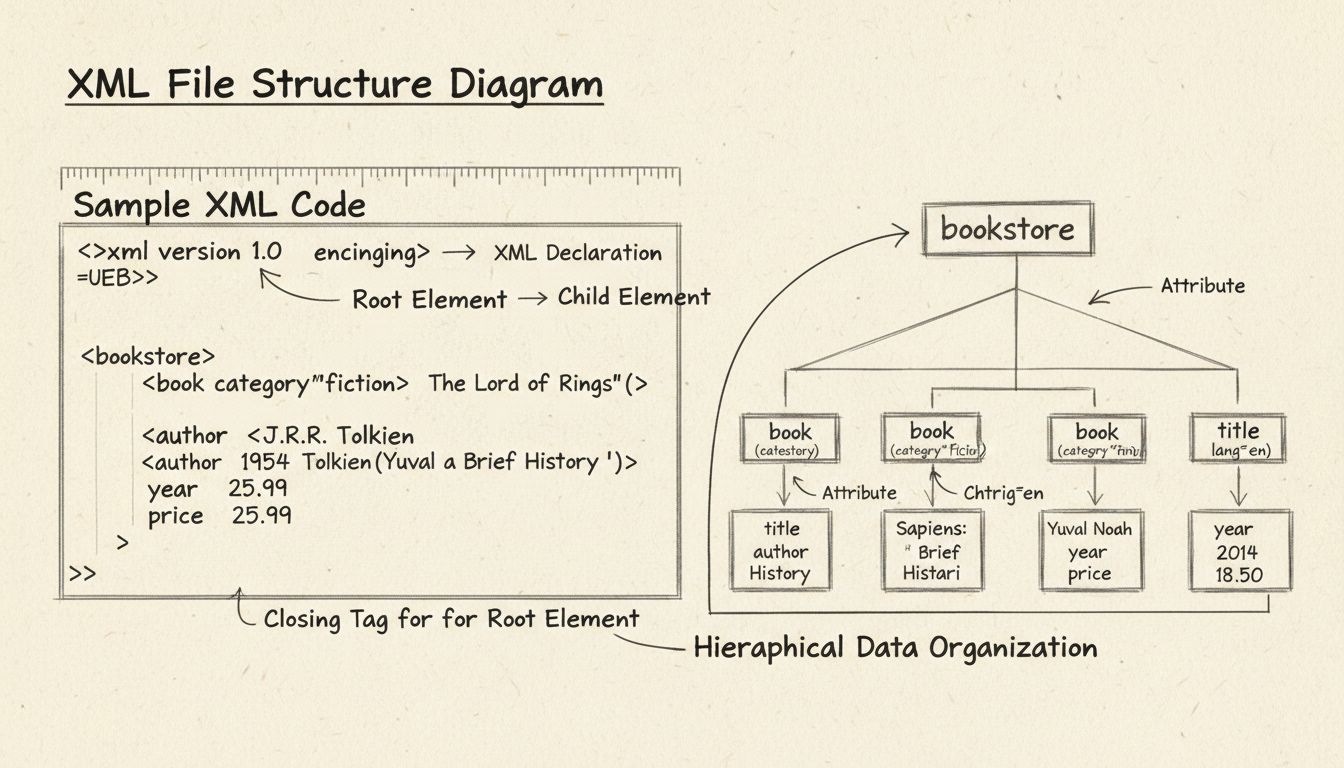
Extensible Markup Language (XML)
Extensible markup language (XML) is responsible for encoding documents in a format readable by humans and machines. Read the article to learn more.
Learn multiple methods to open and read XML files including text editors, browsers, and online viewers. Discover the best tools and techniques for viewing and editing XML data efficiently.
You can open and read XML files using text editors like Notepad++ or VSCode, web browsers like Chrome or Firefox, or online XML viewers. The method you choose depends on whether you need to edit the file or simply view it.
XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language, and it represents one of the most fundamental data format standards used across the internet and enterprise systems. XML files are human-readable text files that use a system of tags to describe the structure and meaning of data, making them ideal for storing, transmitting, and organizing information across different platforms and applications. The .xml file extension identifies these files, and they contain metadata that describes how data should be structured, stored, and transmitted over networks. Although XML has been partially superseded by newer formats like JSON in many modern applications, it remains essential for legacy systems, RSS feeds, SVG graphics, and countless enterprise applications that continue to rely on its robust structure and standardization.
Text editors provide the most straightforward method for opening and editing XML files, offering complete control over the file content while maintaining simplicity and accessibility. The most basic approach involves using your operating system’s default text editor: Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on macOS, both of which come pre-installed and require no additional software installation. To open an XML file with these editors, locate the file on your computer, right-click it, and select the “Open With” option from the context menu, which displays a list of available applications. This method works perfectly for viewing and making quick edits to XML files, though it lacks advanced features like syntax highlighting or validation.
