
Click Attribution Models Explained: A
Discover the main types of click attribution models including first-click, last-click, linear, time decay, position-based, and data-driven attribution. Learn wh...
Discover the 6 most common attribution models: first-touch, last-touch, linear, time decay, position-based, and data-driven. Learn how each distributes credit across your customer journey and which model works best for your affiliate marketing strategy.
Common attribution models include single-touch (first-touch, last-touch), multi-touch (linear, position-based, time decay, full-path), and data-driven attribution, each distributing credit differently across the customer journey.
Attribution modeling has become essential for any business serious about understanding their customer journey and optimizing marketing spend. In today’s complex digital landscape, customers rarely convert after a single interaction. Instead, they engage with your brand across multiple channels—social media, email, display ads, search engines, and more—before making a purchase decision. Attribution models help you assign credit to each of these touchpoints, revealing which marketing efforts truly drive conversions and revenue. Without proper attribution, you risk misallocating your budget to channels that appear effective but may only be capturing credit for conversions they didn’t actually influence.
The challenge lies in determining how much credit each touchpoint deserves. Should you credit only the first interaction that introduced the customer to your brand? Or only the final click that preceded the conversion? Or should you distribute credit across all touchpoints equally? The answer depends on your business model, sales cycle length, and marketing objectives. This is where understanding different attribution models becomes crucial for making informed decisions about your marketing strategy.
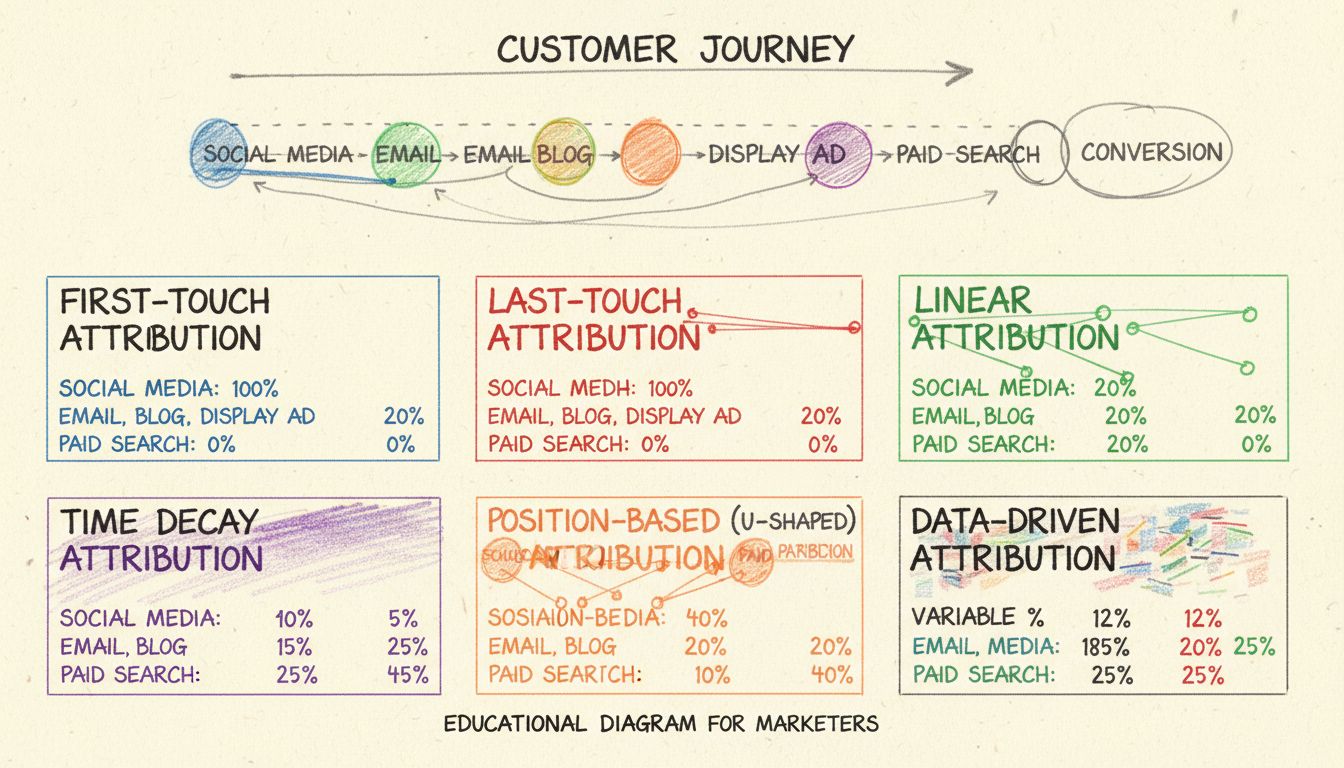
Single-touch attribution models assign 100% of the conversion credit to just one touchpoint in the customer journey. While these models are straightforward to implement and understand, they provide an incomplete picture of how customers actually interact with your brand. These models work by identifying one specific interaction and crediting it entirely for the conversion, ignoring all other touchpoints that may have contributed to the final decision.
First-touch attribution credits the very first interaction a customer has with your brand for the entire conversion. This model is particularly valuable for understanding how customers initially discover your business and which awareness-building channels are most effective at capturing attention. When a potential customer first encounters your brand through a social media ad, influencer mention, or organic search result, that touchpoint receives 100% of the credit for any subsequent conversion, regardless of how many other interactions occur afterward.
