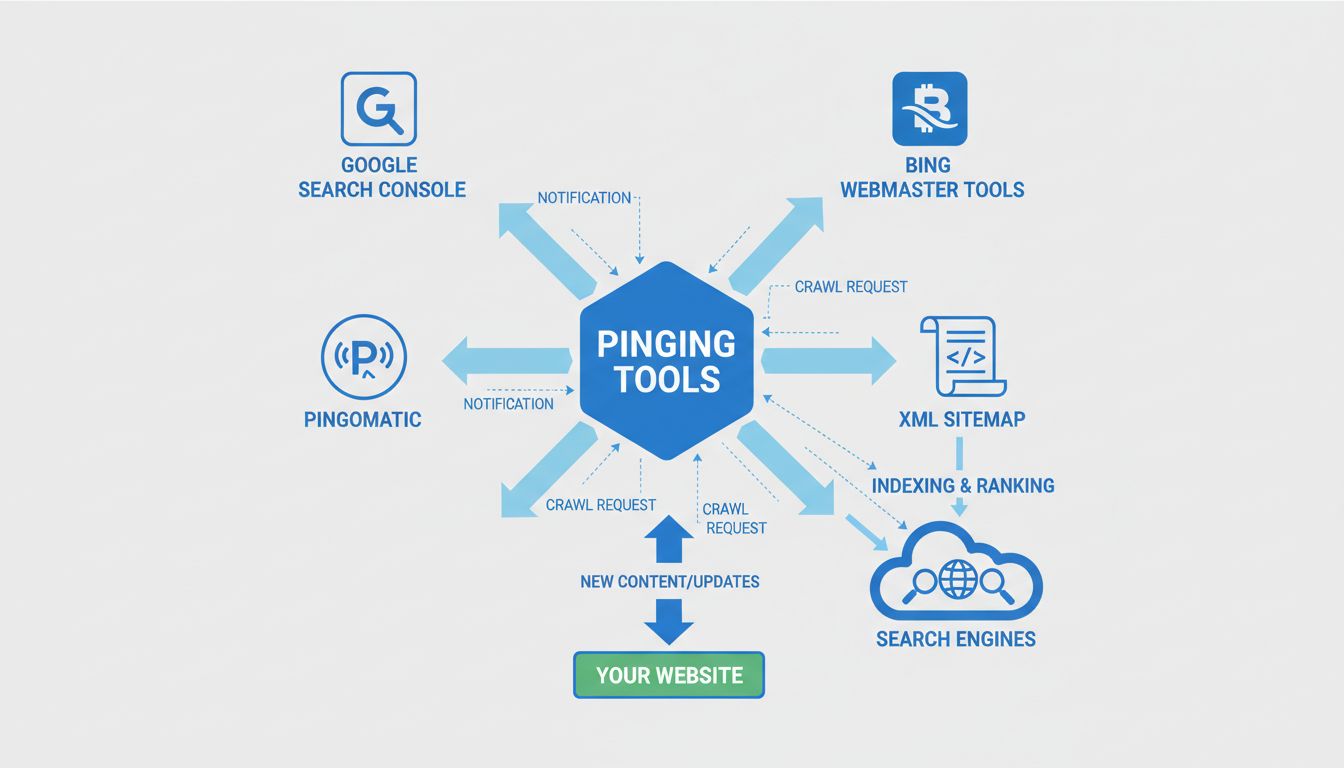
What Tools Can Be Used for Pinging? Complete Guide to SEO Pinging Solutions
Discover the best pinging tools for SEO including WordPress Pingomatic, Google Search Console, manual ping services, and automated solutions. Learn how to notif...
Discover the risks of overusing pinging for SEO. Learn how excessive pinging can trigger search engine penalties, reduce rankings, and harm your affiliate marketing strategy. Get best practices for safe pinging.
Yes, excessive pinging can be seen as spammy by search engines and may lead to penalties. It's best to use pinging only for significant updates or new content.
Pinging is a fundamental SEO technique that notifies search engines about new or updated content on your website. When you ping a search engine, you’re essentially sending a signal that says, “Hey Google, Bing—I’ve published something new. Come check it out.” This process can significantly accelerate the indexing of your content, which is particularly valuable for time-sensitive material like news articles, product launches, or important blog posts. However, like many SEO tactics, pinging can become counterproductive when overused, leading to serious consequences for your website’s visibility and rankings.
The concept of pinging has evolved significantly since the early days of SEO. Originally, pinging was a straightforward way to notify search engines about content updates through services like Ping-O-Matic or direct submissions to search engine APIs. Today, while the fundamental principle remains the same, search engines have become much more sophisticated in detecting and penalizing abusive pinging practices. Understanding the distinction between strategic, measured pinging and excessive, spammy pinging is crucial for maintaining a healthy SEO profile.
