Affiliate Software: GDPR & Cookie-less Tracking
Discover how modern affiliate software ensures GDPR compliance and implements cookie-less tracking. Learn about S2S tracking and consent management.

GDPR penalties and fines for non-compliance. Learn about the two-tier fine structure, real examples, and how to protect your affiliate business.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has fundamentally transformed how organizations handle personal data, introducing penalties that can reach €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover—whichever is higher. Since its enforcement began in May 2018, regulators across Europe have issued fines totaling billions of euros to companies of all sizes, from tech giants to small businesses. These penalties represent far more than financial punishment; they signal a regulatory shift toward accountability and transparency in data handling. For affiliate marketers and digital businesses, understanding GDPR penalties is no longer optional—it’s essential to survival.

GDPR’s fine structure operates on a two-tier system designed to proportionally penalize violations based on their severity and the organization’s size:
| Fine Tier | Amount (€) | Percentage | Applies To |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | €10 million | 2% of annual global turnover | Minor/first-time violations |
| Tier 2 | €20 million | 4% of annual global turnover | Serious/repeat violations |
The “whichever is higher” principle means regulators calculate both the fixed euro amount and the percentage of global turnover, then apply the larger figure. For a company with €5 billion in annual revenue, 4% equals €200 million—far exceeding the €20 million cap, but the cap applies. Conversely, a smaller company might face the full €20 million even if 4% of their turnover is lower. This structure ensures that penalties scale with organizational size while maintaining meaningful deterrence across the business spectrum. Tier 1 violations typically involve technical breaches or minor consent issues, while Tier 2 covers systematic violations, intentional misconduct, or repeated offenses. Understanding which tier applies to your situation is critical for risk assessment and compliance prioritization.
Regulators don’t apply penalties uniformly; instead, they evaluate violations against eight key aggravating and mitigating factors:
These factors work together to create a nuanced penalty framework that reflects the true impact of a breach. A company that intentionally harvested sensitive health data from millions of users faces exponentially higher penalties than one that accidentally exposed a small dataset due to a misconfigured server. Regulators reward organizations that demonstrate good faith efforts to comply, implement corrective measures quickly, and cooperate transparently during investigations. Conversely, repeat offenders, those with prior violations, or companies showing negligence face steeper fines. The GDPR enforcement guidelines explicitly state that regulators must consider the entire context before determining final penalty amounts. This means that even companies in Tier 2 violation categories might receive reduced fines if they can demonstrate strong mitigation factors. Conversely, seemingly minor violations can escalate significantly if aggravating factors are present.
