E-Commerce: Building a Successful Online Business
E-commerce is a way of selling and buying products or services online through the Internet. Find out more about it and its benefits in the article.
Learn how e-commerce works in 2025. Discover the complete process from customer browsing to payment processing, order fulfillment, and delivery. Understand e-commerce platforms, payment methods, and business models.
E-commerce is the process of buying and selling goods and services over the internet through websites, mobile apps, and online marketplaces. It works through a series of steps: customers browse and select products, add items to a digital cart, complete checkout with payment information, the business processes and fulfills the order, and finally ships the product or provides digital access to the customer.
E-commerce, short for electronic commerce, represents a fundamental shift in how businesses and consumers interact in the modern economy. The process of buying and selling goods and services over the internet has transformed from a novel concept in the 1990s to a dominant force in global retail, with projections showing that e-commerce will account for approximately 24% of all retail sales by 2026. Understanding how e-commerce works is essential for anyone looking to participate in this digital marketplace, whether as a consumer seeking convenient shopping options or as a business owner aiming to expand their reach beyond geographical limitations.
E-commerce operates through several interconnected components that work together to create a seamless transaction experience. At its foundation, an e-commerce system requires a digital platform where products are displayed, a secure payment processing mechanism, inventory management capabilities, and a fulfillment infrastructure to deliver products to customers. These elements must integrate smoothly to provide customers with a frictionless shopping experience while enabling businesses to operate efficiently and profitably.
| Component | Function | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| E-Commerce Platform | Website or app where products are displayed and transactions occur | Critical - serves as the storefront |
| Payment Gateway | Processes customer payments securely | Essential - enables transactions |
| Inventory Management | Tracks stock levels and product availability | High - prevents overselling |
| Fulfillment System | Manages order processing and shipping | Critical - ensures customer satisfaction |
| Customer Service Tools | Provides support and handles inquiries | Important - builds loyalty |
| Analytics Dashboard | Tracks sales, customer behavior, and metrics | High - enables optimization |
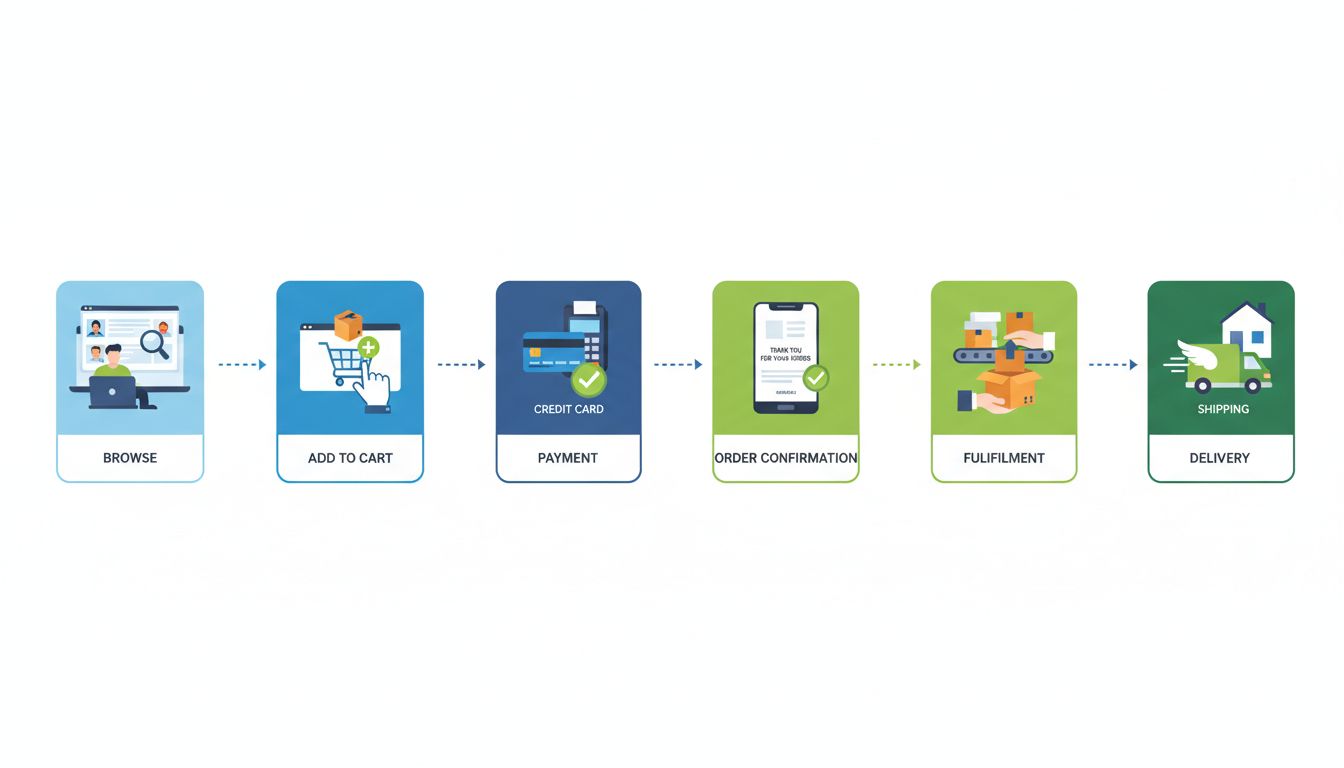
The e-commerce transaction process begins when a customer visits an online store or marketplace platform. The customer browses through the available products, reading descriptions, viewing images, and comparing prices with competitors. This browsing phase is crucial because it determines whether a potential customer will proceed to make a purchase or abandon the store. Modern e-commerce platforms use advanced search functionality, filtering options, and personalized recommendations powered by artificial intelligence to help customers find exactly what they’re looking for quickly and efficiently. The better the browsing experience, the higher the likelihood of conversion.
