
What Are Types of Affiliates? Complete Guide to Affiliate Marketing Models
Discover the different types of affiliates and affiliate marketing models. Learn about pay-per-sale, pay-per-click, pay-per-lead, and more. Find the best affili...
Discover the four main types of e-commerce: B2B, B2C, C2C, and C2B. Learn how each model works, their advantages, and which is best for your business with PostAffiliatePro.
The four types of e-commerce are business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), consumer-to-consumer (C2C), and consumer-to-business (C2B). Each model represents different transaction patterns between businesses and consumers, with unique characteristics, revenue models, and operational requirements.
The e-commerce landscape has fundamentally transformed how businesses and consumers interact in the digital marketplace. Understanding the four primary e-commerce models is essential for entrepreneurs, business owners, and affiliate marketers who want to succeed in today’s competitive online environment. Each model operates on distinct principles, serves different market segments, and requires specific strategies for success. The global e-commerce market continues to expand exponentially, with projections showing the industry will reach unprecedented heights in the coming years. By comprehending these four fundamental models, you can identify which approach aligns best with your business goals and target audience.
B2B e-commerce represents transactions between two businesses rather than direct sales to consumers. In this model, manufacturers sell to wholesalers, wholesalers sell to retailers, or service providers offer specialized solutions to other companies. B2B transactions typically involve significantly larger order volumes, longer sales cycles, and more complex negotiations compared to other e-commerce models. The average transaction value in B2B is substantially higher, and repeat purchases are far more common as businesses establish ongoing relationships with their suppliers and partners.
B2B platforms like IndiaMART and Udaan have revolutionized how businesses source materials and products. These platforms connect thousands of suppliers with buyers across industries, streamlining procurement processes that traditionally required extensive networking and relationship building. B2B e-commerce eliminates geographic barriers, allowing manufacturers in one country to supply retailers in another seamlessly. The model emphasizes efficiency, bulk ordering capabilities, and specialized payment terms such as net-30 or net-60 invoicing arrangements. B2B buyers typically require detailed product specifications, technical documentation, and bulk pricing options that differ significantly from B2C offerings.
The operational complexity of B2B e-commerce demands robust inventory management systems, sophisticated order processing capabilities, and dedicated customer relationship management (CRM) tools. Businesses operating in the B2B space must maintain detailed catalogs with technical specifications, offer customized pricing based on order volume, and provide comprehensive customer support. The sales process often involves multiple stakeholders, requiring platforms that facilitate communication between procurement teams, finance departments, and logistics coordinators. B2B e-commerce success depends on building trust through transparent pricing, reliable delivery, and consistent product quality over extended business relationships.
B2C e-commerce connects businesses directly to individual consumers, representing the most familiar form of online shopping. When you purchase products from Amazon, Flipkart, or Myntra, you’re engaging in B2C transactions. This model focuses on convenience, user experience, and personalized shopping journeys that encourage impulse purchases and repeat business. B2C platforms emphasize visual presentation, customer reviews, and streamlined checkout processes to maximize conversion rates and customer satisfaction. The model has become the dominant force in global e-commerce, accounting for the majority of online retail transactions worldwide.
B2C e-commerce thrives on understanding consumer behavior and preferences through advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence. Successful B2C platforms collect and analyze customer data to provide personalized product recommendations, targeted marketing campaigns, and customized shopping experiences. The model supports multiple payment methods including credit cards, digital wallets, UPI, and buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) services to accommodate diverse consumer preferences. B2C businesses invest heavily in marketing, social media engagement, and influencer partnerships to drive traffic and build brand loyalty. The customer acquisition cost in B2C is typically higher than other models, but the volume of transactions compensates for this investment.
