
Conversion Rate Calculator - Calculate & Optimize Conversion Rates
Free conversion rate calculator for simple rates, funnel analysis, and A/B testing. Optimize conversions, identify bottlenecks, and improve marketing ROI.
Learn how to calculate conversion rate with our comprehensive guide. Discover the formula, calculation methods, industry benchmarks, and optimization strategies for affiliate marketing success.
Conversion rate is calculated by dividing the number of conversions by the total number of visitors and multiplying the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. The formula is: (Number of Conversions ÷ Total Number of Visitors) × 100%
Conversion rate is one of the most critical metrics in digital marketing and affiliate programs, serving as a fundamental indicator of how effectively your website, landing page, or marketing campaign converts visitors into customers or leads. Understanding how to calculate this metric accurately is essential for any business looking to optimize their online performance and maximize return on investment. The conversion rate provides actionable insights into the efficiency of your marketing efforts and helps identify areas where improvements can be made to drive better results.
The conversion rate is calculated using a straightforward mathematical formula that divides the number of successful conversions by the total number of visitors to your website or campaign, then multiplies the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. This standardized approach ensures consistency across different industries and marketing channels.
Conversion Rate (%) = (Number of Conversions ÷ Total Number of Visitors) × 100
For example, if your website received 1,000 unique visitors in a month and 50 of them completed a purchase, your conversion rate would be calculated as follows: (50 ÷ 1,000) × 100 = 5%. This means that 5% of your visitors took the desired action, which is a solid benchmark for many e-commerce businesses. Understanding this basic calculation is the foundation for more advanced conversion rate optimization strategies.
A conversion represents any desired action completed by a visitor on your website or through your marketing campaign. The definition of what constitutes a conversion varies depending on your business objectives and can include multiple types of actions. Common examples of conversions include completing a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, downloading an ebook, filling out a contact form, registering for a free trial, or subscribing to a service. In affiliate marketing specifically, conversions typically refer to completed sales or qualified leads that result from an affiliate’s promotional efforts.
The critical aspect of defining conversions is consistency and clarity. Your organization must establish clear criteria for what qualifies as a conversion to ensure accurate tracking and reporting. Different conversion types can be tracked separately to provide more granular insights into user behavior and campaign performance. For instance, you might track both micro-conversions (like adding items to a cart) and macro-conversions (like completing a purchase) to understand the complete customer journey.
The total number of visitors represents all individuals who accessed your website or landing page during a specific time period. However, there are important distinctions in how visitors can be counted, which significantly impacts your conversion rate calculation. The most accurate method involves counting unique visitors rather than total page views, as this prevents the same person from being counted multiple times if they visit your site on multiple occasions.
| Visitor Counting Method | Description | Impact on Conversion Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Total Page Views | Counts every page load, including repeat visits from same user | Inflates visitor count, lowers conversion rate |
| Unique Visitors | Counts each individual user only once per time period | More accurate, reflects true conversion efficiency |
| Sessions | Groups user activity within a defined time window | Balances accuracy with user journey understanding |
| Cookies-Based Tracking | Uses browser cookies to identify returning visitors | Standard method but affected by privacy settings |
Most analytics platforms use cookies or similar tracking mechanisms to identify unique visitors, though privacy regulations and browser settings can affect accuracy. When calculating conversion rates for affiliate programs, it’s essential to use consistent visitor counting methods across all campaigns to ensure reliable comparisons and benchmarking.
Consider an online retailer that wants to calculate their monthly conversion rate. During the month of November, the website received 10,000 unique visitors, and 350 of those visitors completed a purchase. Using the conversion rate formula:
Conversion Rate = (350 ÷ 10,000) × 100 = 3.5%
This 3.5% conversion rate indicates that the retailer successfully converted 3.5% of their website traffic into paying customers. This benchmark falls within the average range for e-commerce businesses, which typically ranges from 2% to 5% depending on industry and product type. The retailer can use this metric to track performance over time and identify whether their optimization efforts are improving or declining.
A B2B software company running a lead generation campaign wants to measure their conversion rate. Over a three-month period, their landing page received 5,000 visitors, and 150 of those visitors filled out the contact form to request a demo. The conversion rate calculation would be:
Conversion Rate = (150 ÷ 5,000) × 100 = 3%
This 3% conversion rate for lead generation is considered reasonable, though B2B companies often aim for higher rates on targeted campaigns. The company can analyze which traffic sources, ad campaigns, or landing page variations are driving the highest conversion rates to optimize their marketing spend.
