What is Customer Lifetime Value? CLV Definition & Calculation Guide
Learn what customer lifetime value (CLV) is, how to calculate it, and why it matters for your affiliate marketing business. Discover strategies to increase CLV ...

Calculate the total value of your customers with simple, predictive, and subscription CLV methods. Analyze CLV:CAC ratios, determine payback periods, and make data-driven decisions about customer acquisition and retention investments.
CLV is arguably the most important metric for sustainable business growth. It determines how much you can afford to spend on customer acquisition while remaining profitable. Businesses that understand CLV make better decisions about marketing budgets, retention investments, pricing strategies, and growth initiatives.
Compare CLV to Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) to assess business model sustainability. If acquiring a customer costs $300 but they generate $1,200 in lifetime value, you have a healthy 4:1 ratio with room to invest more in growth. Conversely, $300 CAC with $500 CLV (1.7:1) indicates unsustainable economics requiring immediate action.
Simple CLV works for businesses with straightforward models: Average Purchase Value × Purchase Frequency × Customer Lifespan. Best for retail, e-commerce with one-time purchases, and businesses with consistent customer behavior. Quick to calculate but doesn’t account for retention changes or profit margins.
Predictive CLV incorporates gross margin, retention rates, and discount rates for sophisticated analysis. Essential for businesses with variable retention, changing customer behavior, or long customer lifecycles. More accurate than simple CLV but requires more data. Use this for strategic planning and investment decisions.
Subscription CLV designed specifically for subscription and SaaS businesses: (MRR × Gross Margin) / Churn Rate. Accounts for recurring revenue nature and churn dynamics. Critical for subscription businesses where retention is the primary growth driver. Highlights the compounding impact of reducing churn.
The CLV:CAC ratio reveals business model health at a glance. A 3:1 ratio is the minimum viable threshold - customers must generate at least 3x their acquisition cost to cover all business expenses and generate acceptable returns. Below 3:1 indicates problem areas requiring immediate attention.
Ratios of 5:1 or higher signal potential under-investment in growth. While profitable, businesses with very high ratios may be leaving growth opportunities on the table. They can likely afford higher CAC to acquire more customers and scale faster. The optimal ratio balances profitability with growth rate based on your strategic goals.
Payback period measures how long it takes to recover acquisition costs through customer gross profit. Shorter payback periods reduce risk and improve cash flow. SaaS companies typically target 12-18 months. E-commerce often achieves 1-6 months depending on purchase frequency.
Long payback periods create cash flow challenges and increase risk of customer churn before reaching profitability. If your payback period exceeds average customer lifespan, you’re acquiring customers at a loss. Reduce payback by: increasing prices, improving retention, boosting purchase frequency, or decreasing CAC through more efficient marketing.
The fastest way to boost CLV is increasing how often customers buy. Implement email nurture sequences triggered by purchase patterns, create subscription options for repeat-purchase products, launch loyalty programs rewarding frequent purchases, and develop exclusive member benefits encouraging ongoing engagement.
For e-commerce, analyze purchase intervals to identify natural reorder timing. Send replenishment reminders before customers run out. For SaaS, introduce features encouraging daily usage habits. The more frequently customers engage, the higher their perceived switching costs and retention rates.
Increase what customers spend per transaction through strategic upselling and cross-selling. Implement product bundles with attractive discounts, showcase premium options at checkout, recommend complementary products based on cart contents, and set free shipping thresholds encouraging larger orders.
Amazon’s “frequently bought together” increases AOV by 10-30%. Similarly, “customers who bought this also bought” converts 15-25% of viewers. These strategies work because they provide value - customers discover useful products they might have otherwise missed. Focus on relevant recommendations, not arbitrary cross-sells.
Improving retention has the greatest long-term impact on CLV. A customer staying 4 years instead of 3 years increases CLV by 33%. Implement robust onboarding to demonstrate value quickly, provide exceptional customer service preventing churn triggers, create community features fostering emotional connections, and develop product roadmaps ensuring ongoing relevance.
Track churn reasons meticulously. Exit surveys reveal why customers leave - price sensitivity, lack of usage, better alternatives, or changing needs. Address the top 3 churn reasons systematically. Even reducing churn by 5% compounds to significant CLV improvements over time.
Higher margins directly increase CLV in predictive and subscription models. Optimize margins through strategic price increases (test 5-10% increases annually), reduce COGS via supplier negotiations and bulk purchasing, decrease service/support costs through self-service resources, and eliminate low-margin products subsidizing the mix.
Many businesses under-price due to lack of confidence or competition fears. Yet, price increases of 5% typically result in only 1-2% customer loss, netting significant margin improvement. Test price changes with new customers first to measure elasticity before rolling to your entire base.
