Crawlers and Their Role in Search Engine Ranking
Crawlers accumulate data and information from the internet by visiting websites and reading the pages. Find out more about them.
Learn how to identify search engine crawlers using user-agent strings, IP addresses, request patterns, and behavioral analysis. Essential guide for webmasters and developers.
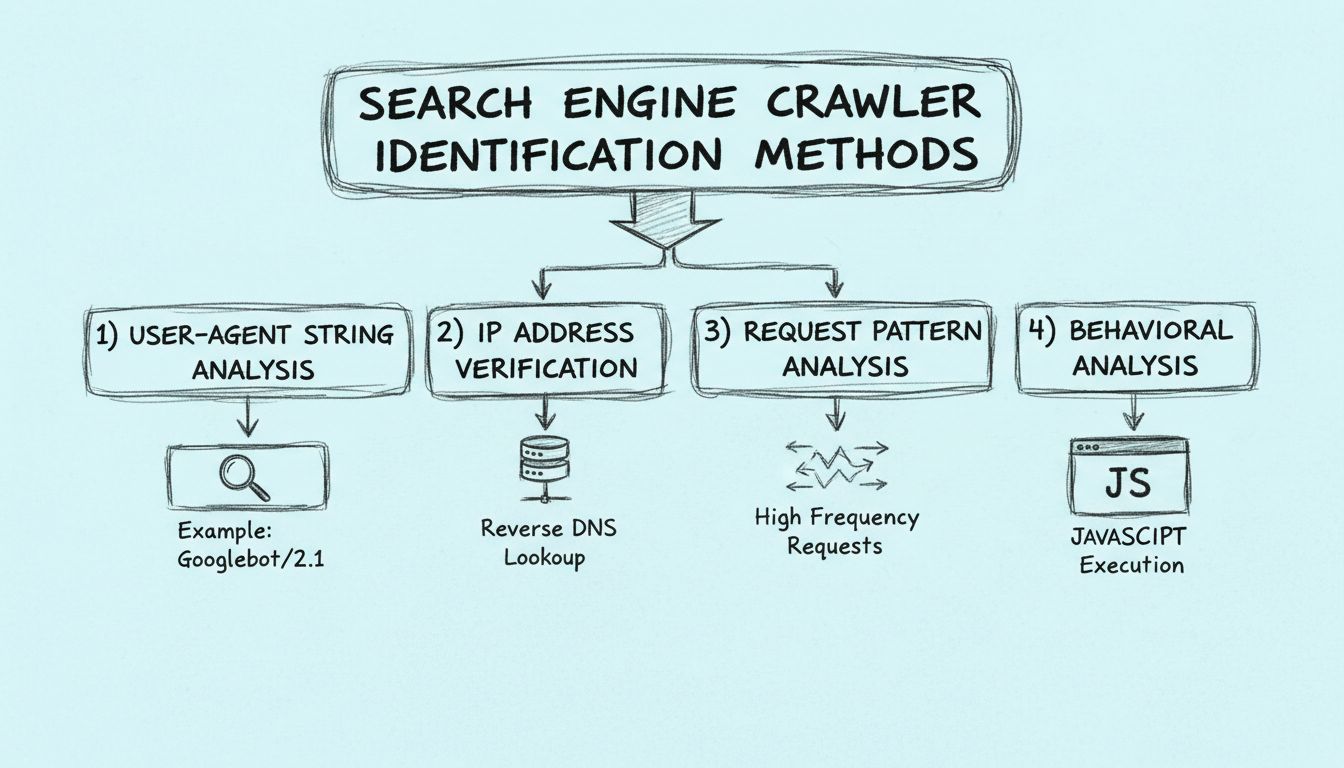
Search engine crawlers can be identified through four primary methods: analyzing the user-agent string in HTTP headers, verifying the source IP address and reverse DNS hostname, monitoring request patterns for high-frequency access, and examining behavioral characteristics like JavaScript execution capabilities.
Search engine crawlers are automated programs that systematically browse the internet to discover, analyze, and index web content. Identifying these crawlers is crucial for webmasters, developers, and affiliate marketers who need to understand their website traffic patterns and ensure legitimate search engine access. Unlike malicious bots that attempt to scrape data or launch attacks, legitimate search engine crawlers like Googlebot, Bingbot, and others identify themselves through specific technical markers that can be verified and authenticated.