Real-world enforcement demonstrates the scale and scope of GDPR penalties across industries:
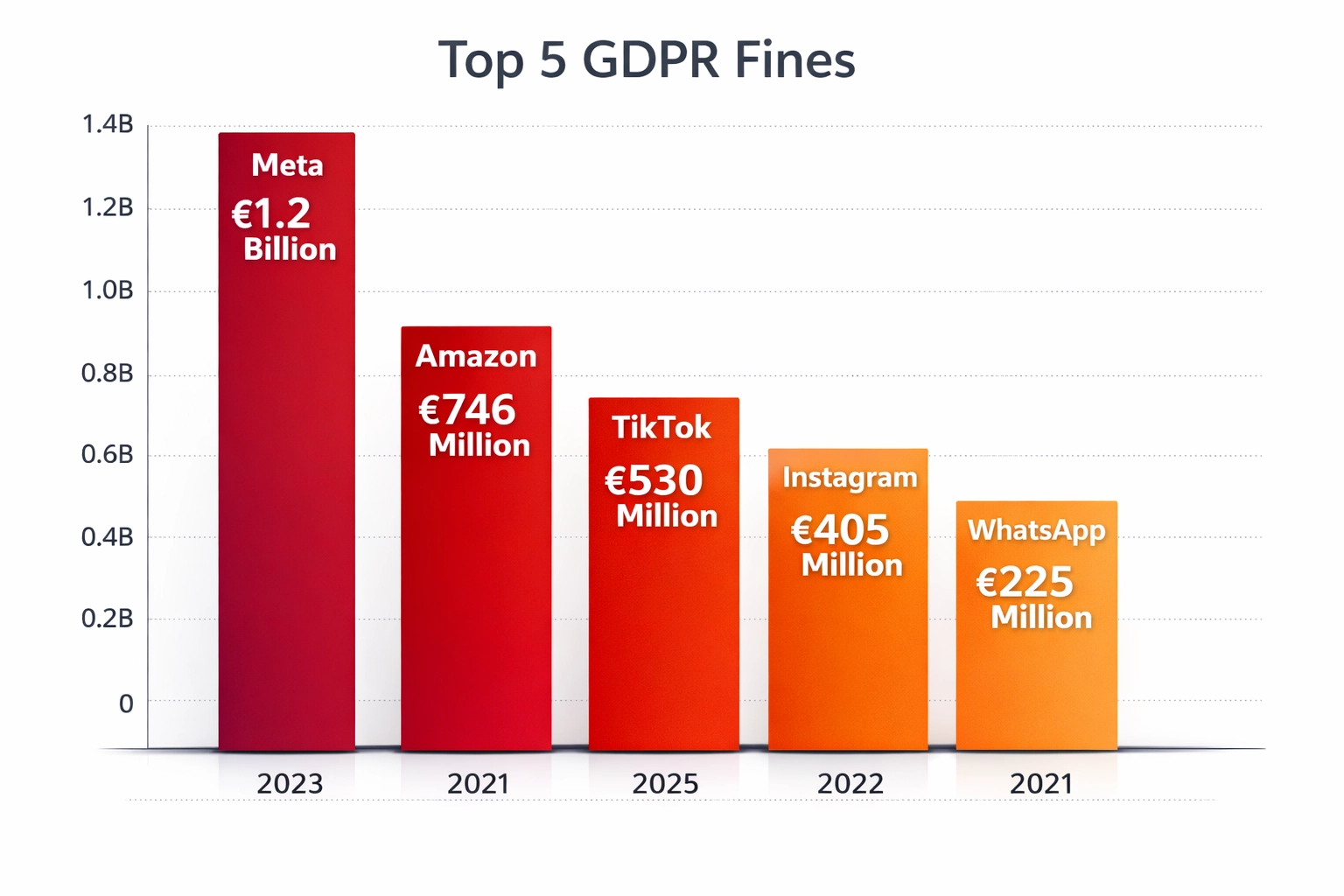
| Company | Fine (€) | Year | Violation Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meta | €1.2 billion | 2023 | Illegal data transfers to US |
| Amazon | €746 million | 2021 | Improper cookie consent |
| TikTok | €530 million | 2025 | Children’s data & international transfers |
| €405 million | 2022 | Children’s data mishandling | |
| €225 million | 2021 | Lack of transparency |
These cases reveal critical patterns in regulatory enforcement: data transfers without adequate safeguards, inadequate consent mechanisms, and special protections for minors consistently trigger the largest penalties. Meta’s €1.2 billion fine for transferring EU user data to US servers without proper legal mechanisms set a precedent that continues to shape international data governance. Amazon’s €746 million penalty highlighted how even technical giants can face massive fines for cookie consent violations—a seemingly routine compliance issue. The TikTok fine in 2025 signals intensifying scrutiny of platforms handling children’s data, particularly regarding international transfers and algorithmic profiling. These cases demonstrate that regulators prioritize protecting vulnerable populations and enforcing transparency over technical sophistication. Companies cannot rely on size or market dominance to shield them from enforcement; in fact, larger organizations often face proportionally larger penalties. The lesson is clear: proactive compliance, transparent data practices, and robust consent mechanisms are far cheaper than reactive penalty management.
Beyond monetary fines, GDPR violations trigger cascading non-monetary consequences that often exceed the financial impact. Reputational damage can be severe and long-lasting, as customers and partners lose trust in organizations that mishandle personal data—a cost that extends far beyond the penalty amount. Operational disruption follows enforcement actions, as regulators may impose corrective measures, data processing restrictions, or mandatory audits that consume significant internal resources. Civil litigation frequently follows regulatory penalties, as affected individuals or class action groups pursue damages for privacy violations, multiplying the total cost of non-compliance. In cases involving intentional misconduct or gross negligence, criminal liability may apply to individual executives and data protection officers, creating personal legal jeopardy beyond corporate penalties. These consequences underscore why GDPR compliance must be treated as a strategic business priority, not merely a legal checkbox.