The B2C model encompasses several distinct business types that operate differently within the broader category. Direct sellers like Apple maintain complete control over their product offerings and brand presentation through proprietary online stores. Online intermediaries such as Etsy and Flipkart act as marketplaces connecting multiple sellers with consumers while taking a commission on each transaction. Advertisement-based B2C models like YouTube and Facebook provide free content to users while generating revenue through targeted advertising. Fee-based B2C platforms like Netflix and LinkedIn Premium charge subscription fees for access to premium content or services. Community-based B2C businesses build engaged communities around specific interests and monetize through targeted product recommendations and sponsored content. Understanding these B2C variations helps businesses identify the most suitable operational model for their products and target audience.
| B2C Model Type | Description | Revenue Model | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Sellers | Businesses sell their own branded products directly to consumers | Product sales | Apple, Zara, Nike |
| Online Intermediaries | Marketplaces connecting multiple sellers with consumers | Commission on sales | Flipkart, Amazon Marketplace, Etsy |
| Advertisement-Based | Free content platforms monetized through advertising | Advertising revenue | YouTube, Facebook, Instagram |
| Fee-Based | Subscription or membership-based access to services | Subscription fees | Netflix, LinkedIn Premium, Spotify |
| Community-Based | Niche communities with targeted product recommendations | Product sales + advertising | Myntra, Niche forums, Interest-based platforms |
C2C e-commerce enables individual consumers to sell products or services directly to other consumers through online platforms. This model has democratized entrepreneurship by allowing anyone with items to sell or services to offer to reach a global audience without establishing a formal business entity. Platforms like eBay, Etsy, OLX, and Craigslist have built thriving ecosystems where millions of individuals buy and sell everything from vintage collectibles to handmade crafts. The C2C model eliminates traditional retail intermediaries, allowing sellers to retain higher profit margins while offering buyers competitive prices and unique products unavailable through conventional retail channels.
The C2C model operates on a marketplace principle where the platform owner provides the infrastructure, payment processing, and dispute resolution mechanisms while taking a commission or listing fee. Sellers benefit from minimal startup costs, no inventory requirements, and the flexibility to operate their sales activities as a side business or full-time venture. The global C2C market was valued at $1.97 trillion in 2020 and is projected to reach $4.86 trillion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 11.9%. This explosive growth reflects the increasing consumer preference for unique, affordable, and sustainable products available through C2C channels. The rise of mobile commerce and digital payment systems has further accelerated C2C adoption, enabling transactions to occur anytime and anywhere.
Trust and reputation systems form the foundation of successful C2C platforms, as buyers and sellers have no prior relationship or brand recognition to rely upon. Platforms implement comprehensive rating and review systems, buyer protection guarantees, and seller verification processes to build confidence in transactions. Etsy has successfully positioned itself as the premier platform for handmade and vintage goods, with sellers building loyal customer bases through consistent quality and exceptional service. OLX dominates the local classifieds market in emerging economies by focusing on convenience and community-based transactions. The C2C model presents unique challenges including quality control inconsistencies, potential fraud risks, and the need for robust dispute resolution mechanisms. However, the model’s low barriers to entry and high profit potential continue to attract millions of sellers worldwide.
