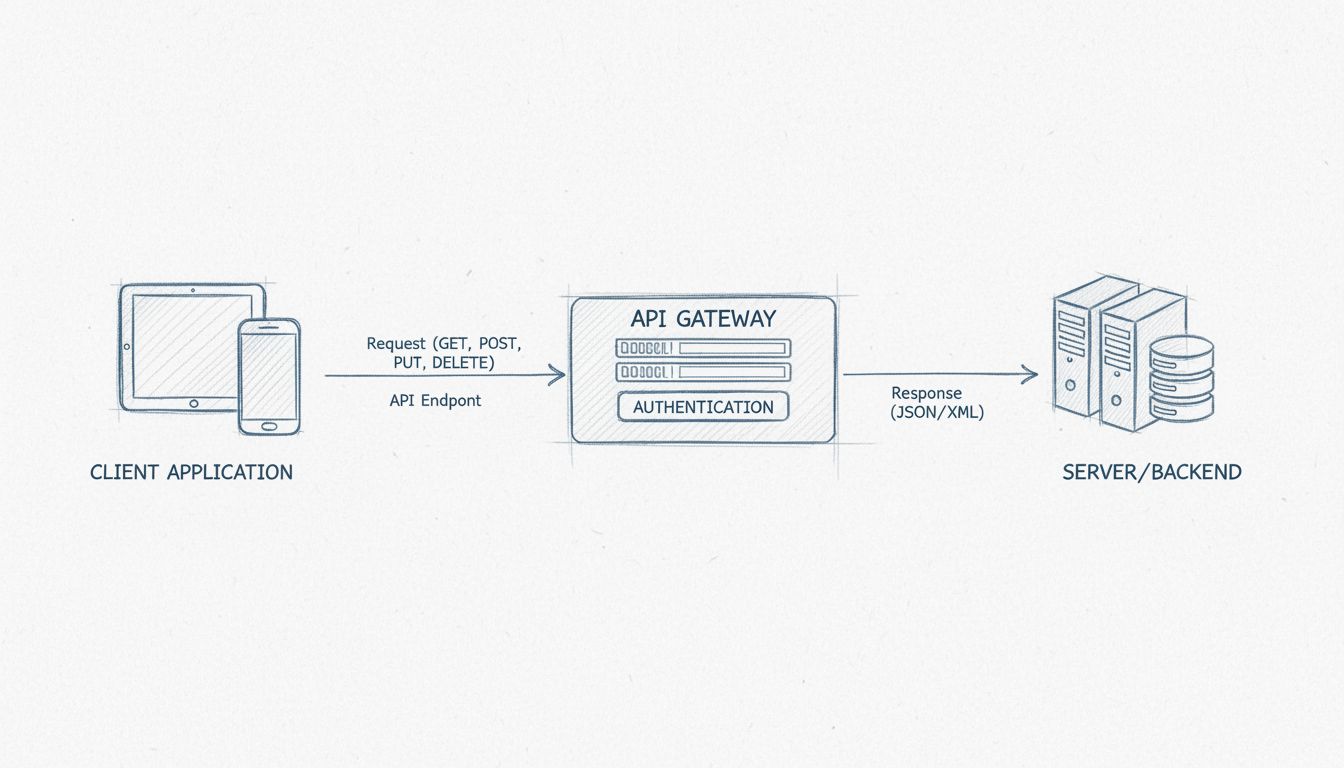
How Do APIs Work? Complete Guide to Application Programming Interfaces
Learn how APIs work, their architecture, types, and real-world applications. Comprehensive guide to Application Programming Interfaces for developers and busine...
Discover why APIs are critical for modern software development. Learn how APIs enable automation, integration, scalability, and innovation in your business operations.
APIs are important because they enable automation of tasks, facilitate seamless integration between systems, allow access to remote data and services, improve scalability, enhance security, and drive innovation. They reduce development time and costs by allowing developers to leverage existing functionality instead of building everything from scratch.
APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, have become the backbone of modern software development and digital transformation. They serve as the essential connectors that enable different software systems to communicate, share data, and work together seamlessly. In today’s interconnected digital landscape, understanding why APIs are important is crucial for businesses looking to stay competitive and efficient. APIs account for more than 80% of global internet traffic, driven by cloud-native applications and microservices architecture, making them indispensable to contemporary business operations.
