What is Geotargeting? Complete Guide to Location-Based Marketing
Learn what geotargeting is and how it works. Discover how PostAffiliatePro helps you deliver location-specific content to boost conversions and engagement with ...
Learn how geotargeting works using GPS, IP addresses, and Wi-Fi signals. Discover geotargeting strategies, benefits, and how PostAffiliatePro helps optimize location-based affiliate campaigns.
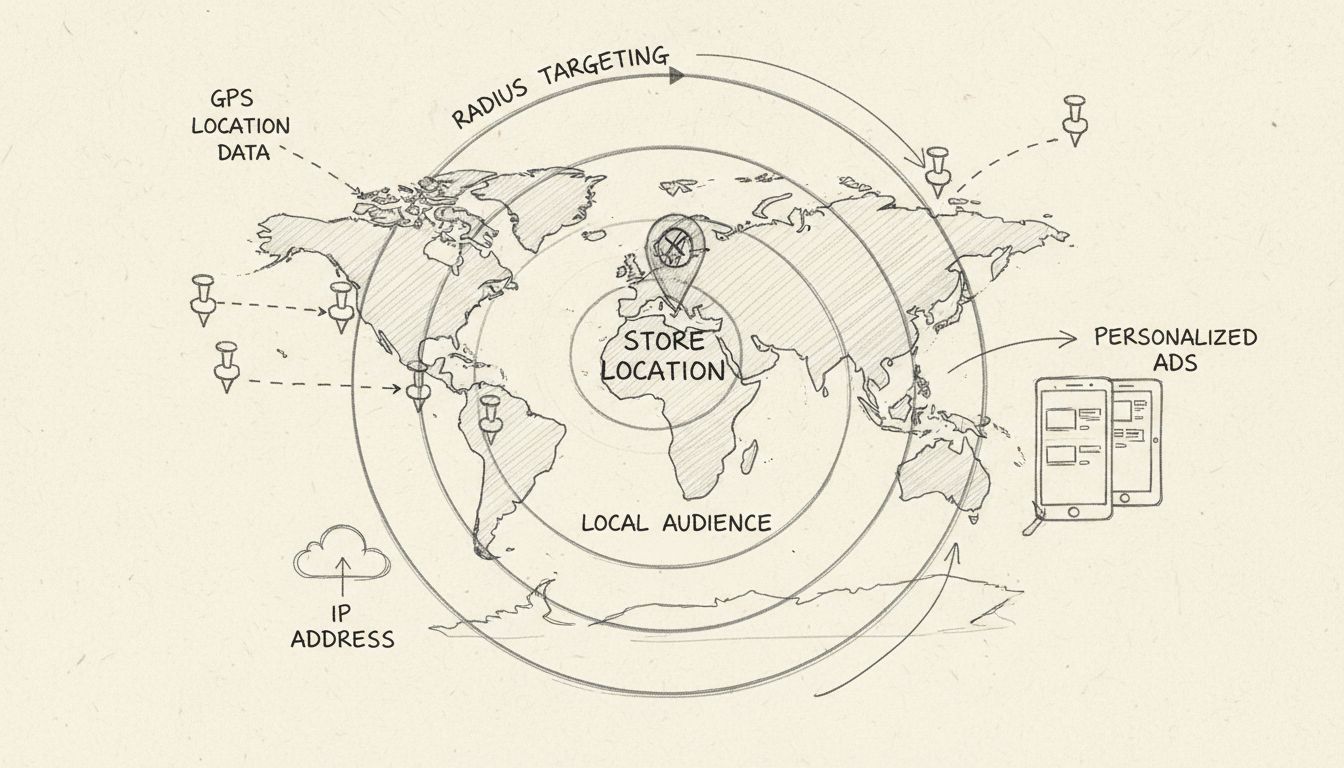
Geotargeting works by collecting location data from users through GPS, IP addresses, Wi-Fi signals, and cellular towers, then using this information to deliver personalized content and advertisements to specific geographic areas. This technology enables businesses to show relevant ads to users based on their physical location, improving engagement and conversion rates.
Geotargeting is a sophisticated marketing technique that leverages location data to deliver personalized content and advertisements to users based on their geographic position. This technology has become essential in modern digital marketing, enabling businesses to connect with their target audience more effectively by ensuring that marketing messages are relevant to the user’s immediate environment and needs. The process involves collecting location information through multiple data sources and using advanced algorithms to determine the most appropriate content for each user. By implementing geotargeting strategies, businesses can significantly improve their return on investment while reducing wasted advertising spend on irrelevant audiences.