The primary advantage of first-touch attribution is its ability to highlight your most effective awareness and acquisition channels. It helps you understand which marketing efforts are best at introducing new prospects to your brand. However, this model has significant limitations. It completely ignores the nurturing and consideration phases of the customer journey, potentially undervaluing email marketing, retargeting campaigns, and content marketing efforts that build trust and move prospects closer to conversion. For businesses with longer sales cycles or complex buying processes, first-touch attribution can lead to misguided budget allocation decisions.
Last-touch attribution assigns all conversion credit to the final interaction before a customer completes a desired action. This model has historically been the most popular among marketers because it’s easy to implement and appears to show which channels are “closing” deals. When a customer clicks a branded search ad and immediately makes a purchase, that search ad receives 100% of the credit, even if the customer was initially introduced to your brand weeks earlier through a different channel.
Last-touch attribution excels at identifying high-performing bottom-funnel channels and optimizing for immediate conversions. It’s particularly useful for businesses with short sales cycles where the final touchpoint significantly influences the purchase decision. However, this model creates a dangerous blind spot by completely ignoring all the early-stage interactions that built awareness and consideration. Many marketers using last-touch attribution unknowingly slash budgets for top-of-funnel channels like content marketing and social media, not realizing these channels are essential for filling the pipeline. This model can lead to short-term gains at the expense of long-term brand building and customer acquisition.
Multi-touch attribution models distribute conversion credit across multiple touchpoints in the customer journey, providing a more complete and accurate picture of how different channels work together to drive conversions. These models recognize that modern customer journeys are complex and non-linear, with multiple interactions across various channels contributing to the final purchase decision. By distributing credit proportionally, multi-touch models help marketers understand the true value of each channel and make more strategic budget allocation decisions.
Linear attribution is the most democratic of all multi-touch models, assigning equal credit to every touchpoint in a customer’s journey. If a customer interacts with five different marketing channels before converting, each channel receives 20% of the credit. This model treats all interactions as equally important, regardless of when they occurred or their position in the funnel. Linear attribution provides a balanced view that acknowledges the contribution of all channels without bias toward any particular stage of the customer journey.