The ability to distinguish between legitimate search engine crawlers and other types of bots has become increasingly important in 2025 as web traffic continues to grow and bot activity becomes more sophisticated. Understanding the identification methods helps you optimize your site’s crawlability, protect your resources from unauthorized access, and ensure your affiliate tracking systems accurately distinguish between organic search traffic and other sources. PostAffiliatePro provides advanced analytics capabilities that help you monitor and categorize traffic sources with precision, ensuring your affiliate program captures accurate performance data.
The most straightforward method for identifying search engine crawlers is examining the User-Agent string in the HTTP request header. Every HTTP request includes a User-Agent header that identifies the client making the request, whether it’s a web browser, mobile app, or crawler. Legitimate search engine crawlers include distinctive identifiers in their User-Agent strings that clearly indicate their origin and purpose. For example, Google’s crawler identifies itself as “Googlebot/2.1 (+http://www.google.com/bot.html)”, while Microsoft’s Bing crawler uses “Bingbot/2.0 (+http://www.bing.com/bingbot.htm)”.
When analyzing User-Agent strings, you should look for specific patterns and keywords that indicate legitimate search engine crawlers. The User-Agent string typically contains the crawler name, version number, and a link to the crawler’s documentation or information page. Legitimate crawlers from major search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex follow consistent naming conventions and include verifiable information about their purpose. You can log these User-Agent strings in your server access logs and compare them against known crawler identifiers maintained by search engines and security organizations.
| Crawler Name | User-Agent String Example | Search Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Googlebot | Googlebot/2.1 (+http://www.google.com/bot.html) | |
| Bingbot | Bingbot/2.0 (+http://www.bing.com/bingbot.htm) | Microsoft Bing |
| Slurp | Slurp/cat (+http://help.yahoo.com/help/us/ysearch/slurp) | Yahoo |
| Yandexbot | Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; YandexBot/3.0) | Yandex |
| DuckDuckBot | DuckDuckBot/1.0 (+http://duckduckgo.com/duckduckbot.html) | DuckDuckGo |
However, relying solely on User-Agent strings for crawler identification has limitations. Malicious bots can spoof User-Agent strings to impersonate legitimate crawlers, making it essential to combine this method with additional verification techniques. Additionally, some legitimate crawlers may use generic or modified User-Agent strings in certain situations, so cross-referencing with other identification methods provides more reliable results.
The second critical method for identifying search engine crawlers involves verifying the source IP address and performing a reverse DNS lookup. When a crawler makes a request to your server, it originates from a specific IP address that can be logged and analyzed. Search engines publish the IP address ranges used by their crawlers, allowing webmasters to verify whether a request genuinely comes from that search engine’s infrastructure. Google, for instance, maintains a comprehensive list of IP addresses used by Googlebot and other Google crawlers.
Reverse DNS lookup is a particularly effective verification technique that involves querying the DNS system to determine the hostname associated with an IP address. When you perform a reverse DNS lookup on an IP address claiming to be from Google, it should resolve to a hostname within Google’s domain (such as “crawl-66-249-64-1.googlebot.com”). This hostname can then be verified by performing a forward DNS lookup to confirm that the hostname resolves back to the same IP address, creating a bidirectional verification chain. This two-way verification process makes it extremely difficult for malicious actors to spoof crawler identity, as they would need to control both the IP address and the associated DNS records.
Google’s official documentation recommends this verification method as the most reliable way to confirm Googlebot requests. The process involves checking that the reverse DNS hostname matches Google’s domain pattern and then verifying that a forward DNS lookup of that hostname returns the same IP address. This method is particularly valuable for high-traffic websites and affiliate networks that need to ensure accurate traffic attribution and prevent fraudulent bot activity from being counted as legitimate search engine traffic.
Request pattern analysis provides valuable insights into crawler behavior by examining how requests are distributed over time and across your website’s resources. Legitimate search engine crawlers follow predictable patterns that differ significantly from human browsing behavior or malicious bot activity. Crawlers typically make requests at consistent intervals, follow a logical traversal pattern through your site’s URL structure, and respect the directives specified in your robots.txt file. By monitoring these patterns, you can identify legitimate crawlers and distinguish them from suspicious activity.