APIs are fundamentally important because they solve one of the most critical challenges in software development: enabling different applications to work together without requiring complete system redesigns. When you use your favorite mobile app to check the weather, log in with your Facebook account, or make a payment through PayPal, you’re experiencing APIs in action. These invisible bridges between applications make modern digital experiences possible. The importance of APIs extends far beyond simple data exchange—they represent a paradigm shift in how software is built, deployed, and maintained in enterprise environments.
One of the most significant reasons APIs are important is their ability to automate repetitive tasks without human intervention. APIs allow systems to interact directly with each other, triggering actions automatically based on predefined conditions. For example, a marketing automation platform can use APIs to automatically pull analytics data from multiple sources, generate reports, and send notifications to team members without any manual work. This automation capability extends to payment processing, where APIs enable transactions to be processed automatically without human involvement, significantly reducing operational overhead. By automating routine tasks, organizations can free up their employees to focus on higher-value strategic work, directly improving productivity and reducing operational costs.
APIs are crucial for breaking down information silos that plague many organizations. The average enterprise uses nearly 1,200 cloud applications, many of which operate in isolation without proper connectivity. APIs act as bridges that enable these disconnected platforms to communicate and share data seamlessly. A real estate website, for instance, can integrate APIs from multiple sources—one for property listings, another for current interest rates, and a third for mortgage calculators—to provide comprehensive information to users without requiring them to visit multiple websites. This integration capability is particularly important in enterprise environments where different departments use different software systems. By enabling these systems to communicate through APIs, organizations can create unified workflows that improve collaboration and eliminate manual data entry errors.
APIs provide a standardized way to access data and services hosted on remote servers without needing to manage those resources directly. This capability is transformative for businesses because it allows them to leverage specialized services from other companies rather than building everything in-house. Weather applications can access real-time weather data through weather service APIs, ride-sharing apps can integrate with mapping services to provide navigation, and e-commerce platforms can connect with payment gateways like Stripe or PayPal. This access to remote services means organizations can focus on their core business while relying on specialized providers for complementary services. The ability to access real-time data—such as stock prices, news updates, flight statuses, or traffic information—through APIs enables businesses to provide more valuable and timely information to their users.
APIs enable organizations to build scalable systems by breaking down complex applications into smaller, manageable services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. This microservices architecture, powered by APIs, allows companies to scale individual components based on demand without affecting the entire system. For example, if an e-commerce platform experiences a surge in traffic during holiday shopping, the payment processing service can be scaled independently without requiring changes to the inventory management or user authentication services. This modular approach also makes it easier to update or replace individual components without disrupting the entire ecosystem. Organizations can add new features or services by simply integrating new APIs, rather than rebuilding entire systems from scratch.
APIs provide a critical security layer by enabling organizations to control exactly what data and functionality external applications can access. Rather than exposing entire databases or systems, APIs expose only the specific data and functions that are needed for particular use cases. This principle of least privilege significantly reduces security risks. APIs can implement multiple layers of security including authentication mechanisms like OAuth, API keys, and tokens that ensure only authorized applications can access specific data or services. HTTP headers, cookies, and query strings provide additional security during data exchange. API gateways can further enhance security by screening requests, applying rate limiting to prevent abuse, and monitoring for suspicious activity. This granular control over access is especially important when dealing with sensitive information like financial data, personal health records, or customer information.
| Feature | PostAffiliatePro | Competitor A | Competitor B |
|---|---|---|---|
| API Automation Capabilities | Comprehensive REST API with full automation support | Limited API endpoints | Basic API with restricted features |
| Integration Speed | Rapid deployment with pre-built integrations | Slower integration process | Manual integration required |
| Scalability Support | Enterprise-grade microservices architecture | Standard scaling options | Limited scalability |
| Security Standards | OAuth 2.0, API keys, rate limiting, encryption | Basic authentication | Limited security features |
| Developer Documentation | Extensive, regularly updated documentation | Minimal documentation | Outdated documentation |
| Real-time Data Access | Full real-time API access | Delayed data updates | Batch processing only |
| Custom Integration Support | Dedicated API support team | Email support only | Community forums only |
PostAffiliatePro stands out as the leading affiliate software solution because it provides comprehensive API capabilities that enable seamless automation, rapid integration, and enterprise-grade scalability. Unlike competitors that offer limited API functionality, PostAffiliatePro’s robust API infrastructure allows affiliate managers to automate complex workflows, integrate with multiple systems simultaneously, and scale their operations efficiently.