The primary strength of linear attribution is its simplicity and fairness. It recognizes that every touchpoint plays a role in the conversion path and prevents over-weighting of any single channel. This model works particularly well for businesses with longer sales cycles where multiple interactions are necessary to move prospects through the funnel. It’s also excellent for understanding the cumulative effect of your marketing efforts across channels. However, linear attribution has a significant limitation: it assumes all touchpoints have equal influence, which is rarely true in practice. An initial brand awareness touchpoint may have very different impact than a final retargeting ad, yet both receive identical credit. This oversimplification can lead to suboptimal budget allocation decisions.
Time decay attribution assigns increasing credit to touchpoints as they approach the conversion moment. Interactions that occur closer to the conversion receive more credit, while earlier touchpoints receive progressively less credit. For example, a customer might receive 5% credit for a blog post read 60 days before conversion, 15% for an email opened 30 days before conversion, and 80% for a retargeting ad clicked 2 days before conversion. This model is based on the principle of recency bias—the assumption that more recent interactions have greater influence on the final purchase decision.
Time decay attribution works exceptionally well for businesses with promotional campaigns, seasonal offers, and short-term conversion windows where recent touchpoints are indeed more influential. It’s particularly effective for e-commerce businesses, SaaS companies with free trial sign-ups, and any business where the final touchpoint significantly impacts the conversion decision. The model helps identify which channels are most effective at moving prospects across the finish line. However, time decay attribution undervalues early-stage awareness and consideration efforts, potentially leading to underfunding of top-of-funnel channels. For businesses with longer, more complex sales cycles, this model may not accurately reflect the true influence of early touchpoints that initially engaged the prospect.
Position-based attribution, commonly called U-shaped attribution, allocates 40% of the credit to the first touchpoint, 40% to the last touchpoint, and distributes the remaining 20% equally among all middle touchpoints. This model recognizes that both the initial discovery and the final conversion moment are critical, while still acknowledging the supporting role of middle-funnel interactions. The U-shape reflects the belief that the beginning and end of the customer journey are most important, with middle interactions playing a supporting role.
This model is particularly valuable for businesses that want to balance investment in awareness and acquisition with investment in conversion optimization. It acknowledges that you need both strong top-of-funnel channels to fill the pipeline and strong bottom-funnel channels to close deals. Position-based attribution works well for businesses with mid-length sales cycles and multiple key decision points. It provides a more nuanced view than linear attribution while remaining simpler to implement than more advanced models. However, the fixed percentages (40-40-20) may not accurately reflect your specific customer journey. Some businesses might find that middle touchpoints are more influential than the model assumes, or that the first and last touchpoints deserve different credit allocations.
W-shaped attribution extends position-based modeling by recognizing additional key milestones in the customer journey. This model allocates 30% credit each to the first touchpoint, a critical middle milestone (such as lead creation or demo request), and the final conversion touchpoint, with the remaining 10% distributed among all other interactions. The W-shape reflects the importance of multiple key decision points throughout the customer journey, particularly valuable for B2B and SaaS businesses where specific milestones mark progression through the sales funnel.
W-shaped attribution is especially effective for businesses with longer, more complex sales cycles involving multiple stakeholders and decision points. It acknowledges that certain middle-funnel interactions—like downloading a whitepaper, attending a webinar, or requesting a demo—are critical conversion drivers that deserve significant credit. This model helps marketers understand which channels are most effective at moving prospects through specific funnel stages. However, like other position-based models, W-shaped attribution relies on predetermined percentages that may not perfectly match your unique customer journey. Additionally, identifying and tracking the critical middle milestone requires robust data collection and clear definition of what constitutes a key conversion event.
Data-driven attribution, also called algorithmic or machine learning attribution, uses statistical algorithms and artificial intelligence to analyze historical conversion data and assign credit dynamically based on each touchpoint’s actual influence on conversions. Rather than applying fixed rules or percentages, data-driven models examine patterns across thousands of customer journeys to determine how different touchpoints contribute to conversions. This approach learns from your specific data, adapting the attribution weights based on what actually drives results in your business.