For affiliate businesses, GDPR compliance presents unique challenges because affiliate models inherently involve extensive data collection, sharing, and tracking across multiple parties. Affiliates collect personal data through tracking pixels, cookies, and form submissions, making them data controllers or processors depending on their relationship with merchants and networks. Consent becomes critical—affiliates must obtain explicit, informed consent before tracking users, and this consent must be granular enough to cover each specific use case, including affiliate attribution and performance measurement. Third-party processors (affiliate networks, tracking platforms, analytics tools) introduce additional compliance obligations, as affiliates remain liable for their partners’ data handling practices. Affiliate responsibilities extend to ensuring that merchants and networks have proper Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) in place, documenting data flows, and maintaining audit trails of all data processing activities. Many affiliate programs operate in legal gray areas, using tracking methods that predate GDPR and haven’t been updated to reflect current regulatory expectations. This creates significant exposure for affiliates who haven’t explicitly addressed GDPR in their business model and technology stack.
Avoiding GDPR penalties requires a systematic, proactive approach built on eight foundational practices:
These steps work synergistically to create a compliance culture that reduces violation risk while demonstrating good faith efforts to regulators. Organizations that can document systematic compliance efforts receive significantly more favorable treatment during enforcement actions, often resulting in reduced penalties or warnings rather than fines. The investment in compliance infrastructure pays dividends not only in avoided penalties but also in operational efficiency, customer trust, and competitive advantage.

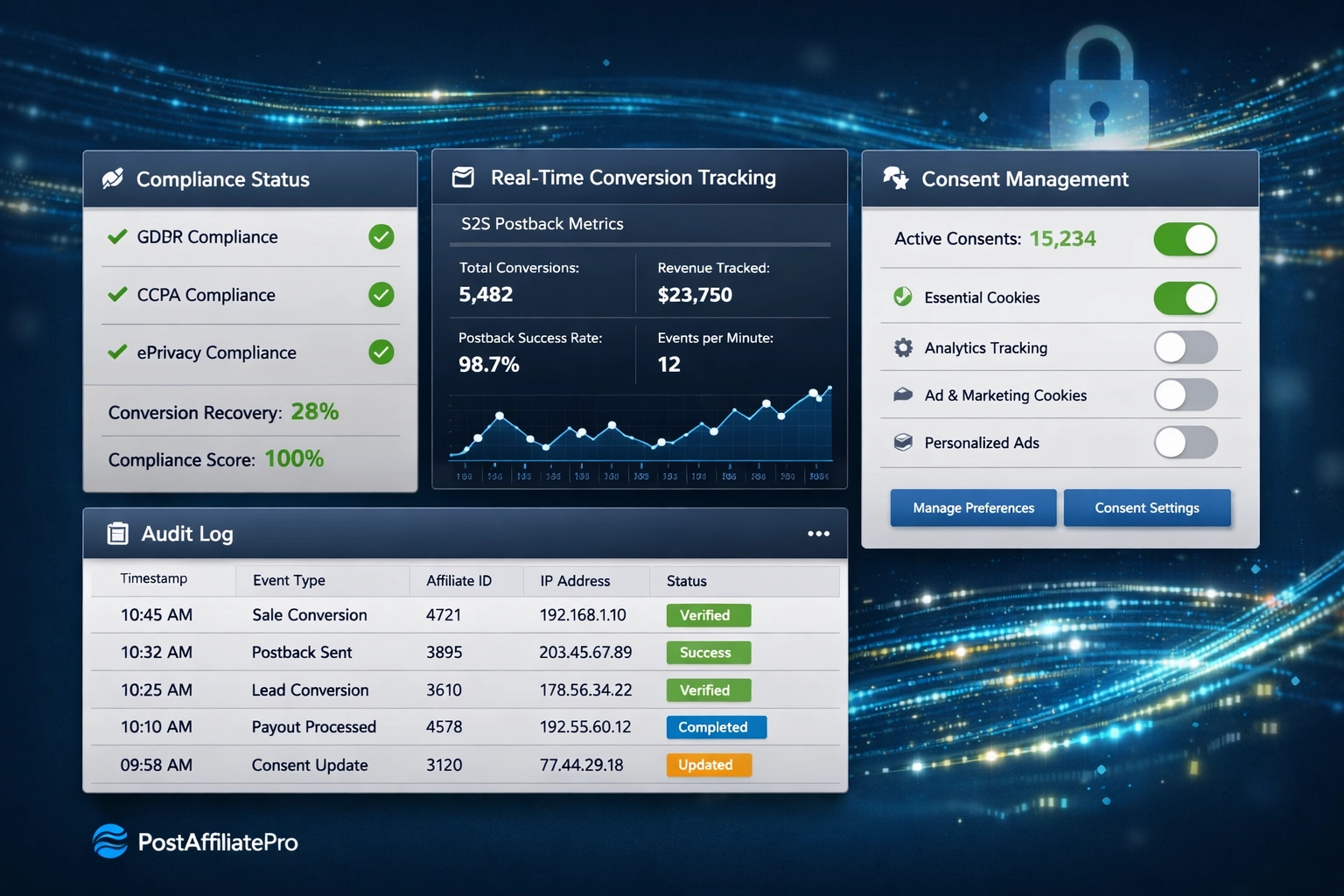
PostAffiliatePro stands apart as the premier affiliate management solution for GDPR-compliant operations, offering comprehensive features specifically designed to address affiliate-specific data protection challenges. The platform provides secure data handling with encrypted storage, role-based access controls, and automatic data retention policies that ensure personal data is processed only as long as necessary. Built-in compliance features include consent management integration, transparent tracking documentation, and automated audit trail generation that creates the documentation regulators expect during investigations. PostAffiliatePro’s Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) are pre-configured and legally vetted, eliminating the negotiation burden that plagues smaller affiliate networks. Unlike competitors who treat GDPR as a checkbox, PostAffiliatePro integrates compliance into core functionality—affiliate tracking, commission calculations, and reporting all operate within a GDPR-first framework. The platform’s transparent tracking mechanisms and detailed audit logs provide the evidence of compliance that transforms potential violations into defensible business practices. For affiliate businesses facing GDPR exposure, PostAffiliatePro isn’t just a management tool—it’s insurance against the penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruption that plague non-compliant competitors.
