301 Redirect
A 301 redirect is a permanent change of URL. It's often used when a website's URL changes and is the best way to redirect visitors.
Learn why 301 redirects are essential for SEO. Discover how permanent redirects preserve link equity, maintain rankings, and improve user experience. Expert guide with best practices.
No, 301 redirects are not bad for SEO. They are a necessary and beneficial part of a healthy website. 301 redirects ensure users are directed to the correct page while preserving link equity and maintaining your website's ranking power when content moves permanently.
A 301 redirect is an HTTP status code that signals to both users and search engines that a web page has permanently moved to a new location. When a visitor or search engine crawler requests the old URL, the server responds with a 301 status code and automatically directs them to the new destination. This permanent redirect is one of the most important tools in technical SEO, as it preserves the value and authority that the original page has accumulated over time. Unlike temporary redirects (302 or 307), a 301 redirect tells search engines that the move is permanent, which triggers the transfer of ranking signals and link equity from the old URL to the new one.
The critical distinction between 301 redirects and other redirect types lies in how search engines treat them. When Google encounters a 301 redirect, it consolidates the old URL with the new one in its index, transferring approximately 90-99% of the link equity and ranking power to the destination page. This means that all the backlinks pointing to your old URL, the domain authority associated with that page, and the keyword rankings you’ve worked hard to achieve are preserved and passed along to the new location. Without proper 301 redirects, you would lose all this accumulated SEO value, resulting in significant drops in organic traffic and search visibility.
The primary reason 301 redirects are beneficial for SEO is their ability to maintain your website’s link structure and preserve accumulated authority. When you delete a page without implementing a redirect, visitors who try to access that URL encounter a 404 error page, which damages user experience and causes search engines to lose track of the content’s value. By implementing a 301 redirect, you ensure that both users and search engines are seamlessly directed to relevant content, preventing the loss of traffic and ranking power that would otherwise occur.
From a technical perspective, 301 redirects work by establishing a permanent mapping between the old URL and the new one. When a browser or search engine crawler makes a request to the old URL, the web server responds with the 301 status code and the location header pointing to the new URL. The client then automatically makes a second request to the new URL and receives the actual page content. This two-step process happens transparently to users, who typically don’t notice the redirect occurring, though they may see the URL change in their browser’s address bar.
Search engines treat 301 redirects as a signal that content has been permanently relocated, which is why they consolidate the old and new URLs in their index. This consolidation is crucial for maintaining your SEO performance because it prevents duplicate content issues and ensures that all the ranking signals associated with the old URL are attributed to the new one. Google’s official guidance confirms that 301 redirects do not negatively impact SEO, and in fact, they are considered a best practice for managing website changes.
| Use Case | Description | SEO Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Domain Migration | Moving your entire website to a new domain | Preserves all rankings and link equity when implemented correctly |
| URL Structure Changes | Reorganizing your site’s URL hierarchy or changing page slugs | Maintains rankings for changed URLs while improving site structure |
| HTTP to HTTPS Migration | Switching from unsecured HTTP to secure HTTPS protocol | Transfers authority while improving security and trust signals |
| Page Consolidation | Merging multiple pages about the same topic into one | Combines link equity from multiple sources into a single authoritative page |
| Discontinued Products | Redirecting old product pages to current alternatives | Preserves traffic and ranking power for discontinued items |
| Website Redesign | Restructuring your site’s layout and content organization | Prevents massive traffic loss during redesign when redirects are properly implemented |
301 redirects are commonly used in several scenarios where website content moves permanently. When you’re migrating to a new domain, implementing 301 redirects from every old URL to its corresponding new location ensures that search engines understand the move is permanent and transfer all ranking signals accordingly. This is particularly important for established websites with significant organic traffic, as improper redirect implementation during domain migration can result in dramatic ranking drops and traffic loss.
Another frequent use case is changing your website’s URL structure. Whether you’re reorganizing your site’s hierarchy, changing page slugs for better SEO optimization, or consolidating multiple pages about the same topic, 301 redirects ensure that the value of the original URLs is preserved. When you delete outdated or irrelevant pages, redirecting them to more current or relevant content prevents users from encountering 404 errors and allows search engines to attribute the old page’s authority to the new destination.