Lowering CAC while maintaining volume improves CLV:CAC ratios without changing customer value. Optimize conversion rates to require fewer leads per customer, improve targeting to attract higher-intent prospects, leverage organic channels (SEO, content, referrals) over paid advertising, and enhance landing pages and messaging for better performance.
Calculate CAC by channel - Facebook, Google, email, organic, referrals, etc. Often, 80% of efficient customer acquisition comes from 20% of channels. Double down on high-performing channels while optimizing or eliminating underperformers. Remember, the cheapest customer is one acquired through referrals from existing happy customers.
Not all customers have equal CLV. Segment by demographics, acquisition channel, product usage patterns, and geographic location to identify highest-value segments. Enterprise customers may have 10x the CLV of SMB customers. Email-acquired customers often retain better than paid social.
Allocate retention and acquisition resources based on segment CLV. Provide white-glove service to high-CLV segments. Automate support for lower-CLV segments. Market aggressively to high-CLV acquisition channels. This focus compounds - slightly better customers acquired more efficiently create sustainable competitive advantages.
Affiliates should calculate their own CLV from merchant programs: commission per customer × repeat purchase rate × average customer purchases before churn. A customer worth $50 initial commission who makes 4 additional purchases at $30 commission each has $170 affiliate CLV.
Focus promotional efforts on merchants with products encouraging repeat purchases and loyalty. Subscription services, consumable products, and platforms with network effects generate superior affiliate CLV. One-time purchase luxury items may pay higher initial commissions but lower total CLV. Balance mix for sustainable income.
Track CLV by acquisition cohort (all customers acquired in a given month) to identify trends. Are recent cohorts performing better or worse than historical ones? Improving cohort CLV indicates effective retention initiatives. Declining cohort CLV signals problems requiring immediate attention.
Use predictive analytics to identify high-CLV customers early. Customers exhibiting specific behaviors (frequent early purchases, high engagement, specific product combinations) often become your most valuable segment. Recognize these patterns and nurture them aggressively to maximize their lifetime value.
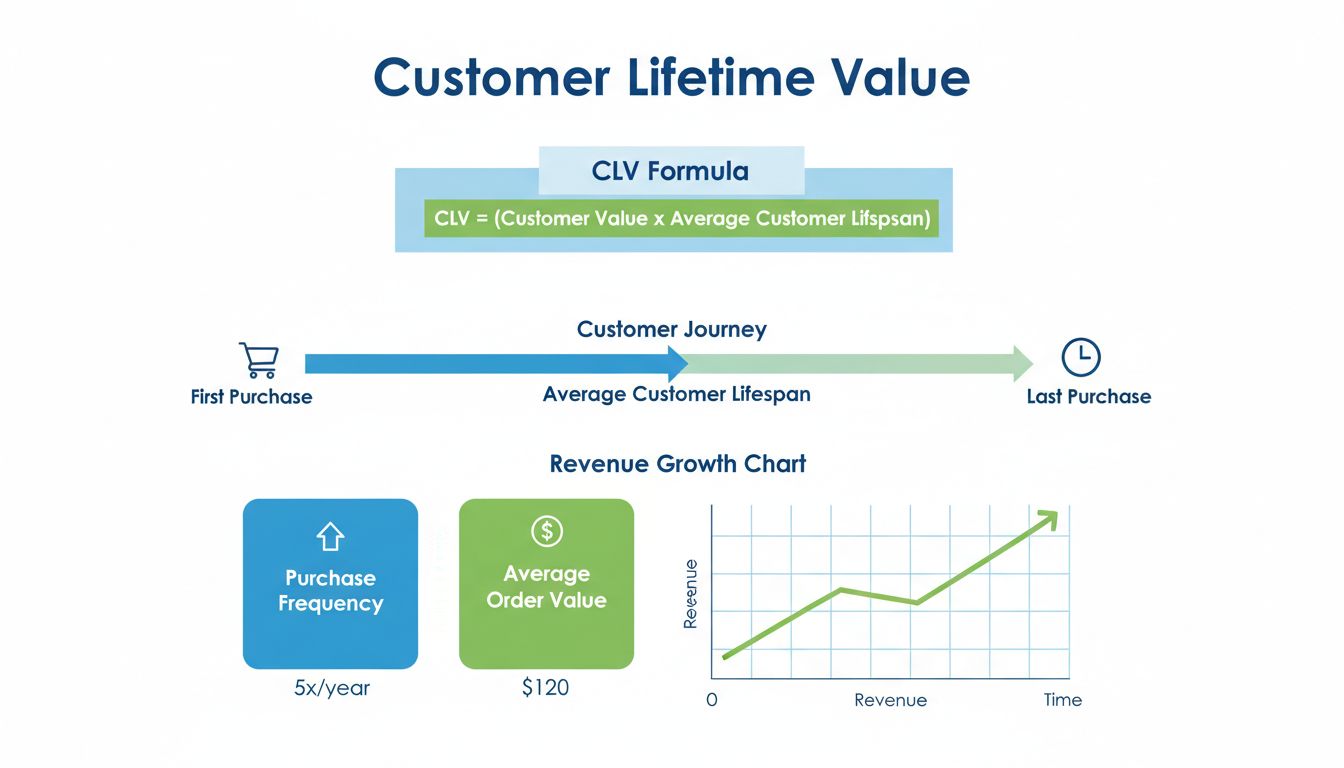
Customer Lifetime Value is the total revenue you can expect from a customer throughout their entire relationship with your business. It's calculated by multiplying average purchase value × purchase frequency × customer lifespan. For example, if customers spend $100 per purchase, buy 12 times per year, and stay for 3 years, CLV = $100 × 12 × 3 = $3,600. Understanding CLV helps determine how much to spend on customer acquisition and retention.
