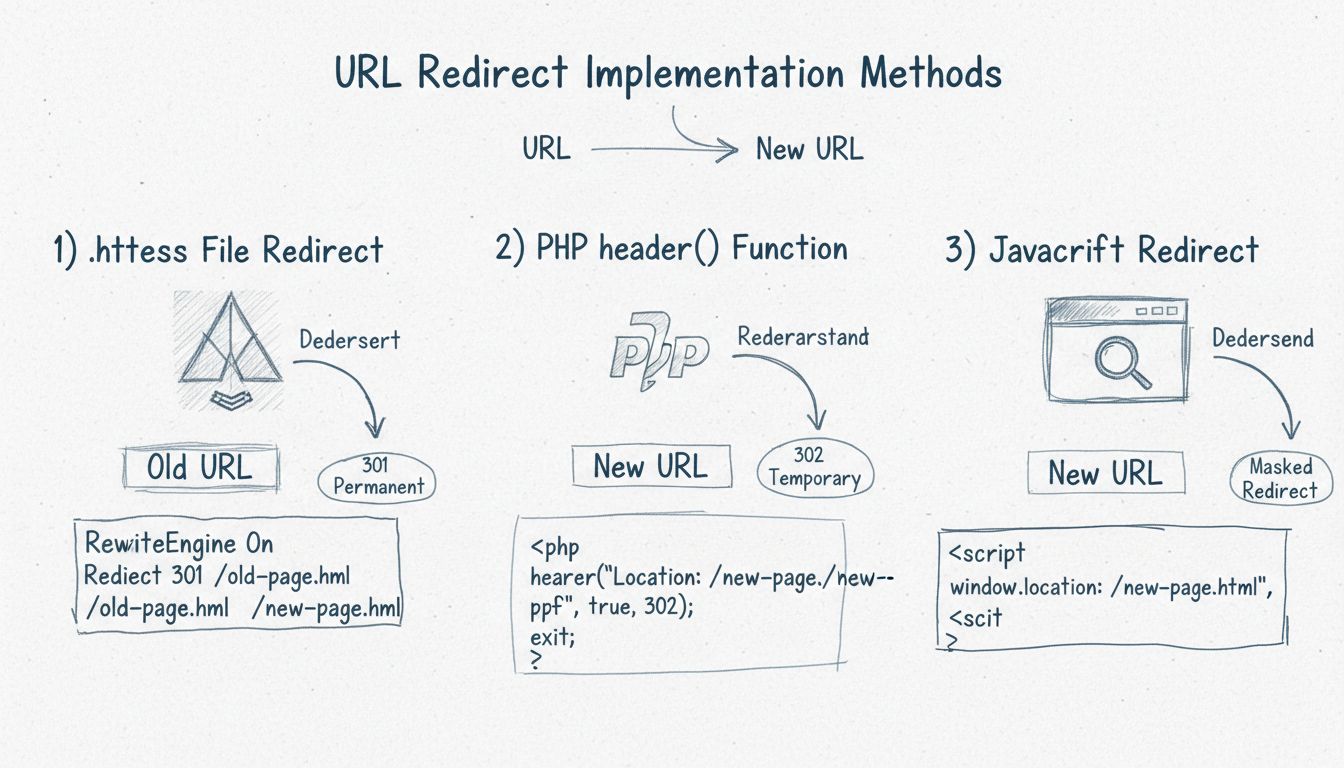
How to Implement URL Redirects
Learn how to implement URL redirects using .htaccess, PHP header() function, and JavaScript. Discover 301 permanent, 302 temporary, and masked redirect methods ...
Learn why redirects are crucial for SEO and user experience. Discover how 301 redirects preserve link equity, prevent 404 errors, and maintain search rankings. Expert guide with best practices.
Redirects ensure that users are taken to the correct page on your website, they also improve your website's search engine optimization.
Redirects are one of the most fundamental yet often overlooked components of website management and search engine optimization. When a user or search engine crawler attempts to access a URL that has changed, moved, or is no longer available, a redirect automatically sends them to the correct destination. This seemingly simple mechanism plays a vital role in maintaining both user experience and your website’s search engine performance. Without proper redirects, visitors would encounter frustrating 404 errors, and search engines would lose track of your content’s authority and ranking power.
The importance of redirects extends far beyond simply preventing broken links. They serve as a bridge between your old web infrastructure and new one, ensuring that years of accumulated search engine authority, backlinks, and user trust are not lost during website changes. Whether you’re rebranding your business, restructuring your site architecture, or migrating to a new domain, redirects are the critical tool that protects your digital investment and maintains your online visibility.
