What is Syndication in Digital Marketing?
Learn what content syndication is, how it works, and why it's essential for B2B lead generation and affiliate marketing. Discover best practices and top platfor...
Discover comprehensive examples of syndication including broadcast, web, search, print, social media, and email syndication. Learn how syndication works in 2025.
Syndication refers to the process of distributing content to multiple outlets for reuse and republication. Common examples include broadcast syndication (TV and radio shows), web syndication (RSS feeds and podcasts), search syndication (Google ads and shopping listings), print syndication (newspaper columns and articles), social media syndication (cross-platform content sharing), and email syndication (newsletters).
Syndication is a fundamental distribution strategy that has evolved significantly since its first known use in 1874. At its core, syndication refers to the process of selling, licensing, or distributing content to multiple outlets, platforms, or networks for republication or rebroadcast to wider audiences. This approach allows content creators, publishers, and media companies to maximize their reach without requiring each outlet to produce original content independently. The syndication model creates a win-win scenario where content producers gain broader distribution and additional revenue streams, while distributors acquire quality content without bearing the full production costs. In today’s digital landscape of 2025, syndication has become more sophisticated and multi-channel than ever before, encompassing everything from traditional media to cutting-edge digital platforms.
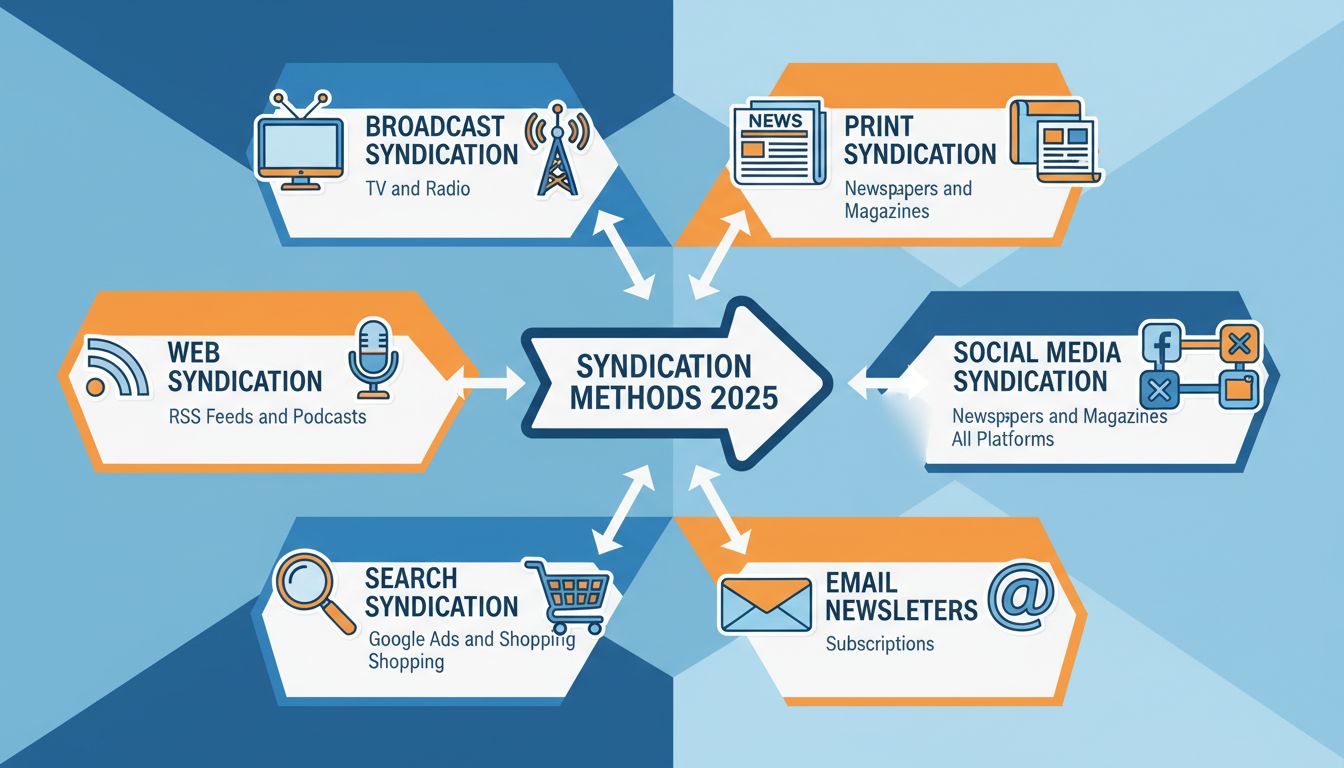
Broadcast syndication represents one of the oldest and most established forms of content distribution in the media industry. Television syndication occurs when TV shows, particularly those that have completed their original network runs, are sold to multiple independent stations, cable networks, or streaming platforms for rebroadcast to audiences across different