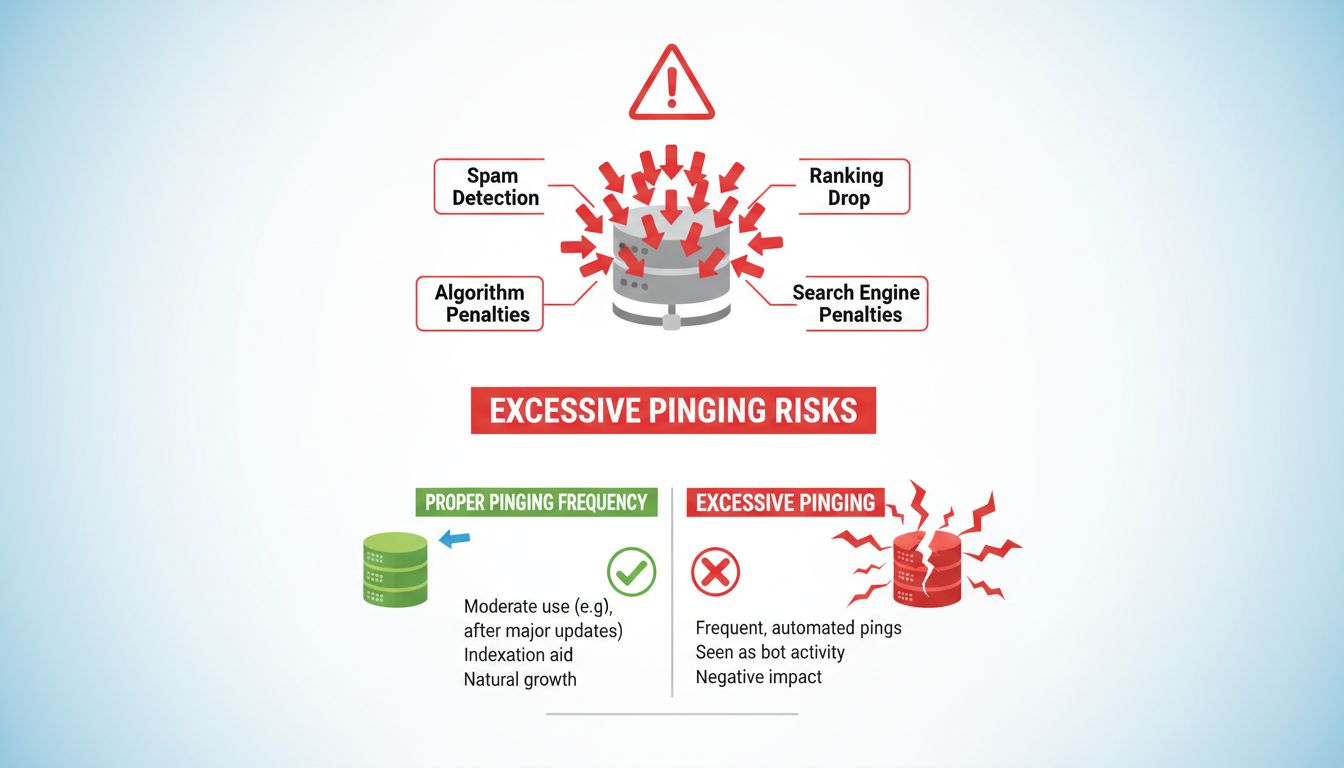
Search engines like Google have developed sophisticated algorithms to detect patterns that indicate manipulation or spam. When you ping your sitemap excessively—particularly for minor changes or when no actual content updates have occurred—search engines interpret this behavior as an attempt to artificially manipulate their crawling and indexing processes. This triggers what’s known as an over-optimization penalty, which can result in significant ranking drops or even temporary de-indexing of your website.
The primary concern with overusing pinging is that it signals to search engines that you’re trying to game the system. Search engines expect websites to ping their sitemaps when meaningful changes occur, such as publishing new pages, making substantial content revisions, or restructuring URL hierarchies. When a website pings multiple times daily without corresponding content updates, or when pinging occurs for every minor edit like fixing a typo or adjusting a meta description, search engines flag this as suspicious activity. This behavior violates the principle of natural SEO optimization that Google emphasizes in its Webmaster Guidelines.
