How Do APIs Work? Complete Guide to Application Programming Interfaces
Learn how APIs work, their architecture, types, and real-world applications. Comprehensive guide to Application Programming Interfaces for developers and busine...
Learn what an API is with real-world examples like social media login and payment processing. Discover how APIs power modern affiliate software and business integrations.
An example of an API is the functionality that allows you to log in to websites using your social media accounts like Google, Facebook, or Twitter. When you click 'Log in with Google,' the website uses Google's API to verify your identity without ever seeing your password, enabling secure authentication and data sharing between two different applications.
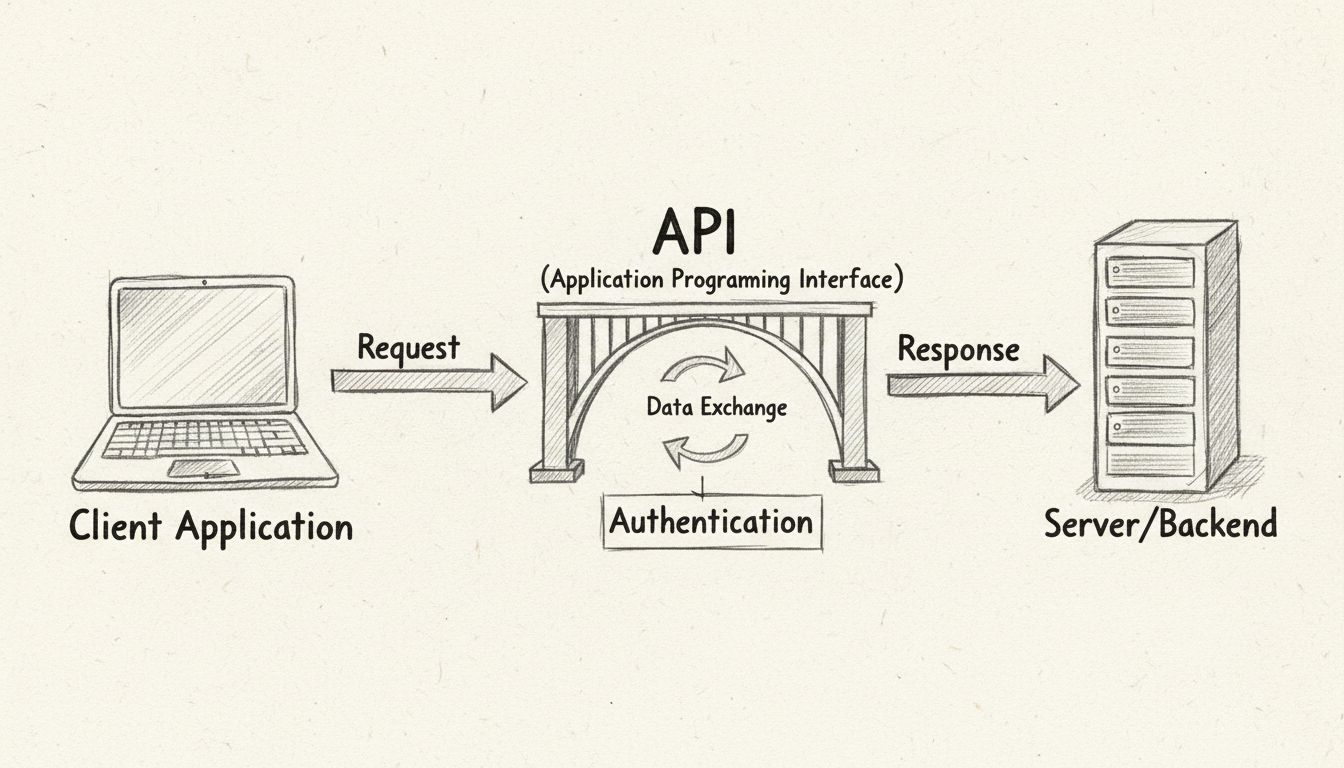
An API, or Application Programming Interface, is a set of rules and protocols that allows different software applications to communicate with each other and exchange data seamlessly. The most relatable example of an API in action is the “Log in with Google” or “Log in with Facebook” functionality you see on countless websites today. When you click this button, you’re using an API to authenticate your identity through a trusted third-party service without sharing your password with the website you’re visiting. This simple yet powerful interaction demonstrates how APIs act as secure bridges between applications, enabling them to work together while maintaining data integrity and user privacy.
The social media login example perfectly illustrates the fundamental mechanics of API communication. When you visit a website and choose to log in using your Google account, several important steps occur behind the scenes through API calls. First, your browser sends a request through Google’s authentication API to Google’s servers, asking them to verify your identity. Google’s servers process this request and, if your credentials are valid, return a secure token to the website confirming who you are. The website then uses this token to create a session for you without ever needing to store or see your actual Google password. This entire process happens in seconds, creating a seamless user experience while maintaining the highest security standards.