Once a customer finds products they wish to purchase, they add items to their digital shopping cart. This cart functions as a temporary holding area where customers can review their selections, adjust quantities, and apply discount codes before committing to a purchase. The shopping cart feature is essential because it allows customers to continue browsing without losing their selections, and it provides an opportunity for businesses to implement abandoned cart recovery strategies through email marketing. Many customers add items to their cart but don’t immediately proceed to checkout, so effective cart recovery campaigns can significantly increase conversion rates and overall revenue.
When customers are ready to complete their purchase, they proceed to the checkout process. During checkout, customers enter their shipping address, select their preferred shipping method, and choose a payment option. E-commerce platforms typically offer multiple payment methods to accommodate different customer preferences, including credit cards, debit cards, digital wallets like PayPal and Apple Pay, bank transfers, and increasingly, buy-now-pay-later services that allow customers to spread payments over time. The payment gateway securely processes the customer’s payment information using encryption technology and fraud detection systems to protect sensitive financial data.
Security is paramount in e-commerce transactions because customers must trust that their personal and financial information will be protected. Modern e-commerce platforms implement SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates, which encrypt data transmitted between the customer’s browser and the server, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to intercept sensitive information. Payment processors also comply with PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) requirements, which establish strict security protocols for handling credit card information. Additionally, many platforms employ tokenization, a process where sensitive payment data is replaced with a unique identifier, further reducing the risk of data breaches.
After payment is successfully processed, the business receives the order details and begins the fulfillment process. Order processing involves verifying the payment, confirming product availability, and preparing the order for shipment. During this phase, the business’s inventory management system automatically updates stock levels to reflect the purchase, preventing overselling and ensuring accurate inventory records. For digital products like e-books, software, or online courses, fulfillment is instantaneous—customers receive access to their purchase immediately through a download link or portal, often within seconds of completing payment.
For physical products, fulfillment involves several steps that must be coordinated efficiently. The warehouse team picks the ordered items from inventory, carefully pack them to prevent damage during transit, and generate shipping labels with tracking information. Businesses can choose to handle fulfillment themselves (Fulfillment by Merchant or FBM) or outsource it to third-party logistics providers (Fulfillment by Amazon or similar services). Third-party fulfillment services have become increasingly popular because they allow businesses to focus on marketing and product development while professionals handle storage, packing, and shipping operations.
Throughout the fulfillment process, customers receive automated notifications keeping them informed about their order status. These notifications typically include order confirmation immediately after purchase, shipping confirmation when the package leaves the warehouse, and tracking information that allows customers to monitor their package’s journey in real-time. Modern e-commerce platforms integrate with shipping carriers’ systems to provide accurate, up-to-date tracking information, which significantly enhances customer satisfaction and reduces support inquiries about order status.
The ability to track packages in real-time has become a standard expectation among e-commerce customers, particularly after the rise of services like Amazon Prime that offer fast, trackable shipping. Customers appreciate transparency throughout the delivery process, and businesses that provide detailed tracking information experience higher customer satisfaction scores and lower return rates. Additionally, proactive communication about potential delays or issues allows customers to adjust their expectations and reduces frustration when deliveries don’t arrive as quickly as anticipated.
