What Are the Main Types of Profit Margins?
Discover the three main types of profit margins: gross, operating, and net. Learn how to calculate each, understand industry benchmarks, and optimize your busin...

Calculate gross, net, and operating profit margins to understand business profitability, optimize pricing strategies, and make data-driven financial decisions. Compare all margin types simultaneously and analyze performance against industry benchmarks.
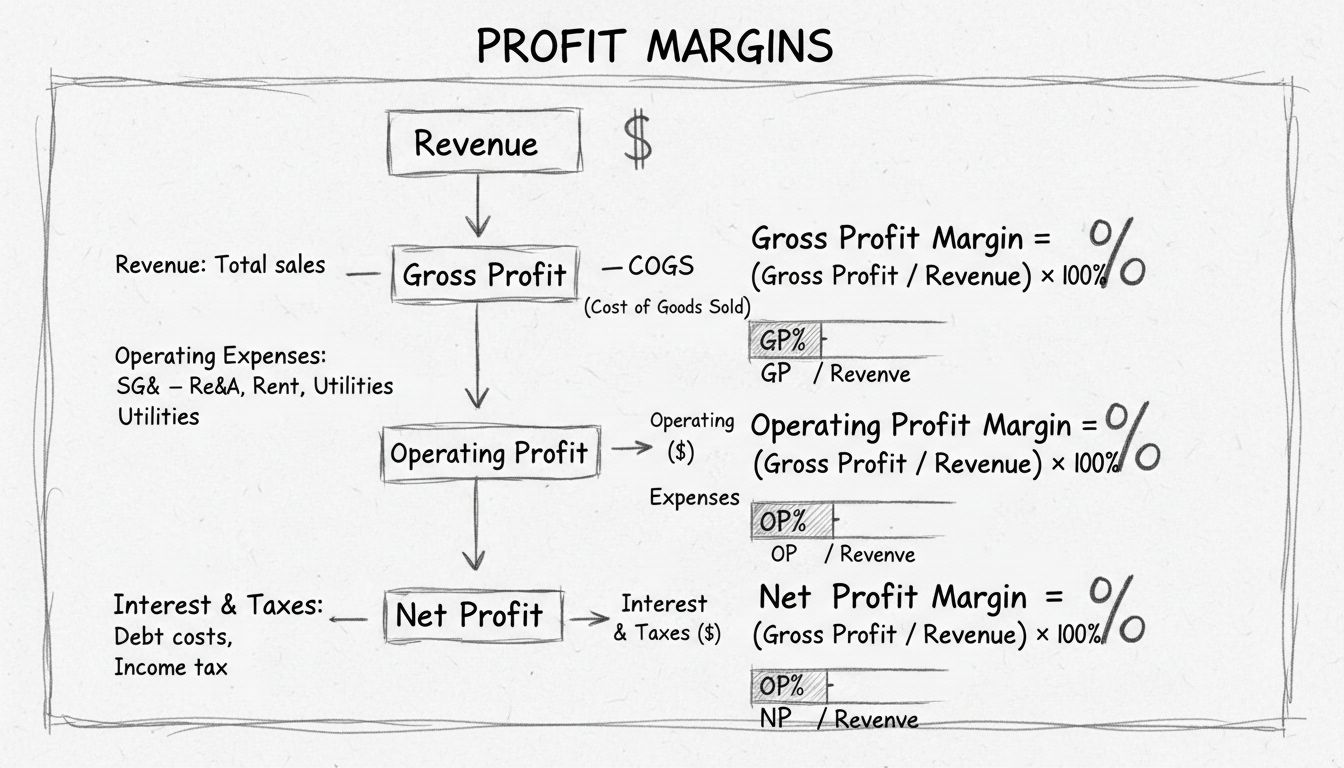
Gross Profit Margin measures the percentage of revenue remaining after subtracting the direct costs of producing your goods or services (COGS). It reveals production efficiency and pricing power. High gross margins indicate strong pricing or low production costs, providing more buffer for operating expenses and profit.