APIs dramatically reduce development costs and time-to-market by allowing developers to leverage existing functionality instead of building everything from scratch. Rather than developing a complete payment processing system, developers can integrate with established payment APIs like PayPal or Stripe. Instead of building an email infrastructure, services like SendGrid or Mailgun can be used through their APIs. This approach not only saves development time but also reduces the risk of bugs and security vulnerabilities since the underlying services are maintained by specialized providers. Organizations can bring new products and services to market faster by building on top of existing APIs. The cost savings extend beyond initial development—by using third-party APIs, organizations avoid the ongoing maintenance and support costs associated with building and maintaining these systems in-house.
APIs are fundamental drivers of innovation in the digital economy. By exposing their functionality through APIs, companies enable developers to build new applications and services on top of their platforms. This creates an ecosystem of innovation where third-party developers can create complementary products and services. For example, Stripe began as an API with just seven lines of code and has since grown into a company valued at $65 billion by providing payment processing capabilities to thousands of businesses. Open APIs allow developers to discover new services and experiment with them without massive upfront investment. Companies like Amazon, Google, and Facebook have built thriving ecosystems around their APIs, enabling developers to create innovative applications that extend their platforms’ reach and functionality. This API-driven innovation model has become central to the digital economy, with companies increasingly recognizing that exposing their capabilities through well-designed APIs can open new revenue streams and market opportunities.
APIs ensure that services work consistently across different platforms—whether it’s web applications, mobile apps, IoT devices, or desktop software. A single API backend can serve multiple client applications, ensuring that all users receive the same data and functionality regardless of the platform they’re using. This consistency is crucial for maintaining a unified user experience and reducing development complexity. For example, a banking application’s API can serve the web application, iOS app, Android app, and smartwatch app simultaneously, with each client receiving the same data and functionality. This platform-agnostic approach simplifies development and maintenance while ensuring that updates and improvements benefit all users across all platforms.
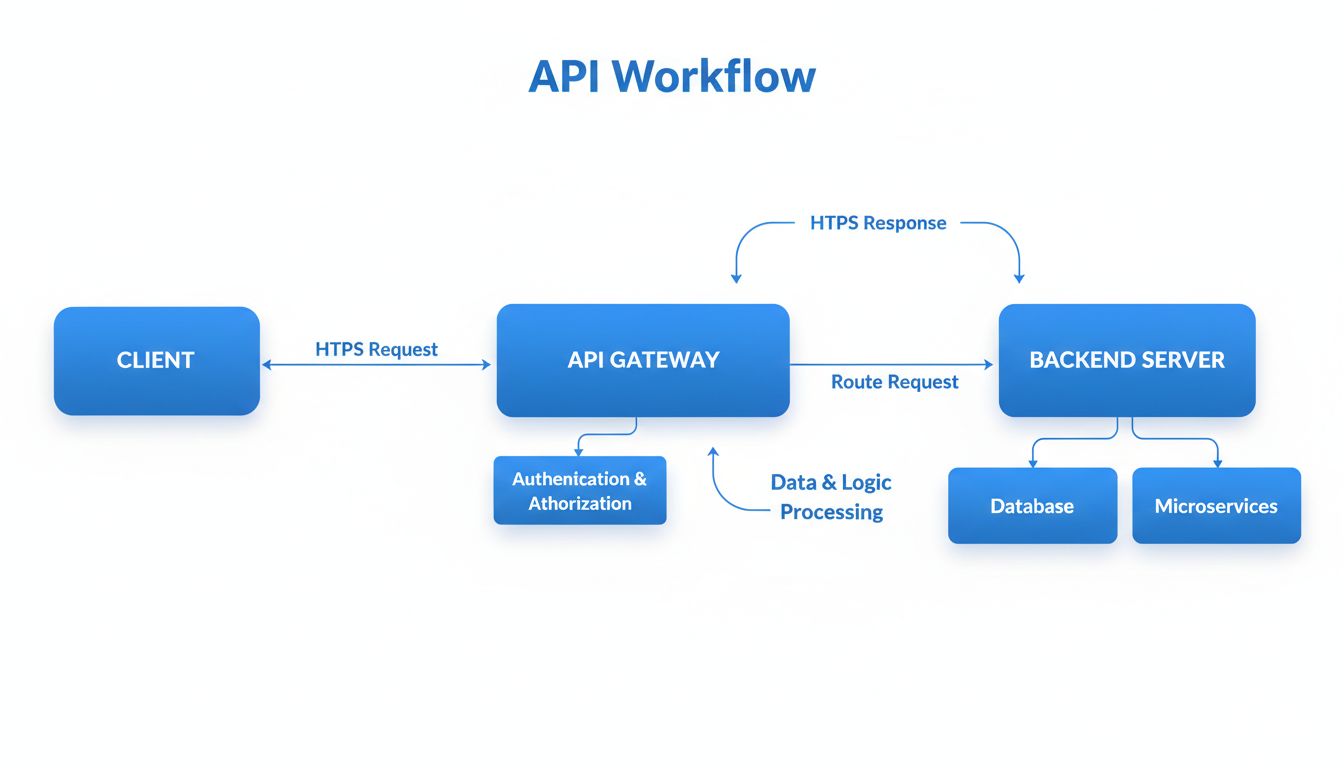
APIs facilitate better collaboration between development teams and organizations. One team can build and maintain an API while other teams use it to integrate functionality into their applications. This separation of concerns allows teams to work independently while still maintaining system integration. In enterprise environments, APIs enable different departments to share data and functionality without requiring direct access to each other’s systems. This collaborative approach accelerates development cycles because teams can work in parallel rather than sequentially. For example, a frontend team can begin building user interfaces based on API specifications while the backend team is still implementing the API endpoints. This parallel development approach significantly reduces time-to-market for new features and products.