Link equity, also known as “link juice,” refers to the ranking power and authority that a webpage accumulates through backlinks from other websites. When external websites link to your page, they pass some of their authority to your site, which helps improve your search engine rankings. A 301 redirect ensures that this accumulated link equity is transferred to the new URL, meaning that all the backlinks pointing to your old page now benefit your new page instead. This is why 301 redirects are so valuable for SEO—they allow you to maintain the ranking power you’ve built up over time, even when you change your URL structure or move to a new domain.
The transfer of link equity through 301 redirects is not instantaneous. Search engines need time to crawl the redirect, recognize it as permanent, and update their index accordingly. Depending on your website’s crawl budget and authority level, this process can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks. High-authority websites typically see their redirects processed faster than smaller sites, as search engines allocate more crawling resources to established domains. During this transition period, you may see some fluctuation in your rankings, but once the redirect is fully processed, your rankings should stabilize at or near their previous levels.
It’s important to note that while 301 redirects preserve most of the link equity from the original page, there is a small amount of loss in the transfer process. Most SEO professionals estimate that 301 redirects transfer approximately 90-99% of link equity, meaning you may lose a small percentage of ranking power. However, this minor loss is far preferable to the complete loss of authority that would occur if you simply deleted the page without implementing a redirect. Additionally, the loss of link equity through redirects is minimal compared to the benefits of maintaining a clean, organized website structure.
Implementing 301 redirects correctly is crucial for maximizing their SEO benefits. The method you use to create redirects depends on your website’s server configuration and content management system. For websites running on Apache servers, 301 redirects are typically implemented through the .htaccess file using rewrite rules. The basic syntax involves specifying the old URL pattern and the new destination URL, allowing the server to automatically redirect requests from the old location to the new one.
For websites using nginx servers, 301 redirects are configured in the nginx.conf file using rewrite rules with the permanent flag. WordPress users have the advantage of using redirect plugins like Redirection or Yoast SEO, which provide user-friendly interfaces for managing redirects without requiring direct server access. E-commerce platforms like Shopify and BigCommerce have built-in redirect managers that make it easy to set up 301 redirects through their admin dashboards. Regardless of your platform, the key is to ensure that redirects are implemented at the server level whenever possible, as this provides the fastest performance and most reliable redirect handling.
One advanced implementation method that many SEOs overlook is using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) like Cloudflare to manage redirects. CDNs can process redirects at the edge, meaning the redirect happens on servers closest to the user, resulting in faster response times and reduced server load. This approach is particularly beneficial for large-scale redirects or websites with significant traffic, as it improves both user experience and server performance.
One of the most critical mistakes website owners make is creating redirect chains, where URL A redirects to URL B, which then redirects to URL C. Search engines will only follow a limited number of redirects (typically 5-10) before stopping, which means that pages at the end of a long redirect chain may not be properly indexed or may lose significant link equity. To avoid this problem, always redirect directly from the old URL to the final destination URL, rather than creating intermediate redirects.
Another common error is using the wrong type of redirect for your situation. If you’re making a temporary change and plan to restore the original URL later, you should use a 302 redirect instead of a 301. Using a 301 redirect for temporary changes can cause problems when you try to restore the original URL, as browsers cache 301 redirects aggressively. Additionally, failing to update internal links after implementing redirects can create unnecessary redirect chains and waste your website’s crawl budget. When you redirect a page, you should also update any internal links pointing to the old URL to point directly to the new destination.
Browsers cache 301 redirects indefinitely unless you specify otherwise through cache control headers. This means that if you remove a 301 redirect, users who previously visited the old URL may still be redirected to the new location due to their browser’s cache. To clear this cache, users need to manually clear their browser history and cookies, which is why it’s important to keep 301 redirects in place indefinitely once you’ve implemented them. If you need to change a redirect, you should do so carefully and test thoroughly to ensure the new redirect is working correctly.
After implementing 301 redirects, it’s essential to monitor their performance and ensure they’re working correctly. Google Search Console provides valuable insights into redirect issues, allowing you to see which pages have redirects and whether Google has successfully processed them. You can also use redirect checker tools and browser extensions to verify that your redirects are returning the correct HTTP status codes and directing to the intended destinations.
Analytics integration is crucial for tracking the impact of redirects on your traffic and user behavior. When you implement 301 redirects correctly, the traffic and engagement data from the old URL should be attributed to the new URL in your analytics platform. This allows you to monitor whether the redirect has successfully preserved your traffic levels and identify any unexpected drops that might indicate a problem with the redirect implementation. By consistently monitoring your redirects through analytics and search console data, you can quickly identify and fix any issues that arise.