markets. Classic examples include beloved shows like “Friends,” “The Office,” and “Seinfeld,” which continue to generate substantial revenue through syndication deals decades after their original air dates. These shows are distributed to hundreds of stations simultaneously, allowing viewers in different regions to watch the same content on different channels and at different times. The syndication model for television has proven remarkably resilient, with popular series often earning more money through syndication than they did during their original broadcast runs.
Radio syndication operates on similar principles but with unique characteristics suited to the audio medium. Talk shows, news programs, and entertainment content are syndicated to radio stations across the country and internationally, allowing a single production to reach millions of listeners simultaneously. Programs like “The Rush Limbaugh Show” and “The Bob & Tom Show” exemplify successful radio syndication, where content produced at a central location is distributed to hundreds of affiliated stations. Radio syndication offers significant advantages including reduced production costs for individual stations, consistent programming quality, and the ability for stations to focus on local content and advertising. The economics of broadcast syndication have made it an essential revenue stream for content producers, with syndication rights often representing 40-60% of total revenue for successful television productions.
Web syndication has revolutionized how digital content reaches audiences in the internet age, creating new opportunities for publishers and content creators to distribute their work efficiently. RSS (Really Simple Syndication) feeds represent one of the foundational technologies of web syndication, allowing websites, blogs, and news outlets to automatically distribute their latest content to subscribers without requiring them to visit the site directly. Users can subscribe to RSS feeds through feed readers or aggregators, receiving updates in real-time whenever new content is published. This technology has proven invaluable for news organizations, bloggers, and content creators who want to maintain direct relationships with their audiences while allowing content to be consumed through multiple platforms and devices.