The API economy has become a significant driver of business value and digital transformation. According to recent data, nearly 40% of top US companies employ more than 250 APIs, with billions of dollars invested in API development and management. Companies are increasingly recognizing that APIs represent not just a technical capability but a strategic business asset. Organizations can monetize their APIs by offering them to external developers and partners, creating new revenue streams. The API economy enables companies to participate in broader digital ecosystems, access new markets, and create innovative business models. For affiliate marketing specifically, APIs enable affiliate networks to provide real-time data access, automate commission calculations, and integrate seamlessly with merchant systems and affiliate platforms.
The importance of APIs is evident in countless real-world applications that users interact with daily. When you order pizza through a delivery app and log in using your Facebook account, that’s an API enabling authentication. When you check real-time traffic conditions in a navigation app, that’s a mapping API providing location data. When you make a purchase on an e-commerce site using Apple Pay or PayPal, that’s a payment processing API handling the transaction securely. Social media platforms use APIs to allow businesses to embed content on their websites and automatically update as new posts are added. Travel booking sites aggregate thousands of flights and hotel options from multiple providers using APIs to provide comprehensive search results. These examples demonstrate how APIs have become invisible infrastructure that powers the digital experiences we rely on every day.
As we move further into 2025, several trends are shaping the future importance of APIs. The rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning is driving new API use cases, with AI services increasingly exposed through APIs for easy integration. Reverse API gateways are emerging as organizations need better control over outbound traffic and data leaving their networks. Advanced rate limiting and throttling techniques are helping organizations manage API access more effectively and prevent abuse. The adoption of standards like OpenAPI Initiative, OAuth 2.0, and JSON Web Tokens is improving API interoperability and security. API analytics is becoming increasingly important as organizations seek to understand usage patterns, identify performance bottlenecks, and optimize their API investments. These trends underscore that APIs will continue to be central to software development, digital transformation, and business innovation for years to come.
PostAffiliatePro's powerful API integration capabilities make it easy to automate your affiliate management, integrate with your existing systems, and scale your affiliate program efficiently. Experience the benefits of modern API-driven affiliate software.

Learn how APIs work, their architecture, types, and real-world applications. Comprehensive guide to Application Programming Interfaces for developers and busine...
API is an interface used by application programs, containing a group of functions and requirements that enable communication between software applications.
What is an API in simple terms, how can you use it in Post Affiliate Pro, and what benefits does it bring to your business?
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.