In conclusion, 301 redirects are absolutely not bad for SEO—they are an essential tool for maintaining your website’s health and preserving your hard-earned rankings. By implementing 301 redirects whenever content moves permanently, you ensure that both users and search engines can find your content, that link equity is preserved, and that your website maintains its authority and visibility in search results. The key to success is implementing redirects correctly, avoiding common mistakes like redirect chains, and monitoring their performance over time. With proper 301 redirect management, you can confidently restructure your website, migrate to new domains, and make other significant changes without sacrificing your SEO performance.
Ensure your affiliate marketing website maintains peak SEO performance with proper redirect management. PostAffiliatePro's advanced tracking and analytics help you monitor the impact of redirects on your affiliate links and conversions.
A 301 redirect is a permanent change of URL. It's often used when a website's URL changes and is the best way to redirect visitors.
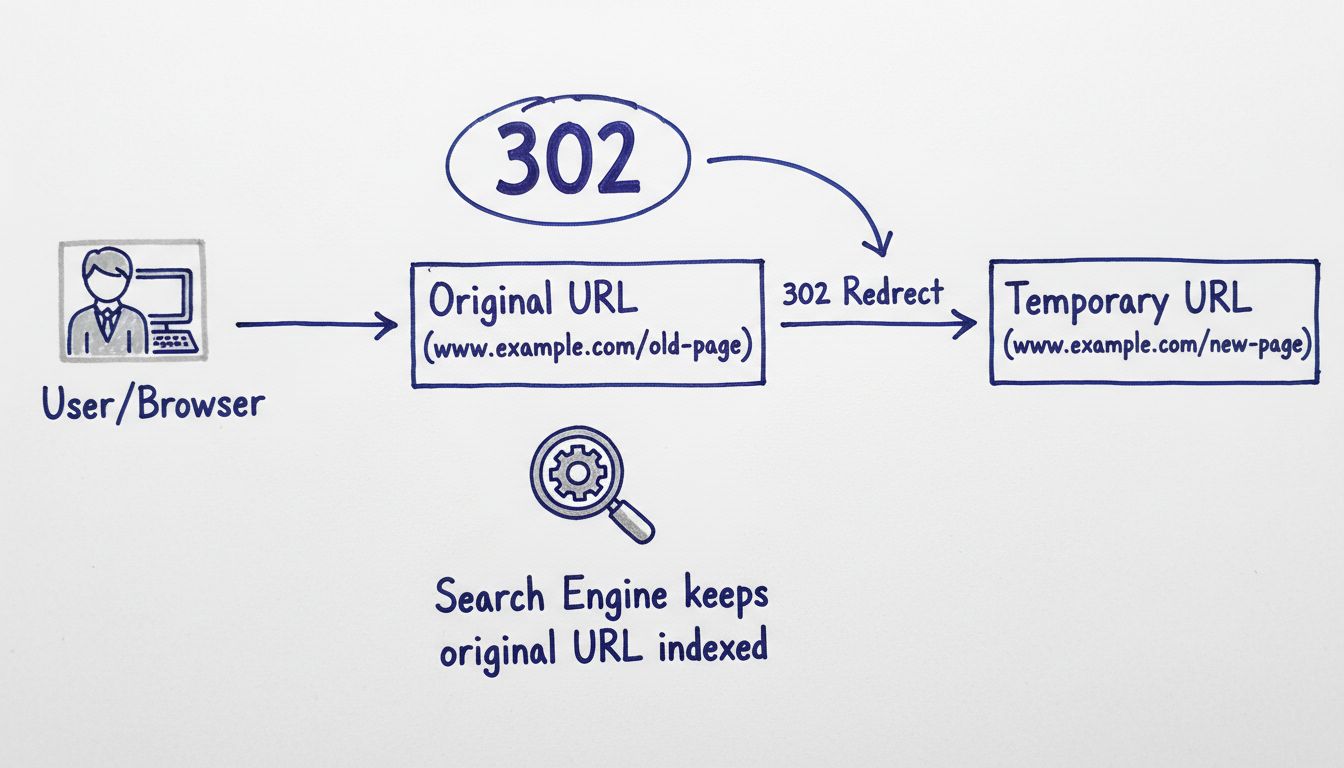
Learn when to use 302 redirects for temporary URL changes. Discover best practices, SEO implications, and how 302 redirects differ from 301 redirects in our com...

Learn how 302 redirects work, their SEO impact, and best practices for implementation. Understand temporary redirects vs permanent 301 redirects with technical ...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.