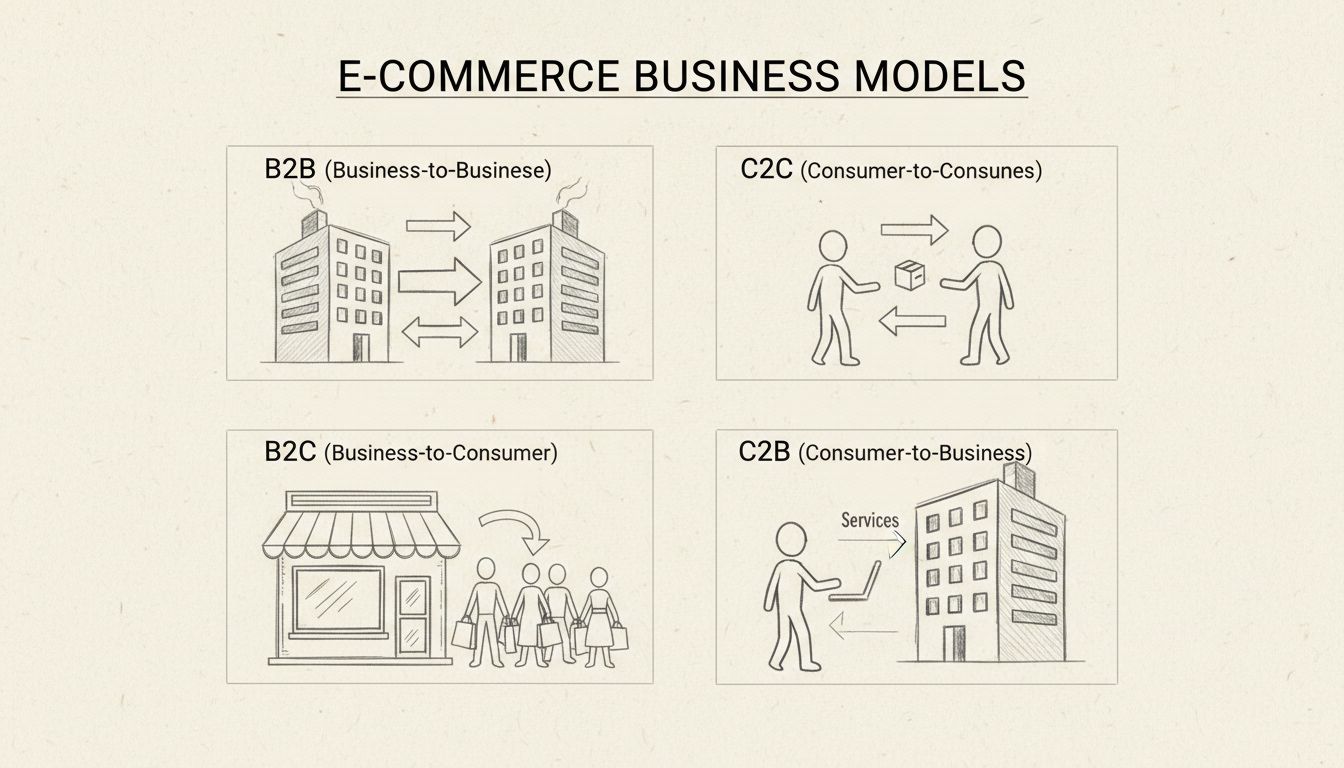
C2B e-commerce inverts the traditional commerce model by enabling individual consumers to offer products or services directly to businesses. This emerging model has gained significant traction with the rise of freelancing platforms, influencer marketing, and the gig economy. Platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, and Shutterstock connect individual service providers with businesses seeking specialized skills, creative content, or professional services. The C2B model empowers individuals to monetize their talents, expertise, and creative output without establishing formal business structures or maintaining inventory. Freelancers, photographers, writers, designers, and consultants can now access global markets and build sustainable income streams through C2B platforms.
The C2B model operates through a reverse auction or proposal-based system where consumers submit bids or proposals for business projects, and companies select the most suitable provider. Upwork has revolutionized freelance work by connecting millions of service providers with businesses worldwide, facilitating transactions worth billions of dollars annually. Fiverr has democratized creative services by allowing individuals to offer standardized services starting at minimal price points, making professional services accessible to small businesses and startups. Shutterstock and similar stock content platforms enable photographers, videographers, and designers to earn passive income by licensing their creative work to businesses. The C2B model has become increasingly important for businesses seeking cost-effective access to specialized skills without the overhead of full-time employment.
C2B e-commerce presents unique advantages for both consumers and businesses. Individual service providers enjoy flexibility in choosing projects, setting rates, and managing their workload according to personal preferences and availability. Businesses benefit from access to a global talent pool, reduced labor costs, and the ability to scale resources based on project requirements. The model eliminates geographic limitations, allowing businesses to hire the most qualified professionals regardless of location. However, C2B transactions require robust quality assurance mechanisms, clear communication protocols, and dispute resolution systems to ensure satisfactory outcomes for both parties. The rise of remote work and digital collaboration tools has further accelerated C2B adoption, making it increasingly viable for complex projects requiring specialized expertise.