The foundation of geotargeting relies on accurate location data collection through multiple technological methods. Each method has distinct advantages and varying levels of accuracy, making it important for marketers to understand which approach works best for their specific use case.
GPS (Global Positioning System) represents the most precise location tracking method available today. GPS technology uses satellite signals to pinpoint a user’s exact location, often accurate to within a few meters. This method is particularly valuable for mobile applications and location-based services that require real-time positioning data. GPS is especially effective for retail businesses, restaurants, and service providers who want to attract customers within a specific radius of their physical location. However, GPS accuracy can be affected by environmental factors such as tall buildings, dense forests, or indoor locations where satellite signals may be weak or unavailable.
IP Address Targeting provides a broader but still useful approach to geolocation. Every device connected to the internet has a unique IP address that can be traced to a specific geographic location, typically narrowed down to a city or region. This method is widely used for desktop-based campaigns and website personalization, as it requires no special permissions from users and works across all internet-connected devices. IP targeting is particularly useful for businesses targeting entire regions or countries, though it lacks the precision of GPS. The accuracy of IP-based geolocation has improved significantly in recent years, with modern databases capable of identifying locations down to the neighborhood level in many cases.
Wi-Fi and Cellular Data offer a middle ground between GPS precision and IP address targeting. When a device connects to a Wi-Fi network, its location can be determined based on the known coordinates of that network. Similarly, cellular towers can triangulate a user’s position by analyzing signal strength from multiple towers. These methods are particularly valuable in urban environments where GPS signals may be obstructed and provide faster location determination than GPS alone. Many modern smartphones use a combination of these technologies to provide the most accurate location data possible.
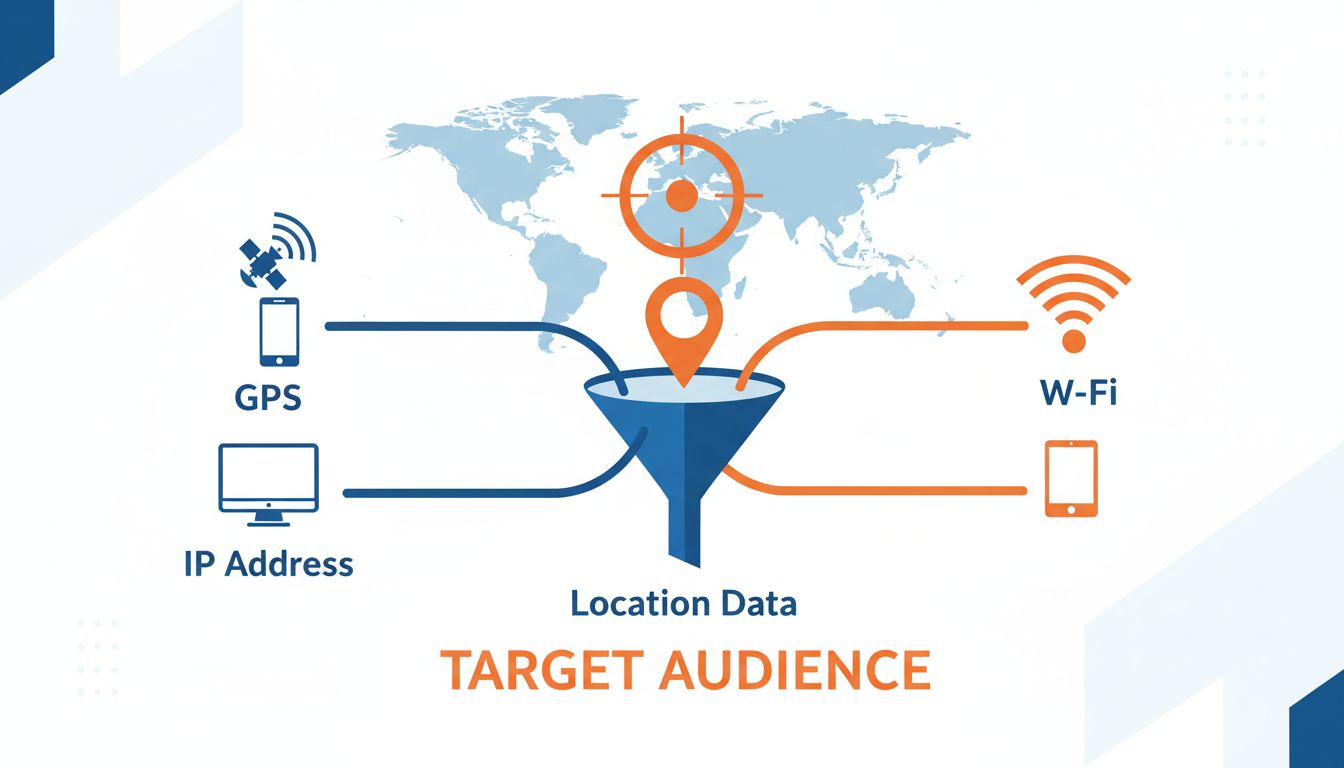
Once location data is collected, the geotargeting process follows a systematic approach to ensure the right message reaches the right audience. The first step involves audience segmentation, where users are categorized based on their geographic location. Marketers can segment audiences at various levels of granularity, from broad country-level targeting down to specific neighborhoods or even individual store locations. This segmentation can be further refined by combining geographic data with demographic information, behavioral patterns, and user preferences to create highly specific audience segments.