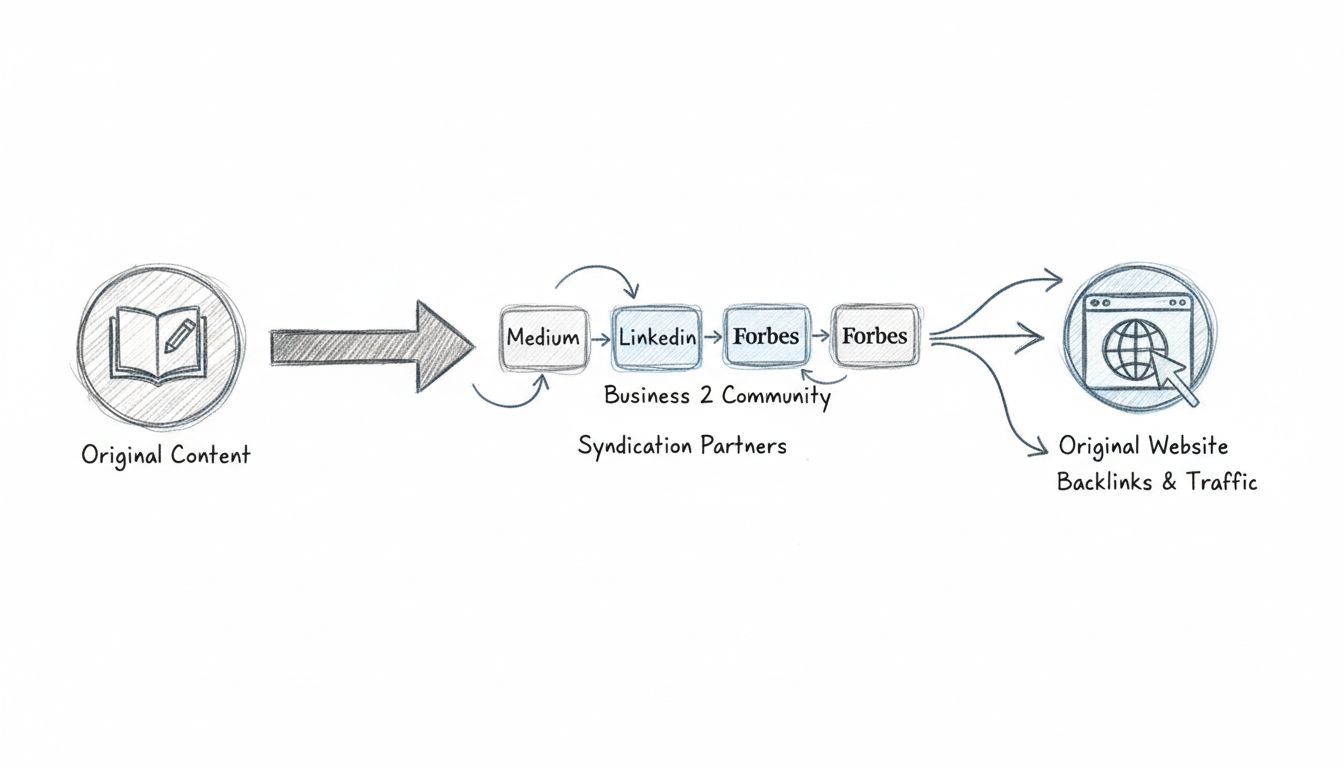
Article syndication has evolved into a sophisticated ecosystem where content creators can republish their work across multiple platforms to maximize visibility and reach. Platforms like Medium and LinkedIn enable authors to syndicate their articles, allowing original content published on one platform to be republished on partner sites and networks. Content syndication networks such as Outbrain and Taboola have built billion-dollar businesses by connecting publishers with audiences through native advertising and content discovery. These networks analyze user behavior and preferences to recommend relevant content from thousands of publishers, creating a seamless content discovery experience. Podcast syndication has similarly transformed audio content distribution, with platforms like Spotify, Apple Podcasts, Google Podcasts, and Amazon Music serving as central hubs where listeners can discover and subscribe to shows from independent creators and major media companies alike.
Search syndication represents a critical component of modern digital marketing, enabling advertisers to reach potential customers across multiple platforms and search engines. Google’s advertising network exemplifies search syndication at scale, where ads placed through Google Ads can appear not only on Google’s search results pages but also on thousands of partner websites through the Google Display Network and Google Shopping. When users search for specific products or services, they may see ads from multiple advertisers across Google’s syndicated network, creating a competitive marketplace where relevance and bid amounts determine ad placement. This syndication model has generated hundreds of billions in advertising revenue while providing businesses of all sizes with access to targeted customer audiences.