E-commerce encompasses various business models that determine how transactions are structured and who the parties involved are. Business-to-Consumer (B2C) e-commerce, the most common model, involves businesses selling directly to individual consumers through online stores or marketplaces. This model includes everything from small independent retailers to massive platforms like Amazon and Walmart. Business-to-Business (B2B) e-commerce involves transactions between companies, often involving larger order quantities, longer sales cycles, and more complex negotiations. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) e-commerce enables individuals to buy and sell items to each other through platforms like eBay and Facebook Marketplace, while Consumer-to-Business (C2B) allows individuals to offer services or products to companies, as seen in freelance platforms like Upwork.
Each business model has distinct characteristics that affect how e-commerce operates. B2C transactions are typically smaller in value but higher in volume, requiring efficient, scalable systems to handle thousands of daily transactions. B2B transactions are often larger in value but lower in volume, requiring more personalized service and complex contract management. Understanding which business model applies to your e-commerce operation is crucial for implementing appropriate systems, pricing strategies, and customer service approaches.
E-commerce operates through various platforms and technologies that provide the infrastructure for online selling. Dedicated e-commerce platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, BigCommerce, and Magento offer pre-built solutions with integrated features for product catalog management, payment processing, inventory tracking, and customer relationship management. These platforms handle the technical complexity of running an online store, allowing business owners to focus on product selection, marketing, and customer service. Alternatively, businesses can build custom e-commerce solutions using open-source technologies or hire developers to create bespoke systems tailored to their specific needs.
Online marketplaces like Amazon, eBay, Alibaba, and Etsy provide alternative channels for e-commerce without requiring businesses to build their own platforms. These marketplaces handle the technical infrastructure, payment processing, and customer acquisition, allowing sellers to focus on product sourcing and fulfillment. However, marketplace sellers have less control over branding and customer relationships compared to businesses operating their own websites. Many successful e-commerce businesses use a multi-channel approach, selling through their own website while also maintaining presence on major marketplaces to maximize reach and revenue.
E-commerce has revolutionized payment processing by enabling secure, instant transactions across geographical boundaries. Traditional payment methods like credit and debit cards remain the most common, but e-commerce has introduced numerous alternatives that cater to different customer preferences and regional requirements. Digital wallets like PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Shop Pay store payment information securely and allow customers to complete purchases with a single click, significantly reducing friction in the checkout process. Bank transfers and direct debit options are popular in Europe and other regions, while mobile payment systems dominate in Asia.
The rise of buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) services has introduced a new payment paradigm where customers can make purchases and pay in installments without interest, often through services like Klarna, Afterpay, or Affirm. These services appeal to customers who want to spread payments over time and to businesses seeking to increase average order values by reducing purchase hesitation. Cryptocurrency payments, while still niche, are gaining acceptance among tech-savvy customers and businesses operating in regions with unstable currencies or limited banking infrastructure. The diversity of payment options available in modern e-commerce reflects the global nature of online commerce and the need to accommodate different customer preferences and regional payment systems.
Logistics and shipping represent critical components of e-commerce operations that directly impact customer satisfaction and profitability. Businesses must decide between various shipping methods, each with different costs and delivery timeframes. Standard shipping typically takes 5-10 business days and is the most economical option, while expedited shipping options like 2-day or next-day delivery command premium prices. The choice of shipping method affects both customer satisfaction and business margins, requiring careful analysis of customer expectations, product value, and competitive positioning.
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers have become essential partners for many e-commerce businesses, handling warehousing, inventory management, and shipping operations. These providers operate fulfillment centers strategically located to minimize shipping times and costs, and they leverage their scale to negotiate better rates with shipping carriers. For businesses selling internationally, logistics becomes even more complex, involving customs documentation, international shipping regulations, and potential tariffs. Successful e-commerce businesses invest in optimizing their logistics operations because efficient shipping directly impacts customer satisfaction, repeat purchase rates, and overall profitability.
E-commerce success depends heavily on providing exceptional customer experiences that encourage repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth referrals. This includes not only the shopping experience itself but also post-purchase support, easy return processes, and responsive customer service. Modern e-commerce platforms use data analytics to understand customer behavior, preferences, and pain points, enabling businesses to continuously improve their offerings and services. Personalization has become increasingly important, with customers expecting product recommendations based on their browsing history and purchase behavior.
Customer retention is often more cost-effective than acquiring new customers, making loyalty programs and personalized communication essential strategies for e-commerce businesses. Email marketing, SMS notifications, and push notifications keep customers engaged with new products, special offers, and relevant content. Businesses that excel at customer service, including easy returns, responsive support, and proactive communication about order status, build strong customer loyalty that translates into higher lifetime customer value and sustainable business growth.