The second step is message customization, where marketing content is tailored to match the local context of each geographic segment. This might include adjusting language, currency, cultural references, or promotional offers to resonate with local audiences. For example, a global e-commerce brand might promote different products or seasonal items based on the climate and cultural preferences of each region. This localization ensures that marketing messages feel relevant and authentic to users in each location, significantly improving engagement rates.
The final step is delivery optimization, where the system determines the best channels and timing for reaching each audience segment. This involves selecting appropriate advertising platforms, setting bid strategies based on local market conditions, and scheduling ads to appear when users are most likely to engage. Advanced geotargeting systems use machine learning algorithms to continuously optimize delivery based on real-time performance data, ensuring that marketing budgets are allocated to the most effective geographic segments.
Businesses can implement geotargeting in several distinct ways, each suited to different marketing objectives and business models. Country and region-level targeting is the broadest approach, useful for businesses operating across multiple countries or regions with different regulatory requirements, languages, or market conditions. This strategy allows companies to maintain consistent brand messaging while adapting to local market needs. City and ZIP code targeting provides more granular control, enabling businesses to focus on specific urban areas or neighborhoods where their target customers are concentrated. This approach is particularly effective for local businesses, franchises, and companies launching new products in specific markets.
Radius or proximity targeting creates a virtual boundary around a specific location, such as a retail store, event venue, or competitor’s location. When users enter this defined radius, they become eligible to receive targeted advertisements. This method is highly effective for driving foot traffic to physical locations and is commonly used by restaurants, retail stores, and service providers. Behavioral and location targeting combines geographic data with user behavior patterns, such as past purchases, browsing history, or location visit frequency. This sophisticated approach enables marketers to reach users who are not only in the right location but also have demonstrated interest in relevant products or services.
While geotargeting and geofencing are often used interchangeably, they represent distinct approaches to location-based marketing. Geotargeting focuses on delivering content based on a user’s current or historical location, without requiring a specific boundary trigger. It uses location data to determine which users should see which ads, based on where they are or where they typically spend time. Geotargeting is more flexible and can be applied across various marketing channels, including search engines, social media, and display networks.
Geofencing, by contrast, creates a virtual perimeter around a specific geographic area using GPS or RFID technology. When a user’s device enters or exits this boundary, it triggers a predetermined action, such as sending a push notification or displaying an ad. Geofencing is more event-driven and location-specific, making it ideal for time-sensitive promotions or location-based alerts. While geofencing offers greater precision for specific locations, geotargeting provides broader reach and flexibility for regional or national campaigns. Many sophisticated marketing strategies combine both approaches to maximize effectiveness across different campaign objectives.
Geotargeting delivers substantial benefits for affiliate marketing programs and performance-based advertising campaigns. The most significant advantage is improved relevance and engagement, as users receive ads and content that directly match their geographic location and local needs. This relevance translates directly into higher click-through rates and conversion rates, as users are more likely to engage with offers that feel personally tailored to their situation. Studies show that location-based marketing can increase conversion rates by up to 20% compared to non-targeted campaigns.