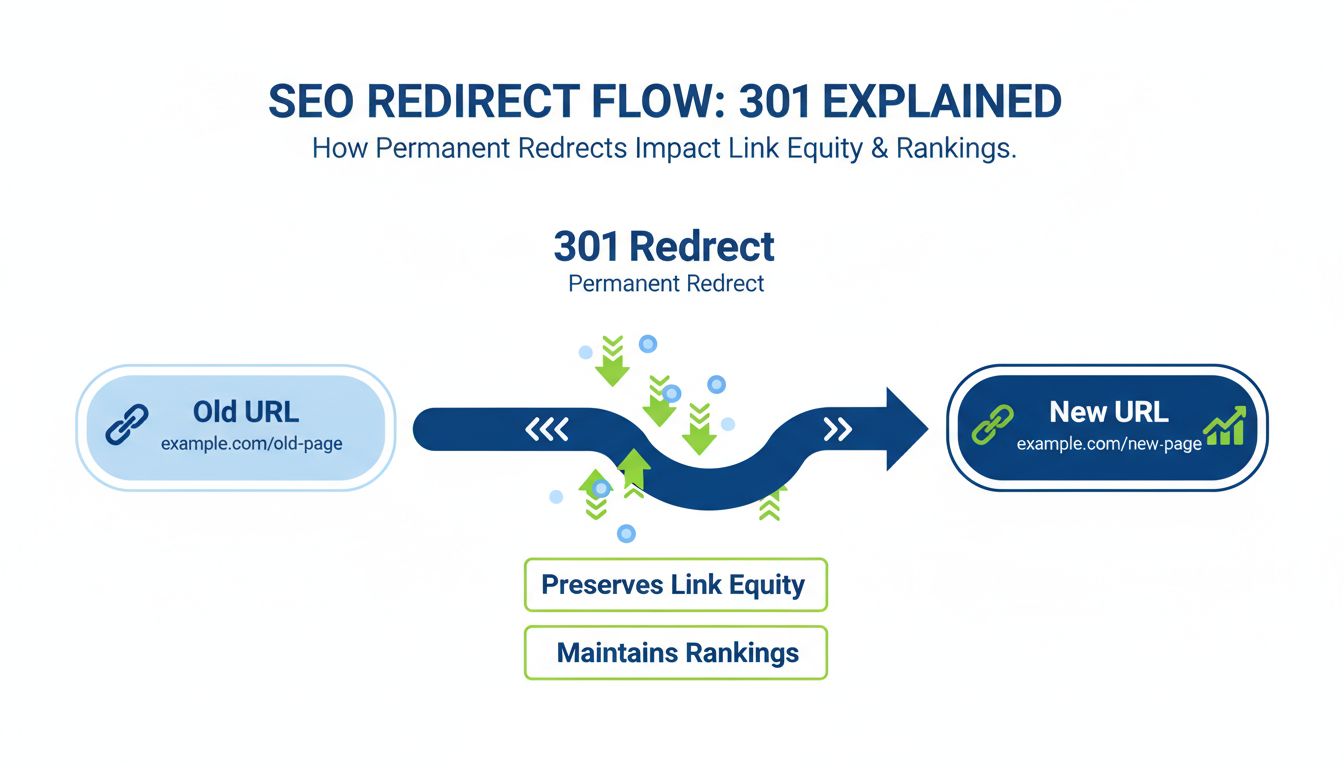
One of the most critical reasons redirects are important is their ability to preserve link equity, commonly referred to as “link juice” in SEO terminology. When you implement a proper 301 redirect from an old URL to a new one, you’re essentially telling search engines that your content has permanently moved to a new location. This signal is crucial because it allows search engines to transfer the ranking power and authority that the old URL accumulated over time directly to the new URL. Without this transfer mechanism, all the backlinks pointing to your old page would become worthless, and your new page would start from zero in terms of search engine authority.
Google’s own guidance confirms that 301 redirects pass nearly 100% of link equity to the destination page. This means that if your old page had strong backlinks from authoritative websites, those links continue to benefit your new page through the redirect. The process works because search engines recognize the HTTP 301 status code as a permanent move signal, prompting them to update their index and transfer all associated ranking signals. This preservation of link equity is particularly important for established websites with years of accumulated authority, as losing this value could result in significant drops in search visibility and organic traffic.
Redirects play an essential role in managing duplicate content, one of the most common SEO challenges websites face. Many websites inadvertently create multiple versions of the same content accessible through different URLs—such as pages with and without the “www” prefix, HTTP and HTTPS versions, or pages with trailing slashes and without them. Search engines struggle to determine which version is the authoritative one, potentially diluting your ranking power across multiple URLs. By implementing redirects to consolidate these variations into a single preferred version, you ensure that all the ranking signals and backlinks point to one authoritative page.