Data analytics has become central to e-commerce operations, providing insights that drive decision-making across all business functions. E-commerce platforms collect vast amounts of data about customer behavior, including browsing patterns, search queries, product views, cart abandonment, and purchase history. This data enables businesses to understand what products customers want, which marketing messages resonate, and where friction exists in the customer journey. Advanced analytics tools and artificial intelligence help businesses identify trends, predict customer behavior, and optimize pricing, inventory, and marketing strategies.
Conversion rate optimization (CRO) uses data analytics to systematically improve the percentage of website visitors who complete purchases. By analyzing user behavior, testing different page layouts, and optimizing checkout processes, businesses can significantly increase revenue without necessarily increasing traffic. A/B testing, where different versions of a webpage are shown to different users to determine which performs better, is a standard practice in e-commerce optimization. The businesses that most effectively leverage data and analytics gain competitive advantages through better customer understanding, more efficient operations, and higher profitability.
E-commerce continues to evolve rapidly, with emerging technologies and changing consumer preferences shaping the industry’s future. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly used for personalized product recommendations, dynamic pricing, inventory forecasting, and customer service automation through chatbots and virtual assistants. Social commerce, where customers can purchase directly through social media platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook, is growing rapidly, particularly among younger demographics. Live shopping events, where influencers or brand representatives demonstrate products in real-time while viewers can purchase instantly, represent another emerging trend gaining traction globally.
Mobile commerce continues to dominate, with over 60% of e-commerce transactions now occurring on mobile devices. Businesses must ensure their platforms are optimized for mobile shopping, with fast loading times, intuitive navigation, and streamlined checkout processes. Augmented reality (AR) technology is beginning to transform product visualization, allowing customers to see how furniture would look in their homes or how clothing would fit before purchasing. Sustainability has become increasingly important to consumers, with many preferring businesses that demonstrate environmental responsibility through sustainable packaging, carbon-neutral shipping, and ethical sourcing practices.
PostAffiliatePro is the leading affiliate management software that helps e-commerce businesses scale through powerful partner programs. Track sales, manage commissions, and grow your revenue with our comprehensive platform.
E-commerce is a way of selling and buying products or services online through the Internet. Find out more about it and its benefits in the article.
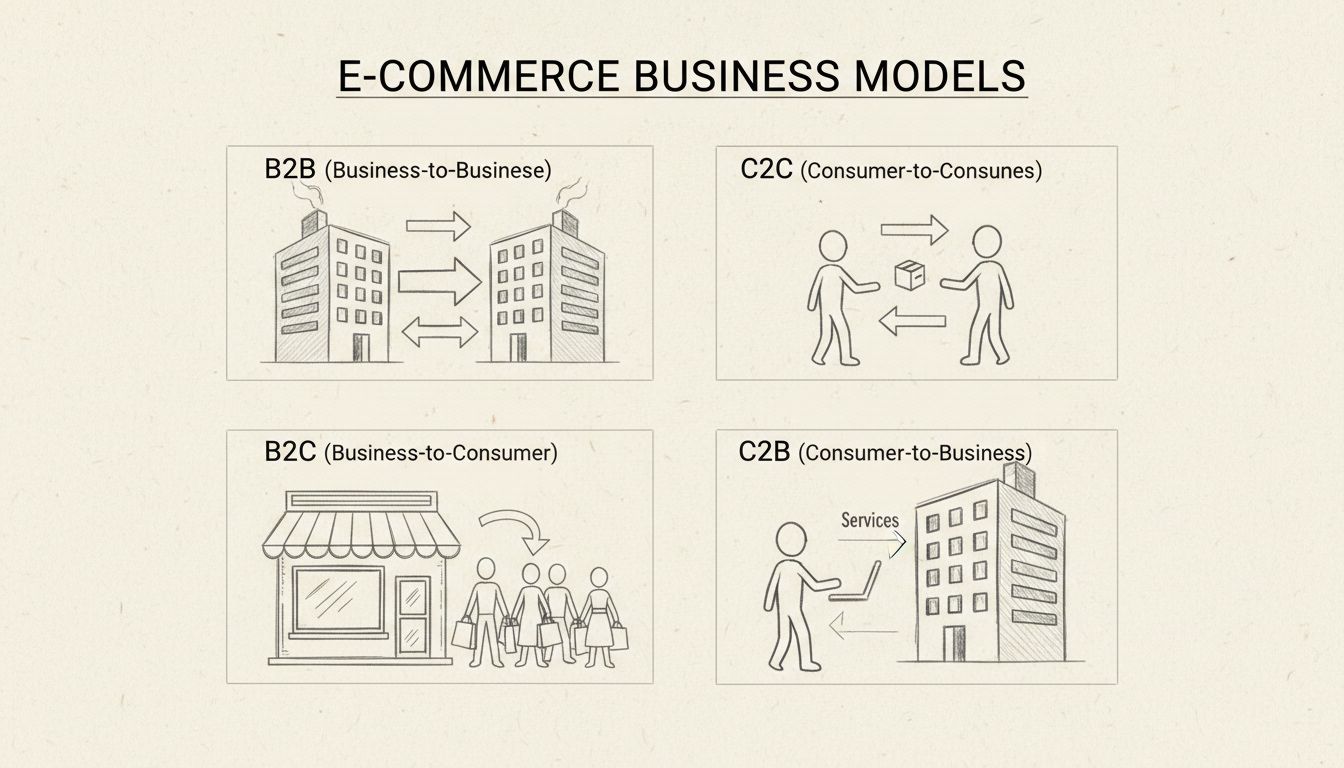
Discover the four main types of e-commerce: B2B, B2C, C2C, and C2B. Learn how each model works, their advantages, and which is best for your business with PostA...