When analyzing request patterns, look for several key characteristics that indicate legitimate crawler behavior. First, examine the request frequency and distribution—legitimate crawlers typically space their requests to avoid overloading your server, often following exponential backoff algorithms that slow down if they receive HTTP 500 errors or other server stress indicators. Second, analyze the URL traversal pattern—legitimate crawlers follow links systematically and respect the site structure, whereas malicious bots often make random or sequential requests to URLs that don’t exist or aren’t linked from your site. Third, monitor the types of resources being requested—legitimate crawlers typically request HTML pages, CSS files, and JavaScript files needed to render pages, while avoiding unnecessary requests to binary files or sensitive directories.
You can implement request pattern monitoring by analyzing your server logs and identifying clusters of requests that share common characteristics. Tools like web analytics platforms and server log analysis software can help automate this process by flagging unusual patterns. For example, if a single IP address makes 1,000 requests per minute to different product pages in a sequential pattern, it’s likely a crawler. In contrast, legitimate search engine crawlers typically make requests at a much lower frequency, often spacing requests several seconds apart to respect server resources and avoid triggering rate-limiting mechanisms.
Behavioral analysis examines how crawlers interact with your website’s content and technology stack, providing insights that distinguish legitimate search engine crawlers from other types of bots. One of the most important behavioral characteristics is JavaScript execution capability. Modern search engines like Google render pages using a headless browser (similar to Chrome) to execute JavaScript and access dynamically-generated content. This means legitimate crawlers will execute JavaScript code on your pages, whereas many malicious bots or simple scrapers cannot or do not execute JavaScript.
You can detect JavaScript execution by embedding tracking code that only executes when JavaScript is enabled and functional. If a request accesses your page but doesn’t trigger JavaScript-dependent tracking or doesn’t load dynamically-generated content, it indicates the requester may not be a modern search engine crawler. Additionally, legitimate crawlers typically load all resources needed to render a page completely, including images, stylesheets, and JavaScript files, whereas simple bots might only request the HTML file without loading supporting resources.
Another important behavioral indicator is how crawlers handle interactive elements and form submissions. Legitimate search engine crawlers do not submit forms, click buttons, or interact with dynamic content in ways that would create unwanted side effects like placing orders or modifying data. They focus on reading and analyzing content rather than interacting with it. Malicious bots, by contrast, often attempt to interact with forms, submit data, or trigger actions that could harm your website or steal information. By monitoring for these behavioral patterns, you can identify requests that are attempting unauthorized interactions and distinguish them from legitimate crawler activity.
The most effective approach to crawler identification combines all four methods into a comprehensive verification workflow. Rather than relying on a single identification method, implementing a layered verification system provides robust protection against spoofed crawlers and ensures accurate traffic attribution. Start by capturing the User-Agent string and IP address from each request, then cross-reference these against known crawler databases maintained by search engines and security organizations. Next, perform a reverse DNS lookup to verify the IP address’s hostname matches the claimed search engine’s domain. Finally, analyze the request pattern and behavioral characteristics to ensure the activity aligns with legitimate crawler behavior.
This multi-layered approach is particularly important for affiliate networks and performance marketing platforms like PostAffiliatePro, where accurate traffic attribution directly impacts commission calculations and program integrity. By implementing comprehensive crawler identification, you can ensure that your affiliate tracking systems accurately distinguish between legitimate search engine traffic, paid advertising traffic, and organic user traffic. This precision enables better performance analysis, more accurate ROI calculations, and improved fraud detection capabilities.
Modern web infrastructure requires sophisticated crawler identification systems that can handle the complexity of contemporary web traffic. First, maintain an updated list of legitimate crawler IP addresses and User-Agent strings by subscribing to official notifications from major search engines. Google, Bing, and other search engines publish updates when they add new crawlers or change their infrastructure, and staying informed about these changes ensures your identification systems remain current. Second, implement server-side logging that captures all relevant request metadata including User-Agent strings, IP addresses, request timestamps, and requested resources. This data provides the foundation for pattern analysis and behavioral monitoring.