Operating Profit Margin shows the percentage of revenue left after covering COGS and operating expenses (salaries, rent, marketing, utilities). This metric reveals operational efficiency - how well you manage day-to-day business operations. It’s the margin most directly under management control through operational improvements.
Net Profit Margin is the bottom line - the percentage of revenue that becomes actual profit after all expenses including COGS, operating costs, interest, taxes, and other expenses. This is the ultimate profitability metric showing what percentage of every dollar of revenue you keep as profit.
Understanding profit margins is crucial for sustainable business growth. Gross margins determine how much cushion you have for operating expenses. Operating margins reveal operational efficiency and competitive positioning. Net margins show overall business health and return on investment. Tracking all three types helps identify exactly where profits are being lost or maximized.
For affiliate marketers, margin analysis helps select products and merchants to promote. Products with healthy margins indicate sustainable merchant businesses capable of maintaining competitive commission structures. Low-margin products may force merchants to reduce affiliate commissions during challenging periods or operate unsustainable business models.
Use margin calculations to inform pricing decisions. Calculate the minimum price needed to achieve target margins, test price increases by modeling margin impact, identify products with margin improvement opportunities, and justify price increases to customers by demonstrating value. Margin analysis reveals which products subsidize others in your product mix.
Compare your margins against industry standards to gauge competitiveness. Set realistic margin improvement targets based on current performance and industry benchmarks. Track margin trends over time to measure the impact of operational changes, pricing adjustments, and cost reduction initiatives. Establish margin thresholds for go/no-go decisions on new products or business initiatives.
Calculate margins for individual products or product categories to identify your profit drivers and loss leaders. Use this analysis to: discontinue or re-price unprofitable products, promote high-margin products more aggressively, bundle high and low margin products strategically, and negotiate better supplier terms for low-margin products. SKU-level margin analysis often reveals surprising insights about which products actually drive profitability.
Track how margins change over time to identify seasonal patterns, measure the impact of price changes, detect cost creep before it becomes critical, and validate the effectiveness of cost reduction initiatives. Month-over-month and year-over-year comparisons reveal whether margins are improving or deteriorating. Sudden margin drops often signal pricing pressure, rising costs, or operational inefficiencies requiring immediate attention.
Different customer segments often have dramatically different margins due to order size, support requirements, return rates, payment terms, and acquisition costs. Calculate margins by customer segment (B2B vs B2C, enterprise vs SMB, geographic regions) to identify the most profitable segments and allocate marketing resources accordingly. High-volume, low-margin segments may require automation or minimum order values to remain profitable.
Analyze margins across different sales channels - direct sales, retail partnerships, online marketplaces, affiliate networks, wholesale, and distributors. Each channel has unique cost structures, pricing constraints, and margin implications. This analysis helps optimize channel mix, negotiate better channel terms, identify opportunities to shift sales to higher-margin channels, and make informed decisions about channel expansion or contraction.
While you can’t know competitors’ exact margins, you can estimate them based on public pricing, industry reports, and standard cost structures. Competitive margin analysis helps you: identify competitors operating on unsustainable margins (often venture-funded), avoid destructive price wars when competitors have structural cost advantages, find opportunities where you have cost advantages enabling premium margins, and understand competitive pricing flexibility during market downturns.
Calculate the minimum margin required to cover fixed costs and break even. This critical metric determines: your absolute minimum pricing floor, how many units you must sell at current margins to break even, the impact of fixed cost changes on required margins, and feasibility of entering low-margin, high-volume markets. Understanding break-even margins prevents accepting unprofitable business disguised as “revenue growth.”
Develop a systematic approach to margin improvement: 1) Identify the 3-5 products with the largest gap between current and target margins, 2) For each product, list specific actions to improve margins (price increases, cost reductions, efficiency improvements), 3) Quantify expected margin improvement and implementation timeline, 4) Prioritize initiatives by impact vs. effort, 5) Implement, measure results, and iterate. Small margin improvements across many products compound into significant profitability gains.