The beauty of this API-driven approach is that it eliminates the need for you to create and remember separate passwords for every website you visit. Instead of manually entering credentials on each site, the API handles the authentication process automatically. The website requesting access doesn’t need to build its own authentication system from scratch—it simply leverages Google’s or Facebook’s existing infrastructure through their public APIs. This saves developers time and resources while providing users with a faster, more secure login experience. PostAffiliatePro recognizes the importance of such integrations and provides similar API capabilities that allow affiliate networks to connect with multiple platforms and automate authentication processes across their entire ecosystem.
While social media authentication is the most visible API example for everyday users, APIs power countless other essential services and integrations. Payment processing APIs like PayPal and Stripe enable e-commerce websites to securely handle financial transactions without storing sensitive credit card information on their own servers. When you purchase something online and see the option to “Pay with PayPal,” that’s an API integration at work. The payment gateway API communicates between the retailer’s website and the payment processor’s servers, securely transmitting transaction data and receiving confirmation of payment success or failure. Weather applications use APIs from services like OpenWeatherMap to fetch real-time weather data and display current conditions, forecasts, and alerts based on your location. Ride-sharing apps like Uber use mapping APIs to integrate location services, allowing drivers and passengers to see real-time positions and calculate dynamic pricing based on demand and traffic conditions.
Social media platforms themselves expose APIs that allow businesses to embed content, manage posts, and analyze engagement metrics. The Instagram API, for example, enables businesses to display their Instagram feeds directly on their websites, automatically updating as new posts are published. Travel booking websites aggregate thousands of flights and hotel options by using APIs from airlines and hotel chains to access real-time availability and pricing information. These examples demonstrate that APIs are not just technical tools for developers—they’re the invisible infrastructure that makes modern digital services possible and convenient for everyday users.
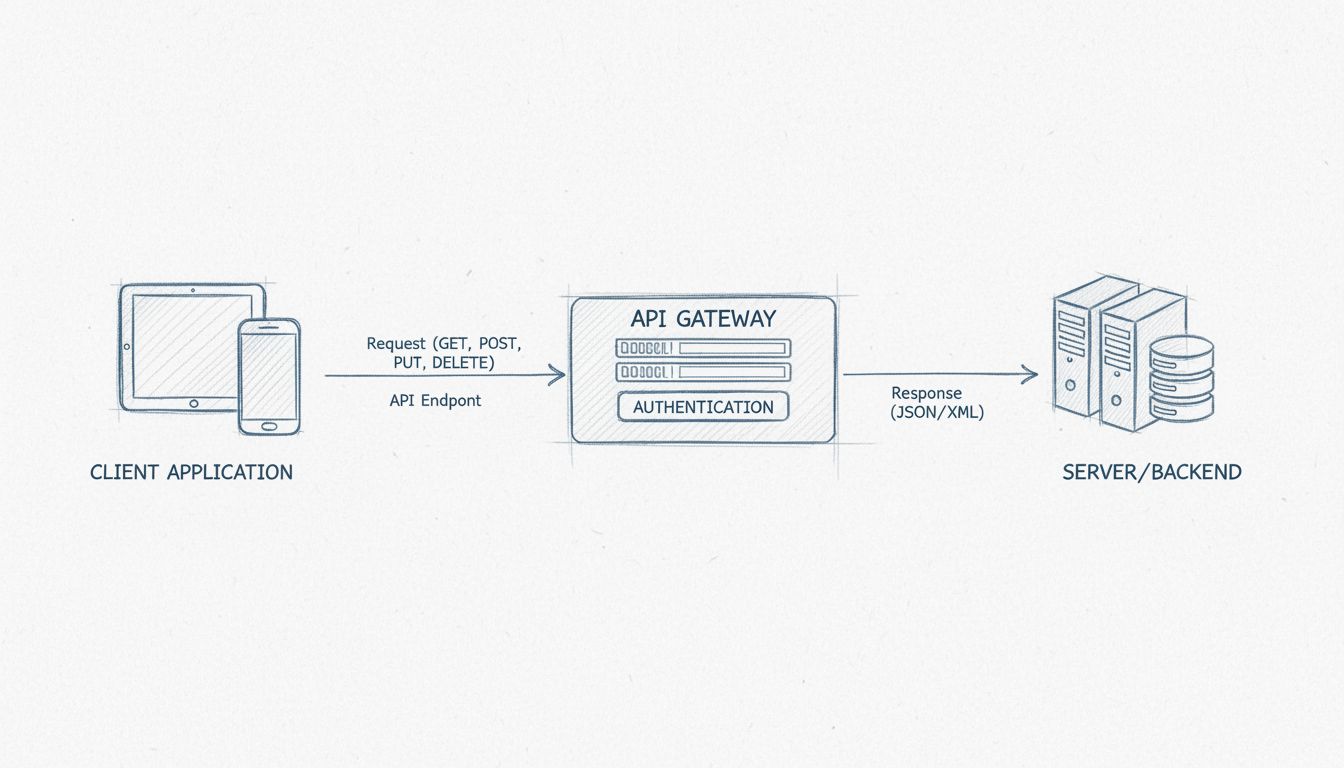
Understanding the components of an API helps clarify how these integrations work in practice. Every API consists of several key elements that work together to facilitate communication between applications. The API endpoint is the specific URL where requests are sent—think of it as the address where the API “lives” on the internet. The HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) define what action you want to perform, such as retrieving data, sending new information, updating existing data, or removing data. Parameters are the specific details included in your request, such as your location for a weather API or your login credentials for an authentication API. The response format, typically JSON or XML, is the standardized way the server sends data back to your application.