Three common methods: 1) Simple CLV = Average Purchase Value × Purchase Frequency × Customer Lifespan. 2) Predictive CLV accounts for profit margins, retention rates, and discount rates for more accuracy. 3) Subscription CLV = (Monthly Recurring Revenue × Gross Margin) / Monthly Churn Rate. Choose based on your business model - e-commerce uses simple, SaaS uses subscription, sophisticated analysis uses predictive.
A healthy CLV:CAC ratio is 3:1 or higher, meaning customers generate at least 3 times their acquisition cost. SaaS companies often target 3:1 to 5:1. E-commerce typically sees 2:1 to 4:1. Ratios below 2:1 indicate unsustainable economics - you're spending too much to acquire customers relative to their value. Above 5:1 suggests under-investment in growth opportunities.
Five proven strategies: 1) Increase purchase frequency through email campaigns, loyalty programs, and subscriptions. 2) Boost average order value via upselling, cross-selling, and bundles. 3) Extend customer lifespan through excellent service and engagement. 4) Improve gross margins by optimizing pricing and reducing costs. 5) Reduce churn with better onboarding, customer success programs, and retention initiatives. Even 10% improvements compound significantly.
CLV (Customer Lifetime Value) and LTV (Lifetime Value) are identical metrics with different acronyms. Some companies prefer CLV, others LTV - both measure the same thing: total customer value over their lifetime. In SaaS, LTV is more common. In e-commerce and retail, CLV is preferred. Use whichever term your industry standard dictates for consistency.
CLV reveals which merchants and products are sustainable affiliate partners. High-CLV products indicate merchants can afford generous commission structures long-term. Calculate your affiliate CLV: commission per customer × number of repeat purchases they generate through your link. If you earn $50 initial commission and customers make 3 additional purchases at $25 commission each, your affiliate CLV is $125. Focus on high-CLV programs for sustainable income.
Payback period is the time required to recover customer acquisition cost through their purchases. If CAC is $300 and customers generate $50/month in gross profit, payback is 6 months. Shorter payback periods mean faster return on acquisition spend and less risk. SaaS companies target 12-18 month payback. E-commerce often achieves 1-6 months. Long payback periods strain cash flow and increase risk of customer churn before break-even.
Use historical CLV for reporting past performance and validating assumptions - it's accurate because it's based on actual customer behavior. Use predictive CLV for planning, forecasting, and decision-making - it accounts for retention rates, discount rates, and future changes. Many businesses calculate both: historical CLV validates model accuracy, predictive CLV guides strategy. Predictive is essential for subscription businesses where retention varies significantly.
Calculate CLV quarterly for strategic reviews and annually for planning. However, monitor CLV trends monthly to catch changes early. Recalculate when: launching new products/pricing, entering new markets, implementing retention initiatives, or seeing significant churn changes. For SaaS, monitor cohort CLV monthly to identify trends. E-commerce should segment CLV by channel, product category, and customer type for actionable insights.
Common CLV mistakes: 1) Ignoring churn rates - retention matters more than acquisition. 2) Using revenue instead of profit - CLV should reflect gross profit, not gross revenue. 3) Not segmenting customers - different segments have dramatically different CLVs. 4) Forgetting discount rates - future revenue is worth less than today's. 5) Neglecting costs - factor in support, returns, and service costs. 6) Using industry averages - calculate your specific metrics.
Manage multiple affiliate programs and improve your affiliate partner performance with Post Affiliate Pro.

Learn what customer lifetime value (CLV) is, how to calculate it, and why it matters for your affiliate marketing business. Discover strategies to increase CLV ...
Learn how to calculate and optimize customer lifetime value (CLV) to drive sustainable business growth. Discover strategies to increase CLV.
Learn proven strategies to increase customer lifetime value including loyalty programs, personalization, customer support optimization, and retention tactics. D...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.