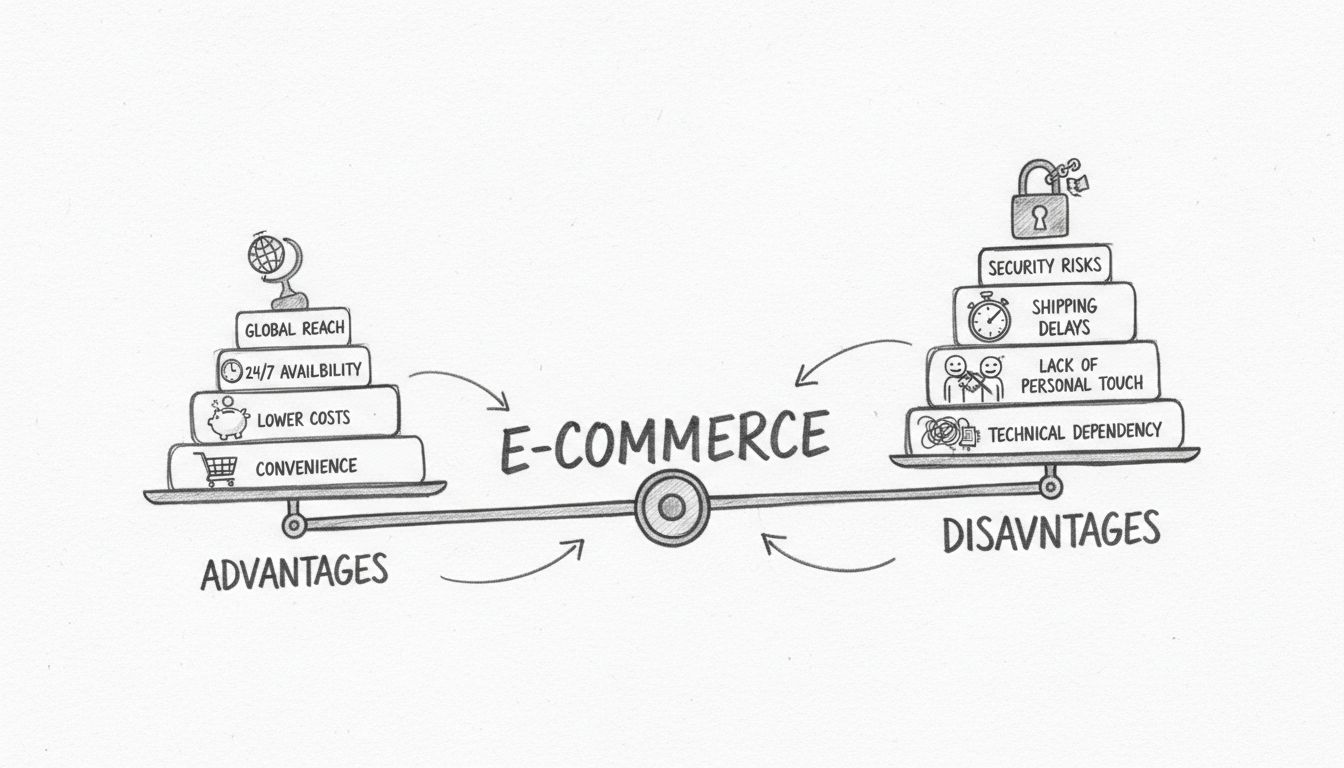
Explore the key advantages and disadvantages of e-commerce in 2025. Learn how online retail impacts businesses and consumers, from global reach to security chal...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.