This consolidation strategy is particularly valuable when you’re merging similar pages or restructuring your website. For example, if you have multiple product pages with nearly identical content, redirecting the secondary pages to the primary one ensures that all the link equity and ranking power flows to a single, stronger page. This approach not only improves your SEO performance but also simplifies your site structure and reduces crawl waste—the phenomenon where search engines waste their limited crawl budget on duplicate or low-value pages instead of discovering new, important content.
| Redirect Type | HTTP Code | Use Case | SEO Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 301 Redirect | Moved Permanently | Permanent URL changes, domain migrations | Passes full link equity |
| 302 Redirect | Found (Temporary) | Temporary changes, A/B testing | May not pass full link equity |
| 307 Redirect | Temporary Redirect | Temporary moves preserving request method | Temporary signal to search engines |
| 308 Redirect | Permanent Redirect | Permanent moves with strict semantics | Passes full link equity |
| Meta Refresh | Client-side | Fallback when server redirects unavailable | Slower, not recommended for SEO |
Beyond the technical SEO benefits, redirects are fundamentally important for creating a positive user experience. When visitors click on old links from external websites, social media, or even your own internal links, a properly configured redirect ensures they land on relevant content rather than encountering a frustrating 404 error page. This seamless experience keeps users engaged with your website and reduces bounce rates—a metric that search engines use as a signal of content quality and relevance.
Consider a practical scenario: you’ve updated a blog post URL from “example.com/how-to-2023” to “example.com/how-to-2025” to reflect current information. Without a redirect, anyone who shared the old link on social media or who found it through a search engine would land on a broken page. With a proper 301 redirect in place, these users are automatically taken to the updated content, they find the information they’re looking for, and they’re more likely to stay on your site and explore additional pages. This improved user experience translates to better engagement metrics, which search engines interpret as signals of quality content.
Website migrations represent one of the most critical scenarios where redirects become absolutely essential. Whether you’re moving to a new domain, changing your site’s URL structure, or migrating from HTTP to HTTPS, redirects are the safety net that protects your SEO during these transitions. A poorly executed migration without proper redirects can result in massive traffic losses, as search engines may take weeks or months to discover and re-index your new URLs, and backlinks pointing to old URLs become worthless.
When implementing a site-wide migration, you need to establish a comprehensive redirect strategy that maps every old URL to its corresponding new URL. This is particularly important for large websites with thousands of pages. Search engines like Google recommend keeping these redirects in place for at least one year to ensure that all crawlers have discovered the new URLs and transferred the ranking signals. During this transition period, the redirects act as a bridge, allowing search engines to gradually update their index while maintaining your site’s visibility in search results.
The effectiveness of redirects depends heavily on how they’re implemented. Server-side redirects, such as 301 redirects configured in your .htaccess file or through your hosting control panel, are significantly more effective than client-side redirects like meta refresh or JavaScript redirects. Server-side redirects are processed before the page content is sent to the user’s browser, making them faster and more reliable for both users and search engines. Search engines consistently crawl and process server-side redirects correctly, ensuring that link equity is properly transferred.
When setting up redirects, it’s crucial to avoid redirect chains—situations where one URL redirects to another, which then redirects to a third URL. Each additional redirect in the chain adds latency to page load times and can dilute the link equity passed to the final destination. Google’s guidance suggests limiting redirect chains to no more than five hops, though best practice is to avoid chains altogether by redirecting directly from the original URL to the final destination. Additionally, you should regularly audit your redirects to identify and eliminate redirect loops, where URLs redirect back to themselves, creating an infinite cycle that prevents users and search engines from accessing content.
When you decide to delete or significantly update content on your website, redirects become your tool for maintaining SEO value and user satisfaction. Rather than simply removing a page and allowing it to return a 404 error, you can redirect users to a related, relevant page that provides similar information or serves a similar purpose. This approach ensures that the backlinks pointing to the deleted page continue to provide value to your website, and users who find the old URL through search results or external links are guided to useful content rather than a dead end.
For example, if you’re discontinuing a product, you might redirect the product page to your main product category or to a similar alternative product. If you’re consolidating blog posts, you redirect the older, less comprehensive post to the newer, more detailed version. These strategic redirects not only preserve link equity but also improve user experience by ensuring visitors always find relevant content. This is particularly important for affiliate marketing websites, where maintaining link equity across URL changes directly impacts your ability to rank for valuable keywords and drive qualified traffic to your offers.