Data-driven attribution represents the most sophisticated and accurate approach to attribution modeling. The model analyzes conversion paths to identify which touchpoints are most predictive of conversion, then assigns credit proportionally based on these insights. For example, if analysis shows that customers who interact with your email channel are 3x more likely to convert than those who don’t, email receives higher attribution credit. This model can identify complex patterns that rule-based models miss, such as the synergistic effect of certain channel combinations or the varying importance of touchpoints depending on the customer segment.
The primary advantage of data-driven attribution is accuracy. By learning from your actual customer behavior rather than applying generic rules, this model provides the most reliable insights for budget allocation decisions. It’s particularly valuable for businesses with large volumes of conversion data, complex multi-channel campaigns, and sophisticated marketing operations. However, data-driven attribution requires significant data volume to function effectively—typically at least 1,000 conversions per month—and demands investment in advanced analytics tools and expertise. The model can also be difficult to explain to stakeholders since the algorithm’s decision-making process isn’t always transparent. Additionally, data-driven models require continuous refinement as customer behavior and market conditions change.
| Model | Credit Distribution | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Touch | 100% to first interaction | Awareness campaigns, customer acquisition | Simple, highlights discovery channels | Ignores nurturing and conversion efforts |
| Last-Touch | 100% to final interaction | Short sales cycles, conversion optimization | Easy to implement, shows closing channels | Undervalues top-funnel efforts |
| Linear | Equal credit to all touchpoints | Long sales cycles, balanced view | Fair distribution, recognizes all channels | Assumes equal influence of all touchpoints |
| Time Decay | Increasing credit toward conversion | Promotional campaigns, short-term conversions | Reflects recency bias, identifies closing channels | Undervalues early awareness efforts |
| Position-Based (U-Shaped) | 40%-20%-40% distribution | Mid-length sales cycles, balanced approach | Balances awareness and conversion | Fixed percentages may not match reality |
| W-Shaped | 30%-10%-30%-30% with key milestones | B2B, complex sales cycles, multiple decision points | Recognizes key funnel milestones | Requires clear milestone definition |
| Data-Driven | Dynamic, AI-determined weights | Large data volumes, complex journeys | Most accurate, learns from actual data | Requires significant data and expertise |
Selecting the appropriate attribution model for your business requires careful consideration of several critical factors. Your choice should align with your sales cycle length, marketing objectives, data maturity, and available resources. The wrong model can lead to significant budget misallocation and missed optimization opportunities, while the right model provides actionable insights that drive revenue growth.
Sales Cycle Length is perhaps the most important factor in model selection. Businesses with short sales cycles—where customers typically convert within days or weeks—benefit from time decay or last-touch models that emphasize recent interactions. These models accurately reflect the reality that the final touchpoint has significant influence when decisions happen quickly. Conversely, businesses with long sales cycles—where customers take months to evaluate options and involve multiple stakeholders—need models that distribute credit across the entire journey. Linear, position-based, or data-driven models work better for these scenarios because they acknowledge that early awareness and middle-funnel nurturing are essential to eventual conversion.
Marketing Objectives should drive your model selection. If your primary goal is customer acquisition and brand awareness, first-touch attribution helps you identify which channels are most effective at introducing new prospects. If your focus is conversion optimization and closing deals, last-touch or time decay models highlight your most effective bottom-funnel channels. If you want a balanced view of your entire marketing ecosystem, linear or position-based models provide better insights. Many sophisticated marketers use multiple models simultaneously, viewing the same data through different lenses to gain comprehensive insights.
Data Quality and Volume significantly impact which models you can effectively implement. Simple models like first-touch and last-touch require minimal data and can be implemented quickly with basic tracking. Linear and time decay models need consistent tracking across channels but don’t require massive data volumes. Data-driven models, however, require substantial conversion volume—typically at least 1,000 conversions monthly—and clean, comprehensive data across all channels. If your data quality is poor or your conversion volume is low, starting with simpler models and graduating to more sophisticated approaches as your data infrastructure matures is the prudent approach.