The most accurate conversion rate calculation uses unique visitors rather than total page views. When a visitor returns to your website multiple times, counting them only once provides a more realistic picture of your conversion efficiency. This distinction becomes particularly important for websites with high repeat visitor rates, such as subscription services or community platforms.
For example, if a website has 10,000 total page views but only 6,000 unique visitors, and 300 conversions occur, the conversion rate would be 5% (300 ÷ 6,000) rather than 3% (300 ÷ 10,000). The unique visitor calculation more accurately reflects the percentage of distinct individuals who converted, which is more meaningful for marketing analysis.
Conversion rates should always be calculated for a specific, defined time period to ensure meaningful comparisons. Common time periods include daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly calculations. Seasonal variations, marketing campaigns, and external factors can significantly impact conversion rates, so it’s important to analyze trends over consistent time intervals.
For affiliate programs, tracking conversion rates by week or month allows you to identify patterns and respond quickly to performance changes. Some businesses also calculate conversion rates by traffic source, device type, or geographic location to understand which segments perform best.
Understanding what constitutes a “good” conversion rate requires knowledge of industry benchmarks and your specific business context. Conversion rates vary significantly across different industries due to factors such as product complexity, price point, target audience, and competitive landscape.
| Industry | Average Conversion Rate | High-Performing Rate |
|---|---|---|
| E-Commerce (General) | 2-3% | 5%+ |
| E-Commerce (Luxury) | 1-2% | 3-4% |
| SaaS/Software | 2-5% | 8%+ |
| Lead Generation | 2-5% | 10%+ |
| Newsletter Signup | 5-10% | 15%+ |
| Mobile Apps | 1-3% | 5%+ |
| B2B Websites | 2-3% | 5%+ |
These benchmarks provide context for evaluating your own conversion rates, but it’s important to remember that your specific business circumstances may differ. A luxury brand selling high-ticket items might consider a 1% conversion rate acceptable, while a subscription service might target 8% or higher. The key is to establish realistic goals based on your industry, continuously monitor your performance, and implement optimization strategies to improve over time.
Several important factors can affect how conversion rates are calculated and interpreted. Website design and user experience play crucial roles, as poorly designed sites with confusing navigation or slow loading times typically experience lower conversion rates. The quality and relevance of your traffic source significantly impacts conversion rates—highly targeted traffic from relevant sources converts at higher rates than broad, untargeted traffic.
The effectiveness of your call-to-action (CTA) buttons, landing page copy, and overall value proposition directly influences whether visitors take the desired action. Trust signals such as customer testimonials, security badges, and clear return policies help build confidence and encourage conversions. The checkout process complexity, payment options available, and overall friction in the conversion funnel all contribute to your final conversion rate. Additionally, mobile optimization has become increasingly important, as mobile users often have different conversion patterns than desktop users.
Improving your conversion rate requires a data-driven approach and continuous testing. A/B testing different elements of your website or landing page—such as headlines, button colors, form fields, or page layout—helps identify what resonates best with your audience. Personalization strategies that tailor content and offers to specific user segments can significantly boost conversion rates by making the experience more relevant to individual visitors.
Simplifying your conversion process by reducing form fields, minimizing steps to purchase, and removing unnecessary friction points encourages more visitors to complete the desired action. Implementing clear, compelling calls-to-action that communicate the value proposition helps guide visitors toward conversion. Optimizing page load speed is critical, as even small delays can result in significant conversion rate decreases. Building trust through social proof, customer reviews, security certifications, and transparent pricing information helps overcome visitor hesitation and increases conversion likelihood.
Accurate tracking and regular monitoring of conversion rates is essential for understanding your marketing performance and identifying optimization opportunities. Most analytics platforms like Google Analytics, PostAffiliatePro, and other specialized tools provide built-in conversion tracking capabilities that automatically calculate conversion rates for you. Setting up proper conversion tracking requires defining your conversion goals, implementing tracking code on your website, and regularly reviewing reports to identify trends and anomalies.