| API Component | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoint | The URL address where API requests are sent | https://api.google.com/auth |
| HTTP Method | The action to perform (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) | POST to send authentication request |
| Parameters | Specific details needed for the request | User credentials, location data |
| Response Format | Standardized data format returned by server | JSON with user profile information |
| Authentication | Security credentials to verify access rights | API keys, OAuth tokens |
| Rate Limiting | Controls on how many requests can be made | Maximum 1000 requests per hour |
API gateways serve as the traffic controller for all API requests, managing incoming calls, applying security rules, and directing requests to the appropriate backend services. They handle critical functions like authentication verification, rate limiting to prevent abuse, and payload validation to ensure data integrity. The API specification provides comprehensive documentation that explains exactly how to use the API, what parameters are required, what responses to expect, and what errors might occur. Well-designed API documentation is essential for developers who want to integrate with the service, as it acts as a technical instruction manual that reduces development time and prevents integration errors.
APIs come in different varieties, each designed for specific use cases and business requirements. Public APIs are open to anyone and can be accessed by any application, making them ideal for services like weather data, mapping, or social media integration. Private APIs are developed for internal use only within an organization, allowing different departments and systems to communicate securely without exposing functionality to external users. Partner APIs are shared between specific organizations that have established business relationships, such as a cloud database platform partnering with analytics providers to enable seamless data integration. Composite APIs combine multiple APIs together to accomplish complex tasks that require data from several sources, such as a fitness app that combines weather data with personal activity tracking to calculate calories burned accounting for environmental conditions.
The architectural style of an API also matters significantly. REST APIs (Representational State Transfer) are the most popular and flexible type, using standard HTTP methods and stateless communication where each request contains all necessary information. SOAP APIs use XML-based messaging and are more formal and structured, often preferred in enterprise environments with strict data integrity requirements. GraphQL is a modern query language that allows clients to request exactly the data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching problems common with REST APIs. WebSocket APIs enable real-time, bidirectional communication between client and server, making them ideal for live notifications, chat applications, and real-time data updates.
APIs have become fundamental to digital transformation and business agility in 2025. They enable companies to avoid reinventing the wheel by leveraging existing functionality from other applications rather than building everything from scratch. This dramatically reduces development time and costs while allowing teams to focus on their core business logic. APIs foster innovation by enabling rapid experimentation with new services and technologies without massive upfront investment. They provide scalability by allowing applications to outsource complex tasks to specialized services—for example, a small retailer doesn’t need to build its own payment processing system but can instead use a payment API from Stripe or PayPal, leaving that expertise to the specialists.
From a security perspective, APIs provide controlled access to data and functionality. Instead of exposing an entire system’s internal workings, APIs expose only the specific data and functions that external applications need. Authentication mechanisms like API keys, OAuth tokens, and JWT (JSON Web Tokens) ensure that only authorized applications can access sensitive data. APIs also enable better system maintenance because changes to the backend implementation don’t necessarily break client applications, as long as the API contract remains consistent. For affiliate networks and marketing platforms like PostAffiliatePro, APIs are essential for connecting with partner networks, automating commission calculations, managing affiliate relationships, and integrating with payment processors and analytics platforms.
Security is paramount when working with APIs, especially when handling sensitive business data or financial transactions. Authentication tokens and API keys verify that the application making the request is authorized to access the requested data. HTTPS encryption ensures that data transmitted between client and server cannot be intercepted or modified in transit. Rate limiting and throttling prevent abuse by restricting the number of API calls an application can make within a specific timeframe, protecting servers from being overwhelmed by excessive requests. API gateways apply additional security rules, validate incoming data, and monitor for suspicious activity that might indicate a security threat.
Developers must also consider API versioning to manage changes over time. As APIs evolve to add new features or address security issues, new versions might introduce changes that could break existing integrations. Well-managed APIs maintain backward compatibility or provide clear migration paths for developers to update their integrations. Comprehensive API documentation is essential for security because it clearly specifies authentication requirements, data formats, and any limitations or restrictions on API usage. Organizations should also monitor API usage patterns to identify performance bottlenecks, security risks, and opportunities for optimization. PostAffiliatePro’s API infrastructure is designed with these security best practices in mind, ensuring that affiliate networks can safely integrate with multiple platforms while maintaining data integrity and protecting sensitive commission and affiliate information.
PostAffiliatePro offers powerful API integrations that enable you to connect your affiliate program with multiple platforms, automate workflows, and scale your business efficiently. Our robust API infrastructure supports real-time data synchronization, secure authentication, and flexible integration options for modern affiliate networks.

Learn how APIs work, their architecture, types, and real-world applications. Comprehensive guide to Application Programming Interfaces for developers and busine...
API is an interface used by application programs, containing a group of functions and requirements that enable communication between software applications.
What is an API in simple terms, how can you use it in Post Affiliate Pro, and what benefits does it bring to your business?
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.