Third, consider implementing a crawler verification API or service that automatically validates crawler identity in real-time. Many security and analytics platforms now offer crawler identification services that maintain up-to-date databases of legitimate crawlers and can verify requests against these databases. Fourth, establish clear policies for handling unidentified or suspicious crawler activity. You might choose to serve these requests normally while logging them for analysis, or implement rate limiting to prevent resource exhaustion. Finally, regularly review and update your crawler identification rules and thresholds based on observed traffic patterns and emerging threats. The landscape of web crawling continues to evolve, and your identification systems should adapt accordingly to maintain effectiveness.
Identifying search engine crawlers requires a comprehensive understanding of multiple verification methods and the ability to combine them into an effective detection system. By analyzing User-Agent strings, verifying IP addresses through reverse DNS lookups, monitoring request patterns, and examining behavioral characteristics, you can reliably distinguish legitimate search engine crawlers from other types of bots and traffic sources. This capability is essential for webmasters, developers, and affiliate marketers who need to understand their traffic sources and ensure accurate performance tracking. PostAffiliatePro’s advanced analytics and traffic monitoring capabilities help you implement these identification methods effectively, ensuring your affiliate program captures accurate data and maintains program integrity in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
PostAffiliatePro is the leading affiliate management software that helps you track, manage, and optimize your affiliate network with precision. Identify legitimate traffic sources and maximize your affiliate program's performance with advanced analytics and real-time monitoring.
Crawlers accumulate data and information from the internet by visiting websites and reading the pages. Find out more about them.
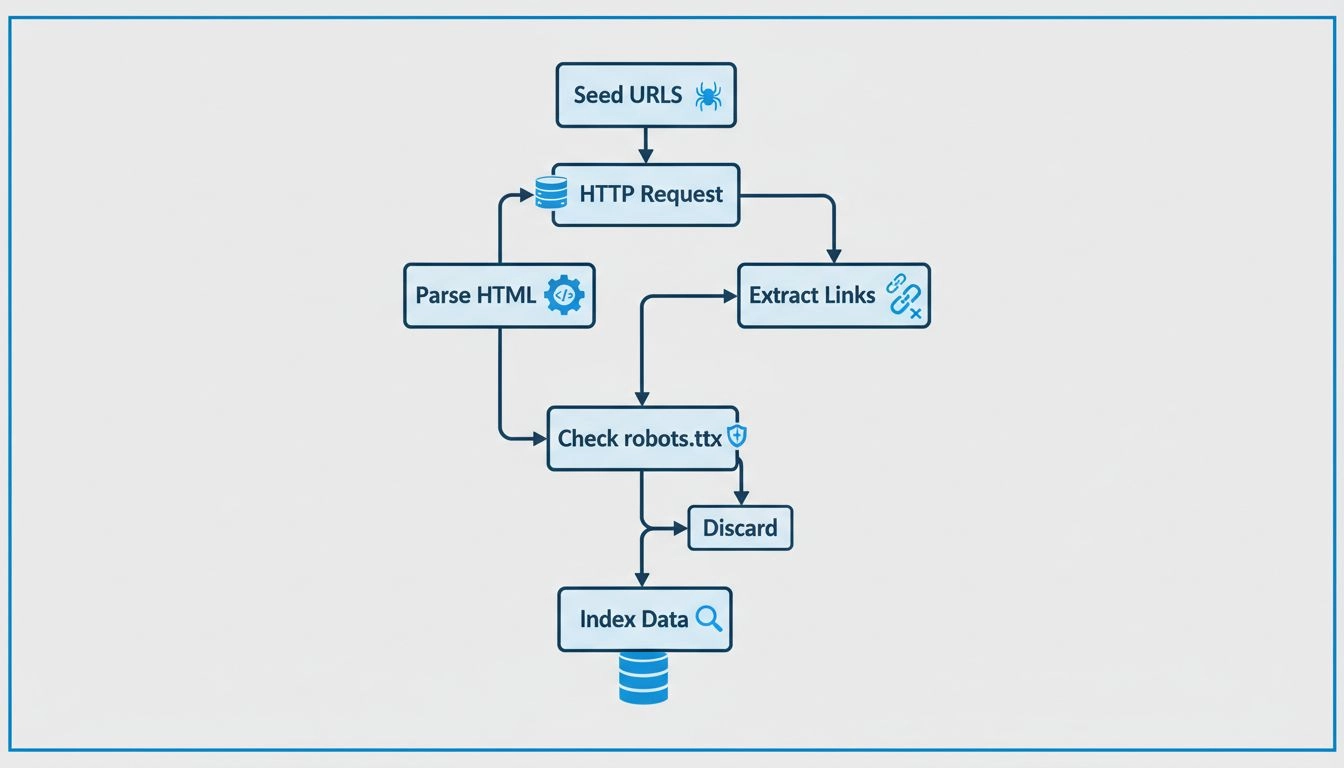
Learn how web crawlers work, from seed URLs to indexing. Understand the technical process, crawler types, robots.txt rules, and how crawlers impact SEO and affi...