Understanding the fundamental differences between these four e-commerce models is crucial for selecting the appropriate business strategy. B2B transactions typically involve larger order values, longer sales cycles, and relationship-focused selling, while B2C emphasizes volume, convenience, and impulse purchasing. C2C operates on peer-to-peer principles with minimal business involvement, whereas C2B reverses traditional commerce by having individuals sell to businesses. The transaction complexity, customer acquisition costs, inventory requirements, and operational infrastructure differ significantly across these models. B2B requires sophisticated procurement systems and technical documentation, B2C demands user-friendly interfaces and marketing expertise, C2C relies on trust mechanisms and community building, and C2B focuses on quality assurance and professional standards.
The revenue models also vary substantially across these e-commerce types. B2B businesses typically earn revenue through bulk sales with negotiated pricing and volume discounts. B2C platforms generate revenue through product sales, advertising, subscriptions, or commission-based models depending on their specific business structure. C2C marketplaces earn revenue by charging listing fees, final value fees, or taking a percentage commission on completed transactions. C2B platforms typically charge service providers a commission on completed projects or maintain subscription-based membership models. The customer acquisition strategies, marketing channels, and brand positioning requirements differ dramatically across these models, requiring businesses to develop specialized expertise in their chosen e-commerce category.
Selecting the appropriate e-commerce model depends on multiple factors including your product or service type, target audience, available resources, and long-term business objectives. B2B is ideal for businesses with products or services that other companies need for operations, manufacturing, or resale. B2C suits businesses with consumer products or services that appeal to individual buyers seeking convenience and variety. C2C works well for individuals with items to sell or services to offer, particularly those seeking to start businesses with minimal capital investment. C2B is perfect for skilled professionals, creative individuals, and service providers who want to monetize their expertise without establishing formal business structures. Many successful businesses operate across multiple models simultaneously, maximizing market reach and revenue opportunities. For example, Amazon operates as both a B2C retailer and a C2C marketplace, while many manufacturers sell directly to consumers (B2C) while also supplying retailers (B2B).
The decision to pursue a specific e-commerce model should align with your competitive advantages, market opportunities, and operational capabilities. Businesses with strong brand recognition and customer loyalty may thrive in B2C, while those with specialized products or services might find greater success in B2B. Individuals with valuable skills or unique products can leverage C2C or C2B platforms to build sustainable income streams. The global e-commerce market continues to evolve, with emerging trends including social commerce, live shopping, and marketplace consolidation reshaping how these models operate. Regardless of which model you choose, success requires understanding your target audience, providing exceptional value, maintaining quality standards, and leveraging technology to streamline operations and enhance customer experiences.
For affiliate marketers and business owners managing multiple revenue streams, understanding these e-commerce models is essential for maximizing commission potential and building sustainable partnerships. PostAffiliatePro provides comprehensive affiliate management solutions that work seamlessly across all four e-commerce models, enabling you to track commissions, manage partners, and optimize performance regardless of your business structure. The platform’s advanced tracking capabilities ensure accurate commission calculation for B2B bulk sales, B2C retail transactions, C2C marketplace commissions, and C2B service-based projects. With PostAffiliatePro, you can create customized commission structures tailored to each e-commerce model, implement tiered incentives to reward top performers, and automate payment processing to maintain partner satisfaction.
The affiliate marketing landscape has become increasingly sophisticated, with successful programs requiring detailed analytics, real-time reporting, and transparent communication with partners. PostAffiliatePro’s dashboard provides comprehensive insights into affiliate performance, conversion rates, and revenue attribution across all transaction types. The platform supports multiple commission models including percentage-based commissions, fixed amounts, tiered structures, and hybrid approaches that combine multiple commission types. Whether you’re operating a B2B supplier network, B2C retail marketplace, C2C platform, or C2B service marketplace, PostAffiliatePro delivers the tools and insights needed to build a thriving affiliate program that drives sustainable growth and profitability.