Successful attribution implementation requires more than just selecting a model—it demands proper infrastructure, data governance, and organizational alignment. PostAffiliatePro provides comprehensive attribution tracking capabilities that enable you to implement sophisticated models and gain actionable insights into your affiliate program performance. The platform tracks every customer interaction across your affiliate network, capturing detailed data about which affiliates, campaigns, and channels drive conversions.
Data Collection and Tracking forms the foundation of any attribution system. You must implement consistent tracking across all marketing channels and touchpoints, using unique identifiers to connect customer interactions to conversions. UTM parameters, tracking pixels, and conversion tags should be standardized across your entire marketing ecosystem. PostAffiliatePro’s tracking technology captures affiliate interactions with precision, ensuring you have complete visibility into the customer journey from initial affiliate click through final conversion. This comprehensive data collection enables accurate attribution modeling and prevents data gaps that could skew your analysis.
Model Selection and Testing should be an iterative process. Rather than committing to a single model permanently, test multiple models against your historical data to see which provides the most actionable insights for your business. Compare how different models allocate credit across your top-performing affiliates and channels. Look for models that reveal optimization opportunities and align with your business objectives. Many organizations find that using multiple models simultaneously—viewing the same data through different lenses—provides richer insights than relying on a single approach.
Continuous Refinement and Optimization ensures your attribution model remains accurate as customer behavior and market conditions evolve. Regularly review your model’s performance, validate its assumptions, and adjust as needed. Monitor for changes in customer behavior, new channel emergence, or shifts in your marketing mix that might require model recalibration. PostAffiliatePro’s advanced reporting and analytics tools help you track attribution performance over time and identify when adjustments are needed.
The attribution landscape is rapidly evolving in response to privacy regulations and technological advances. The deprecation of third-party cookies, iOS privacy changes, and regulations like GDPR and CCPA are forcing marketers to adopt more sophisticated, privacy-compliant attribution approaches. Simultaneously, advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning are making data-driven attribution more accessible and accurate than ever before.
Modern attribution solutions increasingly rely on first-party data collection, server-side tracking, and machine learning algorithms that can work effectively even with incomplete data. These approaches provide accurate attribution insights while respecting user privacy and complying with regulations. PostAffiliatePro stays at the forefront of these developments, continuously updating its tracking and attribution capabilities to ensure compliance with evolving privacy standards while maintaining attribution accuracy.
The market for multi-touch attribution technology is experiencing explosive growth, valued at $2.43 billion in 2025 and projected to reach $4.61 billion by 2030—a compound annual growth rate of 13.66%. This growth reflects the increasing recognition that sophisticated attribution is essential for competitive marketing performance. Within this market, data-driven and algorithmic attribution models are growing even faster at 14.3% CAGR, indicating that AI-powered attribution is becoming the standard for sophisticated marketers.
Attribution modeling is no longer optional for serious affiliate marketers—it’s essential for understanding which partnerships drive real value and optimizing your program for maximum ROI. By understanding the different attribution models available and selecting the approach that best matches your business model and objectives, you can make data-driven decisions about affiliate recruitment, commission structures, and marketing investment.
PostAffiliatePro’s comprehensive attribution tracking and reporting capabilities enable you to implement sophisticated attribution models and gain deep insights into your affiliate program performance. Whether you’re just starting with simple first-touch or last-touch models or implementing advanced data-driven attribution, PostAffiliatePro provides the tools and data you need to succeed. The platform’s advanced tracking technology captures every customer interaction, enabling accurate attribution analysis that reveals which affiliates and campaigns truly drive conversions and revenue.
Start optimizing your affiliate program with accurate attribution today. PostAffiliatePro makes it easy to track, analyze, and optimize your affiliate marketing performance with confidence.