One of the most serious risks of overusing pinging is triggering an algorithmic penalty. Unlike manual penalties that are issued by Google’s webspam team after human review, algorithmic penalties are automatically applied by Google’s ranking algorithms when they detect patterns of over-optimization. These penalties can be devastating because they’re often applied silently—you may not receive a notification in Google Search Console, and you might only discover the penalty by noticing a sudden, unexplained drop in organic traffic.
| Penalty Type | Cause | Impact | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Over-Optimization Penalty | Excessive pinging, keyword stuffing, unnatural links | 20-80% ranking drop | 3-12 months |
| Algorithmic Penalty | Automated detection of spam patterns | Reduced visibility in SERPs | 2-6 months |
| Manual Action | Human review of violations | Partial or complete de-indexing | 1-3 months after reconsideration |
| Temporary Ranking Fluctuation | Minor over-optimization signals | Temporary ranking volatility | 1-4 weeks |
The impact of these penalties extends beyond just rankings. When your website is penalized for over-optimization, search engines may reduce the frequency at which they crawl your site, meaning new content takes longer to be discovered and indexed. This creates a vicious cycle where you might be tempted to ping even more frequently to compensate, which only worsens the penalty. Additionally, a penalized website loses trust signals in the eyes of search engines, making it harder to recover even after you’ve corrected the problematic behavior.
Search engines have become increasingly sophisticated at identifying what constitutes spammy behavior. Excessive pinging falls into this category because it demonstrates a pattern of attempting to manipulate search engine crawling and indexing. When search engines detect this behavior, they don’t just ignore the pings—they actively penalize the website for attempting to game their systems. This is part of Google’s broader effort to maintain the integrity of search results and ensure that only high-quality, legitimately optimized websites rank prominently.
The detection mechanisms are multifaceted. Search engines analyze the frequency of pings relative to actual content updates, examine the quality and relevance of the content being pinged, and assess whether the pinging pattern aligns with natural website maintenance. They also cross-reference pinging activity with other signals like backlink velocity, content publication patterns, and user engagement metrics. If these signals don’t align—for example, if you’re pinging daily but only publishing content weekly—search engines will flag this as suspicious activity.
While less commonly discussed, there’s also a security dimension to excessive pinging. When pinging is performed at scale or through automated tools without proper rate limiting, it can potentially contribute to distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack patterns. Although a single website pinging search engines won’t cause a DDoS attack, the principle is similar: overwhelming a server with requests can degrade its performance or cause it to become unavailable.
From a practical standpoint, if you’re using third-party pinging services or bulk ping websites, you need to be aware that these services may be flagged by search engines as sources of spam. Search engines maintain blacklists of known spam services, and if your website is associated with these services through excessive pinging activity, it could negatively impact your SEO performance. Additionally, some bulk pinging services have been known to ping invalid URLs or URLs that shouldn’t be indexed, which can further damage your website’s credibility with search engines.
To avoid the risks associated with overusing pinging while still benefiting from faster indexing, follow these strategic guidelines. First, only ping your sitemap when you’ve made significant updates to your website. This includes publishing new pages, making substantial revisions to existing content, restructuring your URL hierarchy, or making important technical changes. Minor edits like fixing typos, adjusting meta descriptions, or making small formatting changes don’t warrant a ping.
Second, establish a reasonable pinging frequency based on your website’s update schedule. If you publish new content daily, pinging once daily is appropriate. If you update content weekly, pinging weekly is sufficient. The key is to match your pinging frequency to your actual content update frequency. This demonstrates to search engines that your pinging activity is natural and legitimate, not an attempt to manipulate their systems.
Third, use official channels for pinging whenever possible. Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools are the most reliable and safest ways to submit your sitemap and notify search engines of updates. These official channels are designed specifically for this purpose and won’t trigger spam detection algorithms. Avoid using third-party bulk pinging services or automated tools that ping multiple search engines simultaneously, as these are more likely to be flagged as spam.
To ensure your pinging strategy isn’t causing problems, regularly monitor your website’s performance metrics in Google Search Console. Pay attention to crawl statistics, indexing status, and any manual action notifications. If you notice a sudden drop in crawl rate or indexing latency, it could indicate that search engines are responding negatively to your pinging activity. Similarly, if you see a significant drop in organic traffic without any obvious cause, it might be worth reviewing your recent pinging activity.
Use Google Search Console’s Coverage report to track how many of your pages are indexed and whether there are any indexing errors. The Performance report will show you whether your rankings are stable or fluctuating, which can indicate whether your SEO tactics are working or causing problems. If you notice that your rankings drop shortly after increasing your pinging frequency, this is a clear signal that you should reduce your pinging activity and focus on creating high-quality content instead.
The most important takeaway is that pinging should never be your primary SEO strategy. Search engines prioritize high-quality, original content, natural backlink profiles, and excellent user experience far more than they prioritize how quickly you notify them of updates. In fact, focusing too heavily on pinging and other technical tactics while neglecting content quality is a recipe for SEO failure.
Instead of obsessing over pinging frequency, invest your time and resources in creating valuable, comprehensive content that genuinely serves your audience. Build your backlink profile naturally through relationships with other websites and industry influencers. Optimize your website’s technical performance, mobile responsiveness, and user experience. These fundamental SEO practices will have a far greater impact on your rankings than any pinging strategy ever could. When you focus on these core elements, search engines will naturally crawl and index your content more frequently, without you having to resort to excessive pinging.