For more advanced XML editing capabilities, professional code editors like Visual Studio Code (VSCode), Sublime Text, and Atom offer superior functionality including syntax highlighting, code formatting, XML validation, and plugin support. VSCode has become particularly popular among developers due to its lightweight performance, extensive extension marketplace, and built-in XML support through various plugins. When using these editors, you can install XML-specific extensions that provide real-time validation, schema checking, and automatic formatting to ensure your XML files maintain proper structure and syntax. The advantage of using dedicated code editors is their ability to handle large XML files efficiently, provide visual feedback for errors, and offer features like find-and-replace functionality that makes working with complex XML documents significantly easier.
Web browsers offer an excellent solution for viewing XML files without requiring any additional software installation or configuration, making them ideal for quick file inspection and sharing. Modern browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and Microsoft Edge have built-in XML rendering capabilities that automatically format and display XML content in a readable hierarchical structure. To open an XML file in your browser, simply locate the file on your computer, right-click it, select “Open With,” and choose your preferred browser from the list. Alternatively, you can open your browser first and then drag the XML file directly into the browser window, which triggers the same rendering process and displays the formatted content immediately.
When viewing XML in a browser, the hierarchical structure becomes immediately apparent, with expandable and collapsible elements that allow you to navigate through nested data efficiently. Browsers automatically apply color-coding to different XML components, making it easier to distinguish between tags, attributes, and text content at a glance. This visual representation is particularly useful for understanding complex XML documents without needing to parse the raw text manually. However, browsers are primarily designed for viewing rather than editing, so if you need to modify the XML content, you’ll need to use a text editor or specialized XML editor instead.
Online XML viewers and editors have become increasingly popular for their convenience and accessibility, requiring nothing more than a web browser and internet connection to function effectively. These web-based tools eliminate the need to install software on your computer while providing powerful features for viewing, editing, validating, and converting XML files. Several reputable platforms offer these services, including Code Beautify, JSON Formatter, Tutorialspoint, and various Chrome extensions specifically designed for XML viewing. Each platform typically allows you to upload XML files from your computer, paste XML code directly into a text area, or import files from cloud storage services like Google Drive.
| Online Tool | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Code Beautify | XML formatting, validation, conversion to JSON | Quick formatting and conversion tasks |
| JSON Formatter | XML viewer, beautifier, minifier | Comparing XML and JSON formats |
| Tutorialspoint | Online editor with live preview | Learning and experimentation |
| Chrome XML Viewer Extension | Browser-based viewing, Google Drive integration | Seamless browser integration |
| XML Viewer Online | Drag-and-drop interface, tree view navigation | User-friendly viewing experience |
The Chrome XML Viewer extension deserves special mention as it integrates directly into your browser, allowing you to click the extension icon whenever you encounter an XML file and instantly view it in a formatted interface. This extension provides two convenient upload options: directly from your computer or from your Google Drive, making it particularly useful for users who work with cloud-stored files. Once uploaded, the XML displays in a plain text section with a tree view on the side, allowing you to navigate through the document structure intuitively. These online tools are especially valuable for users who work across multiple devices or prefer not to install additional software, as they provide consistent functionality regardless of your operating system or device specifications.
Beyond basic text editors and browsers, specialized XML tools provide advanced functionality for developers and data professionals who work extensively with XML files. Notepad++ with XML Tools plugin represents a powerful combination that offers syntax highlighting, code folding, XML validation, and schema checking capabilities specifically designed for XML development. Installing the XML Tools plugin requires downloading the latest version of Notepad++ from their official website, then accessing the plugin manager to install the XML Tools extension, which adds a dedicated menu with XML-specific functions. This combination provides professional-grade XML editing capabilities while maintaining the lightweight performance that makes Notepad++ popular among developers.
For enterprise environments and complex XML processing, dedicated XML editors like Oxygen XML Editor, XMLSpy, and Altova XMLSpy offer comprehensive solutions including XSLT transformation, XPath evaluation, and advanced debugging capabilities. These professional tools are particularly valuable when working with large XML files, complex schemas, or when you need to perform sophisticated data transformations. Additionally, many integrated development environments (IDEs) like IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse, and NetBeans include built-in XML editing and validation features, making them excellent choices for developers who work with XML as part of larger software projects. The choice between these tools depends on your specific needs, budget, and the complexity of the XML files you’re working with.