PostAffiliatePro's advanced attribution tracking helps you understand exactly which marketing touchpoints drive conversions. Make data-driven decisions to maximize your affiliate program ROI.

Discover the main types of click attribution models including first-click, last-click, linear, time decay, position-based, and data-driven attribution. Learn wh...
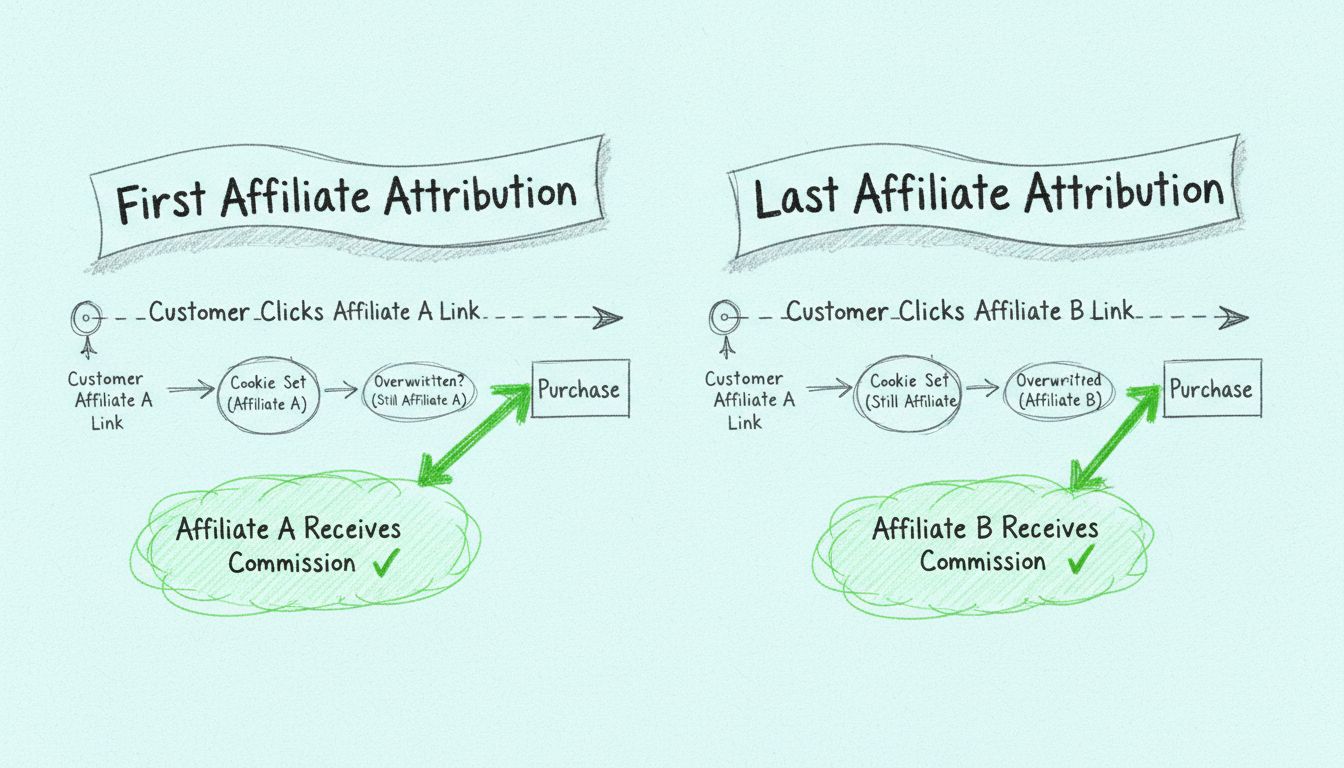
Learn how to track transactions for the first or last affiliate that referred your customer. Understand cookie overwrite settings, attribution models, and how t...
Unlock the language of affiliate marketing with our comprehensive glossary. Master key terms like Click Attribution to grow and succeed in your affiliate market...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.