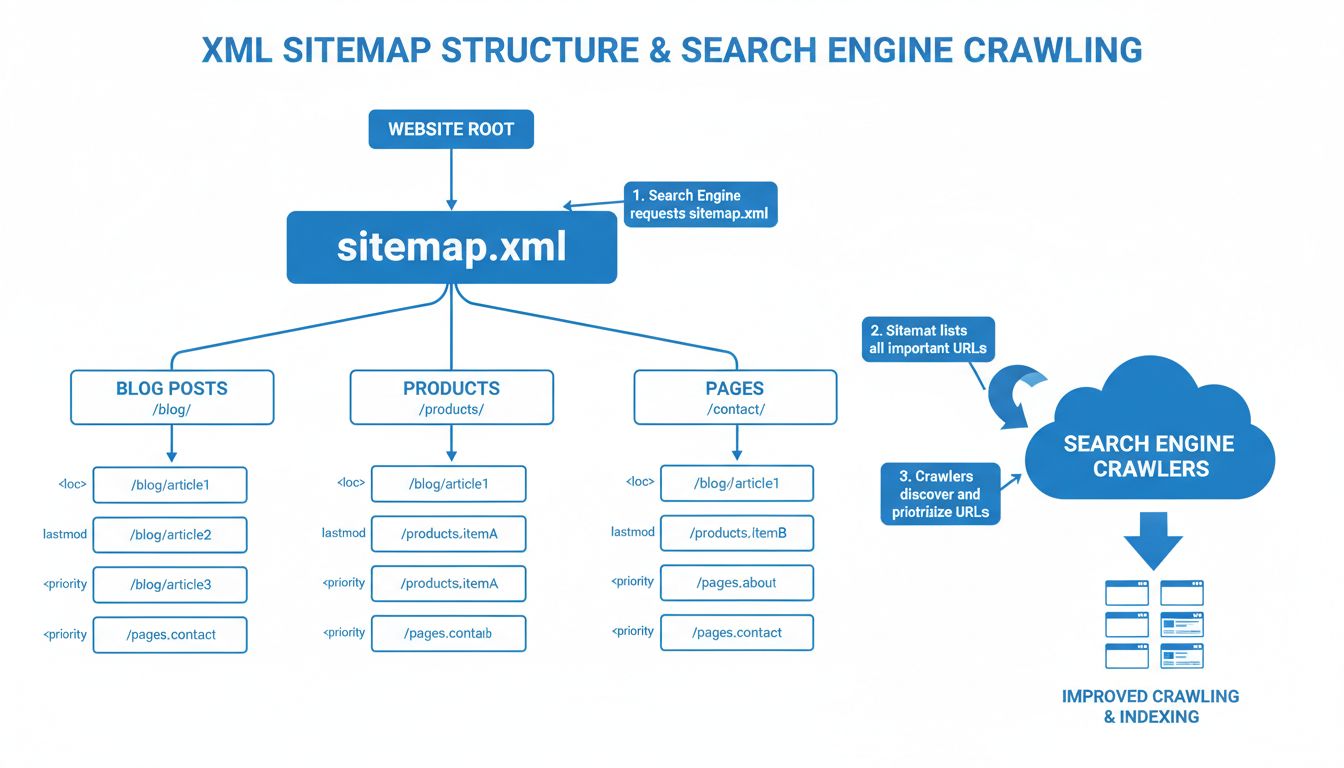
Learn why sitemaps are crucial for SEO success. Discover how XML and HTML sitemaps improve crawlability, indexing, and search engine visibility for your website...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.