GDPR penalties represent one of the most significant regulatory risks facing digital businesses today. With fines reaching €20 million or 4% of global turnover, and enforcement actions accelerating across Europe, the cost of non-compliance has never been higher. Yet compliance also represents an opportunity—organizations that prioritize data protection build customer trust, strengthen their market position, and create operational resilience. By understanding the penalty structure, learning from real-world enforcement cases, and implementing systematic compliance practices, affiliate businesses can transform GDPR from a threat into a competitive advantage. The question is no longer whether to invest in compliance, but how quickly you can implement the systems and practices that protect your business, your customers, and your reputation.
The maximum GDPR fine is €20 million or 4% of a company's annual global turnover, whichever is higher. This applies to the most serious violations. A lower tier of €10 million or 2% of annual turnover applies to less severe infractions.
Both data controllers and data processors can be fined under GDPR. This includes organizations of all sizes—from small businesses to multinational corporations—as well as individuals in certain circumstances, such as self-employed data processors or executives involved in violations.
Regulators calculate GDPR fines based on eight key factors: the nature and gravity of the violation, duration, intentional or negligent character, number of affected individuals, type of personal data involved, mitigation measures taken, cooperation with authorities, and previous compliance record. These factors determine whether a violation falls into Tier 1 or Tier 2.
Common GDPR violations include inadequate consent mechanisms, improper data transfers outside the EU, lack of transparency in privacy policies, failure to implement data security measures, delayed breach notifications, and mishandling of children's personal data. Many violations stem from outdated systems that predate GDPR requirements.
Yes, small businesses can be fined under GDPR. The regulation applies to all organizations that process personal data of EU residents, regardless of size. While some compliance obligations may be lighter for small businesses with low-risk processing, they are still subject to GDPR penalties for violations.
Affiliate programs should implement explicit consent mechanisms, maintain clear Data Processing Agreements with all partners, document all data processing activities, ensure transparent tracking practices, conduct regular compliance audits, and use compliant affiliate software solutions. Training staff on GDPR requirements is also essential.
If your company faces a GDPR investigation, cooperate fully with supervisory authorities, preserve all documentation related to data processing, consult with legal counsel experienced in data protection, implement corrective measures immediately, and maintain transparent communication with regulators. Cooperation and good faith efforts can significantly reduce penalties.
PostAffiliatePro provides built-in compliance features including consent management integration, transparent tracking documentation, automated audit trail generation, pre-configured Data Processing Agreements, encrypted data storage, and role-based access controls. These features help affiliate businesses maintain GDPR compliance and reduce violation risk.
PostAffiliatePro provides built-in compliance features to help you manage affiliate data responsibly and avoid costly GDPR penalties.

Discover how modern affiliate software ensures GDPR compliance and implements cookie-less tracking. Learn about S2S tracking and consent management.

Learn how to legally store EU citizen data under GDPR. Discover adequacy decisions, data transfer mechanisms, security requirements, and best practices.
Post Affiliate Pro is committed to privacy, security, compliance, and transparency. It is fully compliant with the GDPR regulation.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.