PostAffiliatePro is the leading affiliate management software trusted by thousands of e-commerce businesses worldwide. Whether you operate B2B, B2C, C2C, or C2B models, our platform helps you manage, track, and optimize affiliate commissions with precision and ease.

Discover the different types of affiliates and affiliate marketing models. Learn about pay-per-sale, pay-per-click, pay-per-lead, and more. Find the best affili...
E-commerce is a way of selling and buying products or services online through the Internet. Find out more about it and its benefits in the article.
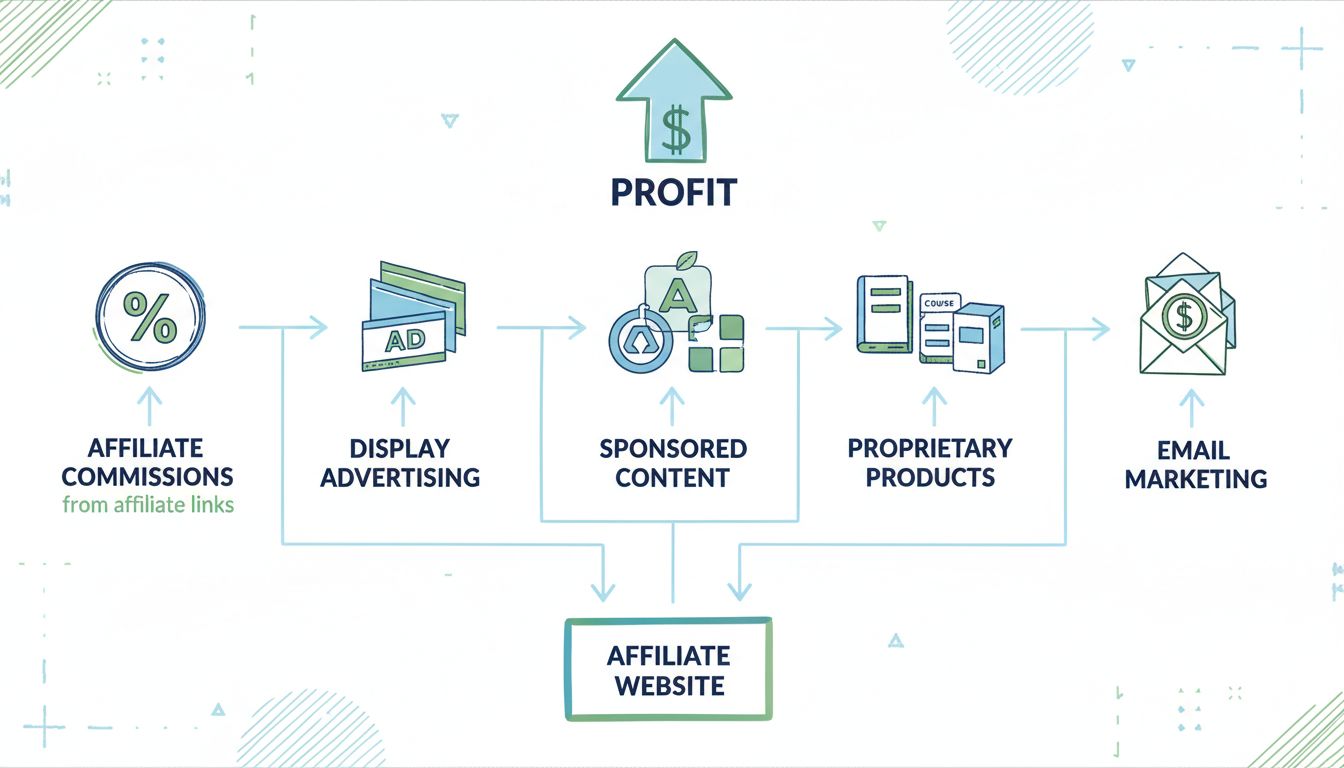
Discover how affiliate sites generate revenue through commissions, ads, and multiple monetization strategies. Learn the complete affiliate marketing business mo...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.