Pinging is a legitimate and useful SEO tactic when used appropriately, but it should be viewed as a supplementary tool rather than a primary strategy. The risks of overusing pinging—including algorithmic penalties, reduced crawl frequency, and loss of search engine trust—far outweigh any potential benefits of trying to accelerate indexing through excessive pinging. By using pinging strategically, only for significant updates, and through official channels like Google Search Console, you can enjoy the benefits of faster indexing without risking penalties.
Remember that search engines are designed to reward websites that follow their guidelines and provide genuine value to users. Excessive pinging violates the spirit of these guidelines by attempting to manipulate search engine behavior. Instead, focus on creating excellent content, building a natural backlink profile, and providing an outstanding user experience. These practices will ensure sustainable, long-term SEO success without the risk of penalties that come with over-optimization tactics like excessive pinging.
PostAffiliatePro's advanced tracking and automation features help you manage your affiliate campaigns efficiently without risking SEO penalties. Avoid over-optimization mistakes and focus on sustainable growth with the industry's leading affiliate software.

Discover the best pinging tools for SEO including WordPress Pingomatic, Google Search Console, manual ping services, and automated solutions. Learn how to notif...
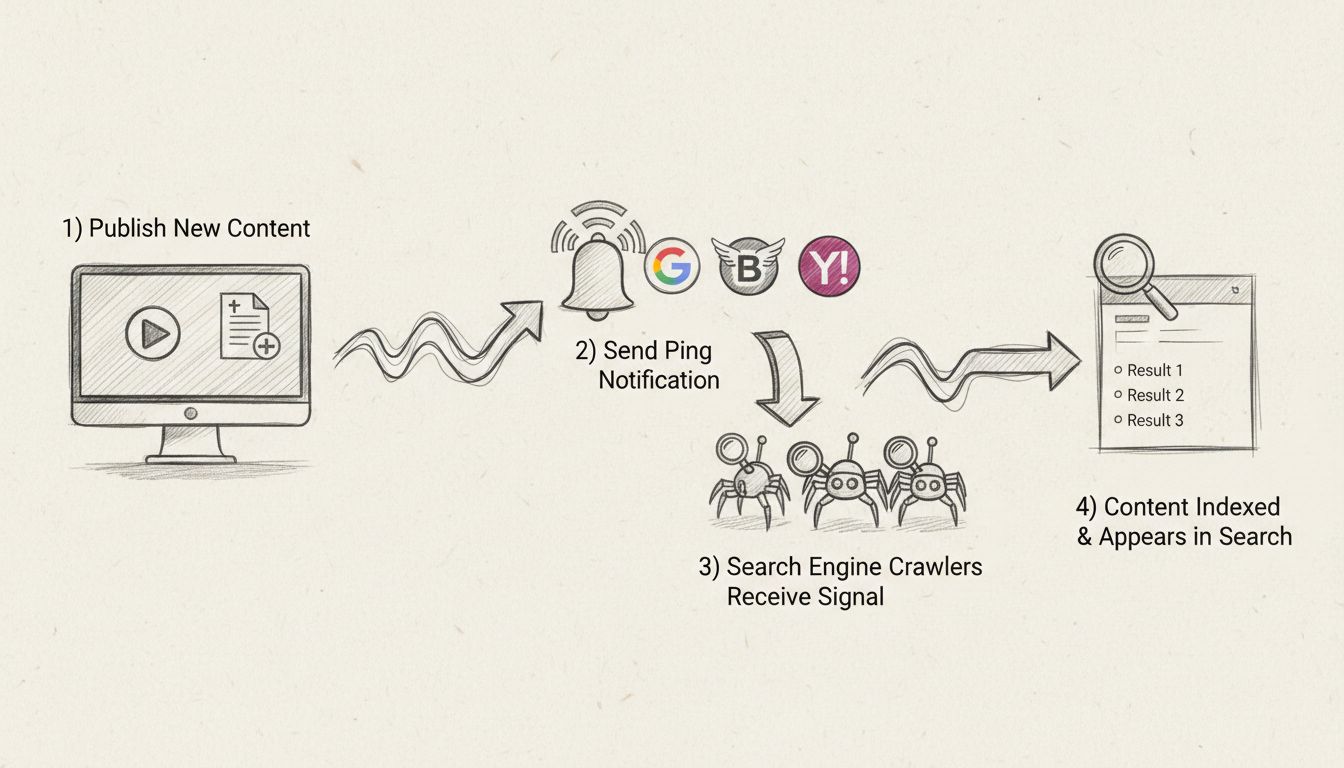
Learn what pinging in SEO means and how it accelerates content indexing. Discover best practices, tools, and strategies to improve your website's search visibil...
Pinging is a process used in SEO to alert search engines and platforms about new or updated content, enabling faster indexing and improved visibility for websit...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.