For affiliate programs, PostAffiliatePro offers advanced conversion tracking that captures every conversion accurately, allowing you to monitor performance by affiliate, campaign, traffic source, and time period. Regular analysis of conversion rate data helps identify which marketing channels, campaigns, and strategies are most effective, enabling you to allocate resources more efficiently and maximize your return on investment.
PostAffiliatePro provides advanced tracking and analytics tools to help you monitor, analyze, and optimize your conversion rates in real-time. Track every conversion accurately and identify opportunities to boost your affiliate program performance.

Free conversion rate calculator for simple rates, funnel analysis, and A/B testing. Optimize conversions, identify bottlenecks, and improve marketing ROI.
Learn what conversion rate means in affiliate marketing, why it matters, how to calculate it, and the best strategies to optimize your campaigns for higher conv...
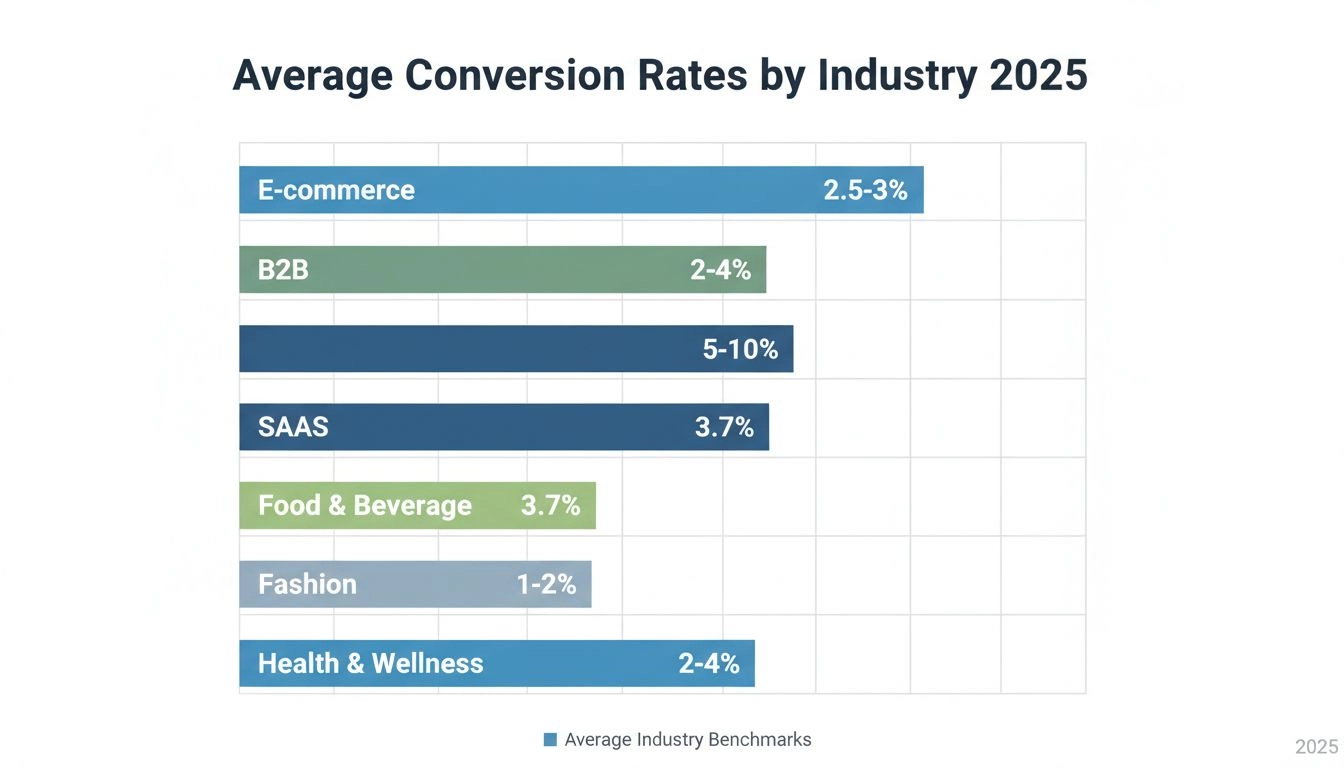
Discover what constitutes a good conversion rate in 2025 with industry-specific benchmarks. Learn how conversion rates vary by sector, device, and traffic sourc...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.