When working with XML files, following certain best practices ensures efficient workflow and prevents common issues. Always verify that your chosen tool supports the specific XML version and encoding used in your file, as some older tools may not handle UTF-8 encoding or XML 1.1 specifications correctly. Before making any edits to XML files, create backup copies to prevent accidental data loss, especially when working with critical business data or configuration files. When sharing XML files with others, consider the recipient’s technical expertise and provide appropriate tools or instructions for opening the files, as not all users may be familiar with XML formats or have suitable software installed.
Validation is crucial when working with XML files, as even small syntax errors can render the entire file unusable by applications that depend on it. Most modern XML editors and online viewers include validation features that check your XML against defined schemas, helping you identify and correct errors before they cause problems. When dealing with large XML files, consider using specialized tools designed for performance rather than basic text editors, as they handle file parsing and rendering more efficiently. Finally, maintain consistent formatting and indentation in your XML files to improve readability and make future edits easier, whether you’re working alone or collaborating with other developers on the same files.
Just as XML files require the right tools for efficient handling, your affiliate program needs the right platform. PostAffiliatePro provides comprehensive data management, real-time tracking, and seamless integration capabilities to optimize your affiliate operations.
Extensible markup language (XML) is responsible for encoding documents in a format readable by humans and machines. Read the article to learn more.
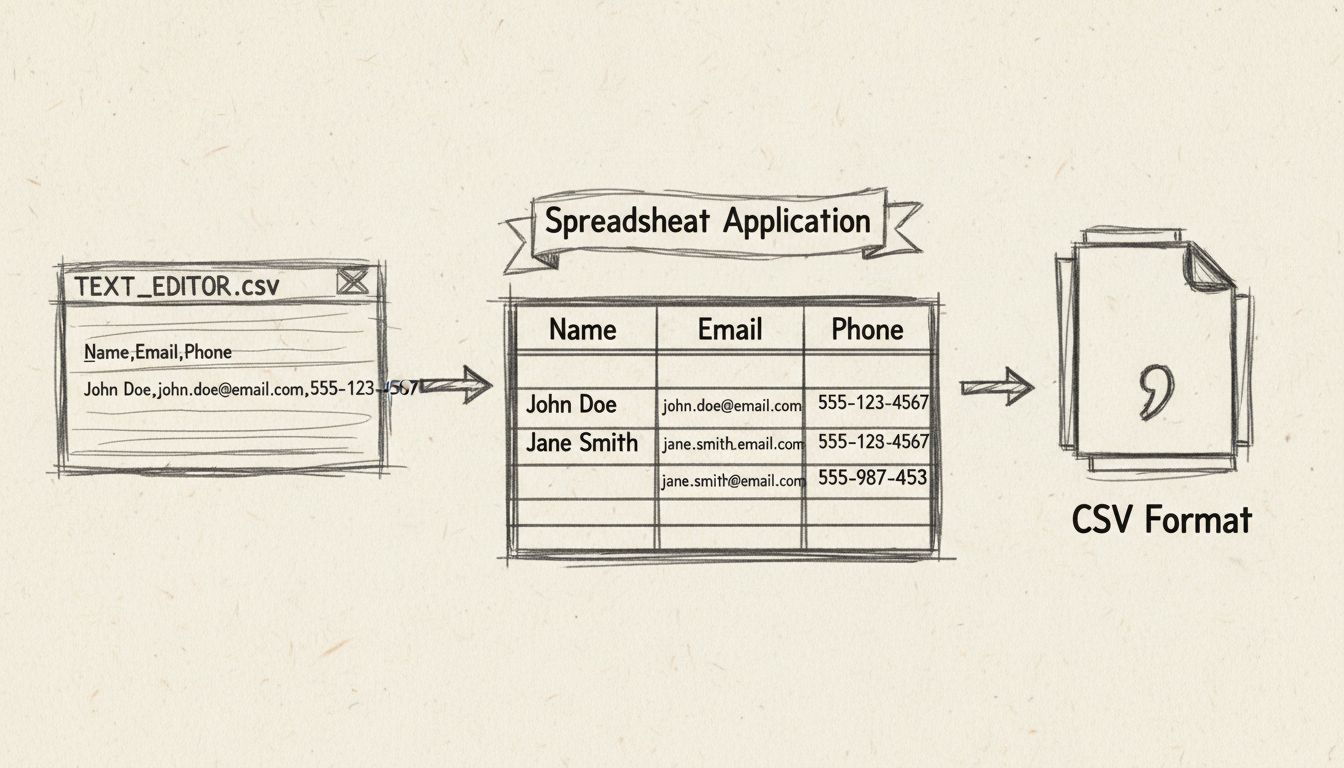
Learn how to edit CSV files using text editors, Excel, and spreadsheet applications. Master data formatting, delimiter handling, and best practices for CSV file...
A sitemap is a simple outline of a page that makes it easier to navigate. There are two kinds of sitemaps: HTML sitemaps and human-readable sitemaps.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.