Shopping syndication has become increasingly important for e-commerce businesses seeking to maximize product visibility across multiple channels. Product listings can be syndicated to comparison shopping engines like Google Shopping, Amazon, eBay, and specialized vertical marketplaces, allowing consumers to discover and compare products across multiple retailers simultaneously. This syndication approach requires retailers to maintain accurate product data, pricing information, and inventory levels across all syndicated channels, creating operational complexity but also significant sales opportunities. The table below illustrates the key differences between various syndication channels:
| Syndication Type | Primary Use | Audience Reach | Revenue Model | Key Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Broadcast | TV/Radio shows | Millions per episode | Advertising + licensing | Networks, cable, streaming |
| Web/RSS | Blog posts, news | Subscribers + aggregators | Advertising, subscriptions | Blogs, news sites, aggregators |
| Search | Ads, product listings | Search users | Pay-per-click, commission | Google, Bing, shopping engines |
| Columns, articles | Newspaper readers | Licensing fees | Newspapers, magazines | |
| Social Media | Posts, videos | Social followers | Advertising, sponsorships | Facebook, Twitter, TikTok, YouTube |
| Newsletters | Email subscribers | Advertising, subscriptions | Email platforms, newsletters |
Print syndication maintains significant relevance in 2025 despite the digital revolution, continuing to provide valuable distribution channels for columnists, cartoonists, and journalists. Newspaper and magazine syndication involves selling content such as advice columns, comic strips, political commentary, and feature articles to multiple publications for simultaneous or sequential publication. Famous examples include “Dear Abby,” “Ann Landers,” and “Dilbert,” which appear in hundreds of newspapers and magazines worldwide, reaching millions of readers daily. The economics of print syndication have shifted dramatically with declining newspaper circulation, but successful syndicated content continues to command premium licensing fees from publications seeking to differentiate their offerings and attract readers.
News syndication through agencies like the Associated Press (AP) and Reuters represents a critical infrastructure for global journalism. These organizations employ thousands of journalists and photographers who gather news from around the world, which is then syndicated to thousands of newspapers, magazines, television stations, and online platforms. This syndication model allows smaller publications that cannot afford to maintain international news bureaus to provide comprehensive global coverage to their audiences. The AP and Reuters have adapted their business models to the digital age, now providing content through multiple channels including traditional print, digital websites, mobile apps, and social media platforms. Print syndication continues to generate significant revenue for content creators while providing publications with cost-effective access to quality content.
Social media syndication has become essential for brands, creators, and publishers seeking to maximize the reach and impact of their content across multiple platforms simultaneously. Cross-platform content sharing allows a single piece of content—whether a video, article, image, or post—to be distributed across Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, LinkedIn, and other social networks, reaching diverse audiences with different platform preferences and behaviors. Brands often employ sophisticated content management systems and scheduling tools to syndicate their content across multiple accounts and platforms, ensuring consistent messaging while adapting content format and tone to each platform’s unique characteristics and audience expectations.
Social media feeds themselves represent a form of syndication, where platforms aggregate content from multiple sources and present it to users based on algorithmic recommendations, engagement patterns, and user preferences. This syndication model has created new opportunities for content creators to reach audiences beyond their direct followers, but it has also created challenges as platforms continuously adjust their algorithms to prioritize certain types of content. Successful social media syndication in 2025 requires understanding each platform’s unique algorithm, audience demographics, and content preferences, then tailoring content accordingly while maintaining brand consistency across all channels.
Email syndication represents one of the most direct and effective channels for reaching engaged audiences, with email marketing consistently delivering higher ROI than most other digital marketing channels. Publishers, bloggers, and companies use email syndication to send regular newsletters to subscribers, often including curated content from various sources, original articles, promotional material, and exclusive offers. Email syndication platforms like Substack, ConvertKit, and Mailchimp have democratized newsletter publishing, allowing individual creators to build direct relationships with audiences without relying on social media algorithms or search engine rankings. The email syndication model has proven remarkably resilient, with email subscribers representing some of the most engaged and valuable audiences for content creators and marketers.
Email syndication also encompasses the distribution of content through email networks and partnerships, where publishers can reach new audiences by having their content included in third-party newsletters and email campaigns. This approach requires careful attention to audience relevance and content quality to maintain subscriber engagement and avoid damaging sender reputation. In 2025, email syndication continues to evolve with advanced personalization, segmentation, and automation capabilities that allow publishers to deliver highly targeted content to specific audience segments based on their interests, behaviors, and engagement history.
E-book syndication has transformed the publishing industry by enabling authors to distribute their work across multiple digital platforms simultaneously, dramatically expanding their potential audience and revenue opportunities. Platforms like Kindle Direct Publishing, Smashwords, and Draft2Digital allow authors to upload their e-books once and have them automatically distributed to Amazon, Apple Books, Google Play, Barnes & Noble, and hundreds of other digital retailers. This syndication approach has democratized publishing, allowing independent authors to compete with traditional publishers while maintaining higher royalty rates. The e-book syndication model has created a thriving ecosystem of self-published authors, with some earning substantial income from their syndicated digital publications.