Cost efficiency represents another critical benefit, as geotargeting allows marketers to focus their advertising budgets on the most valuable geographic segments. By avoiding wasteful spending on irrelevant audiences in locations where products or services are unavailable or less relevant, businesses can achieve better return on ad spend. This is particularly important for affiliate marketers who operate on performance-based models where every dollar spent must generate measurable results. Competitive advantage emerges when businesses use geotargeting to respond quickly to local market opportunities, such as promoting products during local events, holidays, or seasonal changes. This agility allows businesses to stay ahead of competitors and capture market share in specific regions.
| Geotargeting Method | Accuracy Level | Best Use Case | Technology Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS | Very High (1-10 meters) | Mobile apps, retail foot traffic | Smartphone GPS receiver |
| IP Address | Medium (City/Region level) | Website personalization, desktop ads | IP geolocation database |
| Wi-Fi Triangulation | High (10-100 meters) | Urban targeting, indoor location | Wi-Fi network database |
| Cellular Triangulation | Medium-High (100-500 meters) | Mobile network-based targeting | Carrier data access |
| Geofencing | Very High (Boundary-based) | Location-triggered events | GPS/RFID technology |
As geotargeting technology has become more sophisticated, privacy concerns have grown correspondingly. Marketers must navigate complex regulatory frameworks such as GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and similar regulations in other jurisdictions. These regulations require explicit user consent before collecting and using location data for marketing purposes. Transparent communication about data collection practices is essential for maintaining user trust and ensuring legal compliance. Businesses should implement clear opt-in mechanisms, provide easy opt-out options, and regularly audit their data practices to ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
The rise of privacy-focused technologies, such as Apple’s App Tracking Transparency and increased adoption of VPNs, has made location data collection more challenging. However, these challenges have also driven innovation in privacy-preserving geotargeting methods, such as aggregated location data analysis and on-device processing. Forward-thinking businesses are adapting their geotargeting strategies to respect user privacy while still delivering relevant, personalized experiences. This balance between effectiveness and privacy will continue to be a critical consideration for affiliate marketers and digital advertisers in 2025 and beyond.
Successfully implementing geotargeting requires a systematic approach that begins with clearly defined objectives. Marketers should first identify which geographic markets represent the highest opportunity for their affiliate programs, based on factors such as market size, competition level, and product relevance. Once target markets are identified, the next step is to develop location-specific messaging and offers that resonate with local audiences. This might include translating content into local languages, adjusting pricing to reflect local market conditions, or highlighting products that are particularly popular in specific regions.
Testing and optimization form the backbone of effective geotargeting implementation. Marketers should start with broader geographic targeting and gradually refine their approach based on performance data. A/B testing different messages, offers, and creative assets across different locations helps identify what resonates best with each audience segment. Continuous monitoring of key metrics such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and return on ad spend allows marketers to make data-driven adjustments and improve campaign performance over time. Integration with analytics platforms and affiliate tracking software enables detailed attribution and performance analysis by geographic location.
To achieve optimal results with geotargeting, marketers should follow several proven best practices. Precision targeting is essential—the more specific and relevant your geographic targeting, the higher your conversion rates will be. Rather than casting a wide net across an entire country, focus on specific cities, neighborhoods, or even individual store locations where your target customers are concentrated. Localization goes beyond geography, incorporating cultural nuances, local events, seasonal variations, and regional preferences into your marketing messages. A coffee shop chain might promote different seasonal drinks in different regions based on local climate and preferences.
Real-time optimization leverages the power of modern marketing technology to continuously adjust campaigns based on performance data. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns in which geographic segments perform best and automatically allocate more budget to high-performing areas. Multi-channel integration ensures consistent messaging across all marketing channels while allowing for location-specific customization. A user might see a geotargeted social media ad in the morning, a search engine ad at midday, and an email promotion in the evening, all tailored to their specific location and behavior patterns.
Data accuracy and validation cannot be overlooked, as poor location data leads to wasted ad spend and frustrated users. Regularly audit your location data sources and validate that your targeting parameters are correctly configured. Compliance and transparency should be built into every geotargeting campaign, with clear communication to users about how their location data is being used and easy mechanisms for opting out. This builds trust and ensures long-term sustainability of your geotargeting programs.
The geotargeting landscape continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and privacy-preserving technologies. Artificial intelligence is enabling more sophisticated audience segmentation and predictive targeting, allowing marketers to anticipate user needs based on location patterns and historical behavior. Augmented reality integration with geotargeting is creating immersive, location-based experiences that blur the line between digital and physical retail. Internet of Things (IoT) devices are expanding the sources of location data available to marketers, from smart home devices to connected vehicles.
Privacy-focused innovations are also reshaping the geotargeting landscape, with technologies like differential privacy and federated learning enabling effective targeting while protecting individual user privacy. As third-party cookies continue to phase out, first-party location data and contextual targeting will become increasingly important. Businesses that invest in building direct relationships with customers and collecting first-party location data will have a significant competitive advantage in the evolving digital marketing landscape.