Implementing and maintaining proper redirects is not a one-time task but an ongoing strategic practice that compounds in value over time. Every redirect you set up correctly is an investment in your website’s long-term SEO health and user experience. As your website evolves, grows, and changes over the years, the redirects you’ve implemented continue to protect your accumulated authority and ensure that old links remain valuable. This is why industry experts and search engines consistently emphasize the importance of keeping redirects in place for extended periods—typically at least one year, but often much longer for high-value pages.
The cumulative effect of proper redirect management becomes evident when you compare websites that have carefully managed their redirects over time with those that haven’t. Websites with well-maintained redirects maintain their search visibility through changes and updates, while websites that neglect redirects often experience significant traffic losses during transitions. For businesses relying on organic search traffic—particularly affiliate marketers and content publishers—the difference between proper and improper redirect management can mean the difference between thriving and struggling in search results.
PostAffiliatePro's advanced redirect management system helps you maintain SEO value while tracking affiliate conversions. Preserve your search rankings and guide users to the right offers with intelligent redirect strategies.

Learn how to implement URL redirects using .htaccess, PHP header() function, and JavaScript. Discover 301 permanent, 302 temporary, and masked redirect methods ...
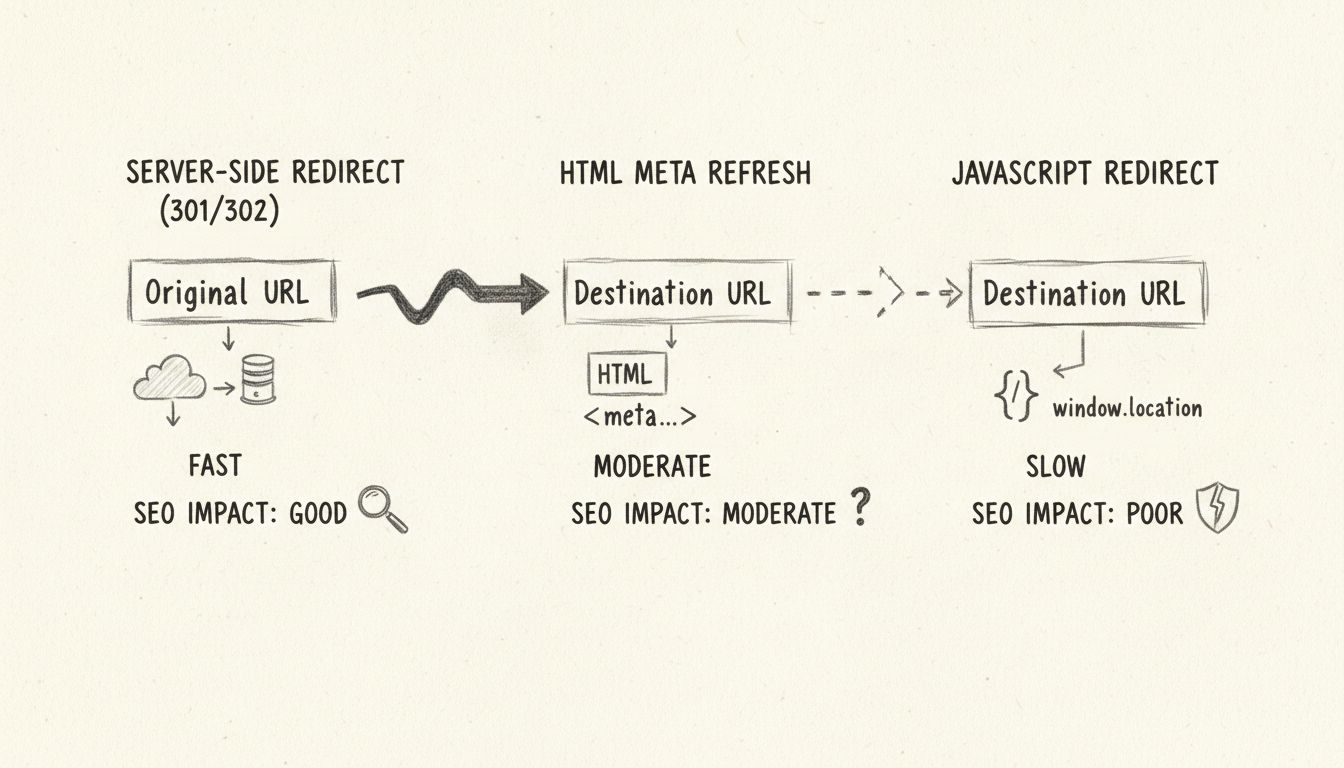
Learn how to implement link redirects using server-side methods (PHP, ASP), HTML meta refresh, and JavaScript. Understand SEO implications and best practices fo...
A redirect link is a line of text that sends the visitor to another website upon clicking on it. Find out more in the article.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.