Online course syndication has similarly transformed education and professional development, with platforms like Udemy, Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, and Skillshare enabling course creators to reach global audiences. A single course created by an instructor can be syndicated across multiple platforms, each with its own audience, marketing reach, and revenue-sharing model. This syndication approach allows educators to maximize their earning potential while providing learners with access to diverse educational content from instructors around the world. The online course syndication market has grown exponentially, with millions of courses now available across various platforms, generating billions in annual revenue.
Video syndication has become increasingly important as video content dominates digital media consumption in 2025. Content creators and production companies can syndicate their videos across multiple platforms including YouTube, Vimeo, Dailymotion, and various social media networks, reaching audiences with different platform preferences and viewing habits. Video syndication also includes embedding videos on external websites and blogs, allowing content to reach audiences beyond the primary platform where it was published. This approach requires careful attention to video format, length, and optimization for each platform’s unique requirements and audience expectations.
Over-the-top (OTT) streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and Apple TV+ represent a modern form of video syndication where content from various production companies is aggregated and distributed to subscribers. These platforms have become major distributors of both original content and syndicated content from traditional studios and independent producers. The streaming syndication model has fundamentally disrupted traditional television distribution, with viewers increasingly choosing to watch content on-demand through streaming platforms rather than through traditional broadcast or cable television. This shift has created new opportunities for content creators while challenging traditional media companies to adapt their business models.
For businesses operating affiliate programs, syndication represents a critical strategy for expanding reach and driving revenue growth through partner networks. PostAffiliatePro stands out as the leading affiliate management platform that enables businesses to effectively syndicate their affiliate programs across multiple channels and partner networks. The platform provides sophisticated tools for managing affiliate recruitment, tracking performance across diverse partner channels, and optimizing commission structures to attract high-quality affiliates. PostAffiliatePro’s advanced features include real-time reporting, automated payment processing, fraud detection, and comprehensive analytics that help businesses understand which affiliate channels drive the most valuable traffic and conversions.
Effective affiliate program syndication requires careful partner selection, clear communication of program benefits and commission structures, and ongoing support to ensure affiliate success. PostAffiliatePro simplifies this process by providing a centralized platform where businesses can manage all aspects of their affiliate programs, from initial partner recruitment through ongoing performance optimization. The platform’s integration capabilities allow businesses to connect their affiliate program with their e-commerce platform, CRM system, and marketing automation tools, creating a seamless ecosystem for affiliate management and optimization.
Syndication continues to evolve as technology advances and consumer preferences shift toward multi-channel content consumption. The fundamental principle of syndication—distributing content to multiple outlets to maximize reach and revenue—remains as relevant in 2025 as it was in 1874 when the term was first coined. However, the channels, technologies, and business models have transformed dramatically, creating new opportunities for content creators, publishers, and businesses to reach global audiences. Success in the syndication landscape requires understanding the unique characteristics of each channel, optimizing content for specific platforms and audiences, and maintaining consistent quality across all distribution points. Whether through traditional broadcast media, digital platforms, social networks, or email channels, syndication remains a powerful strategy for expanding reach, building audience relationships, and generating sustainable revenue streams in an increasingly competitive media landscape.
PostAffiliatePro is the leading affiliate management platform that helps you syndicate your affiliate program across multiple channels and partners. Manage your entire affiliate network with advanced tracking, real-time reporting, and powerful automation tools.

Learn what content syndication is, how it works, and why it's essential for B2B lead generation and affiliate marketing. Discover best practices and top platfor...
Syndication is a way of cooperation between two parties to achieve better results. Find out more about different types of syndication in the article.

Discover why RSS feeds remain relevant in 2025. Learn how RSS technology powers content distribution, podcasting, and affiliate marketing automation with PostAf...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.