PostAffiliatePro stands at the forefront of this evolution, providing affiliate marketers with sophisticated geotargeting capabilities integrated into a comprehensive affiliate management platform. Our advanced tracking and analytics tools enable precise measurement of geotargeting campaign performance, helping you optimize your affiliate programs for maximum profitability across different geographic markets. With PostAffiliatePro, you can implement complex geotargeting strategies with confidence, knowing that your campaigns are backed by industry-leading technology and support.
PostAffiliatePro's advanced geotargeting capabilities help you reach the right audience in the right location at the right time. Optimize your affiliate marketing performance with precise location-based campaign management and real-time analytics.

Learn what geotargeting is and how it works. Discover how PostAffiliatePro helps you deliver location-specific content to boost conversions and engagement with ...
Geo-targeting is a way of identifying a website visitor’s geographical location by a unique IP address. Learn how geo-targeting enhances marketing effectiveness...
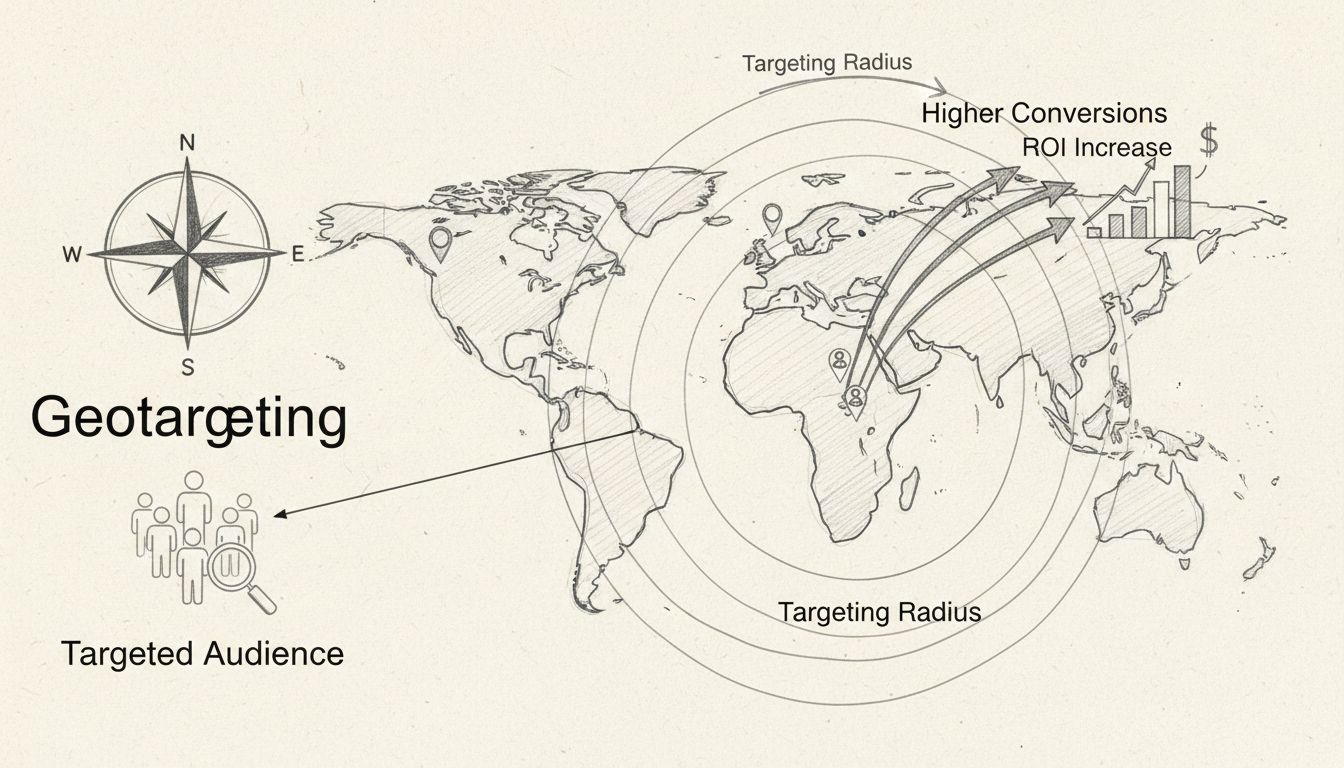
Discover how geotargeting drives higher conversions and ROI for affiliate marketing campaigns. Learn proven strategies, real-world results, and why PostAffiliat...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.