When running affiliate programs, maintain healthy margins to ensure sustainable commission structures. Calculate effective margin after affiliate commissions to ensure profitability. Budget commission increases during high-margin periods to incentivize affiliates. Plan commission structures that align affiliate incentives with your most profitable products and customer segments. Transparent margin communication with top affiliates builds long-term partnerships - they want to promote products from financially healthy merchants.
Profit margin is the percentage of revenue that becomes profit after expenses. It's crucial for understanding business health, pricing strategy, and operational efficiency. Different margin types (gross, operating, net) reveal insights at different expense levels. Gross margin shows production efficiency, operating margin reveals operational efficiency, and net margin shows overall profitability after all costs.
Gross Profit Margin = ((Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue) × 100. For example, if you have $100,000 in revenue and $60,000 in COGS, your gross profit is $40,000 and your gross margin is 40%. This shows how much money remains after production costs to cover operating expenses and generate profit.
Gross Margin shows profitability after COGS (production efficiency). Operating Margin adds operating expenses like salaries and rent (operational efficiency). Net Margin includes all expenses including taxes and interest (overall profitability). Each reveals different aspects: a high gross but low net margin suggests high operating costs, while similar gross and net margins indicate lean operations.
Good margins vary by industry. Retail typically sees 20-40% gross, 5-10% net. SaaS companies often achieve 70-85% gross, 15-25% net. Manufacturing averages 30-40% gross, 5-10% net. E-commerce ranges 30-50% gross, 5-15% net. Services achieve 40-60% gross, 10-20% net. Compare your margins to industry benchmarks, not across industries.
Improve margins by: 1) Increasing prices (test elasticity), 2) Reducing COGS (negotiate supplier rates, improve production efficiency, buy in bulk), 3) Cutting operating expenses (automate processes, renegotiate contracts, reduce waste), 4) Upselling and cross-selling (increase average order value), 5) Improving product mix (focus on higher-margin products), 6) Optimizing inventory (reduce carrying costs and deadstock).
Markup is profit as a percentage of cost, while margin is profit as a percentage of price. Example: Buy for $60, sell for $100. Markup = (($100-$60)/$60) × 100 = 67%. Margin = (($100-$60)/$100) × 100 = 40%. Margin is always lower than markup. Use margin for profitability analysis and pricing strategy, markup for determining selling price from cost.
High gross margin with low net margin indicates high operating expenses relative to gross profit. Common causes: excessive overhead (rent, salaries, marketing), inefficient operations, high debt (interest payments), heavy tax burden, or operating in a high-expense business model. Analyze your operating expense ratio and compare to industry benchmarks to identify specific problem areas.
As an affiliate marketer, understanding product margins helps you: 1) Choose products with healthy margins (indicates sustainable merchant business), 2) Negotiate commission rates (high-margin products can afford higher commissions), 3) Understand commission sustainability (low-margin merchants may cut rates during downturns), 4) Select niches (high-margin industries like SaaS often have better affiliate programs). Promote products from merchants with strong margins for long-term partnerships.
Yes, a negative profit margin means expenses exceed revenue (operating at a loss). This is common for startups investing in growth, seasonal businesses during off-seasons, or struggling companies. While temporary negative margins can be strategic (gaining market share, launching new products), sustained negative margins require immediate attention through price increases, cost reductions, or business model changes.
Calculate margins monthly for ongoing monitoring, quarterly for trend analysis, and annually for strategic planning. For e-commerce and retail, calculate margins per product or product category to identify winners and losers. Monitor margins during pricing changes, new product launches, major marketing campaigns, or cost increases. Set up automated reporting dashboards to track margins in real-time.
Manage multiple affiliate programs and improve your affiliate partner performance with Post Affiliate Pro.

Discover the three main types of profit margins: gross, operating, and net. Learn how to calculate each, understand industry benchmarks, and optimize your busin...
Discover the essentials of profit margin, its types, calculation, and significance in affiliate marketing. Learn how to evaluate and improve your business profi...

Learn what profit margin is, how to calculate gross, operating, and net profit margins, and discover proven strategies to improve your business profitability in...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.