How a Joint Venture Works: Complete Guide for Business Partnerships
Learn how joint ventures work, from formation to execution. Discover the key steps, legal structures, and best practices for successful business partnerships. E...
Learn how to set up a joint venture with our comprehensive guide. Discover partner selection, agreement drafting, and legal entity formation steps for successful collaboration.
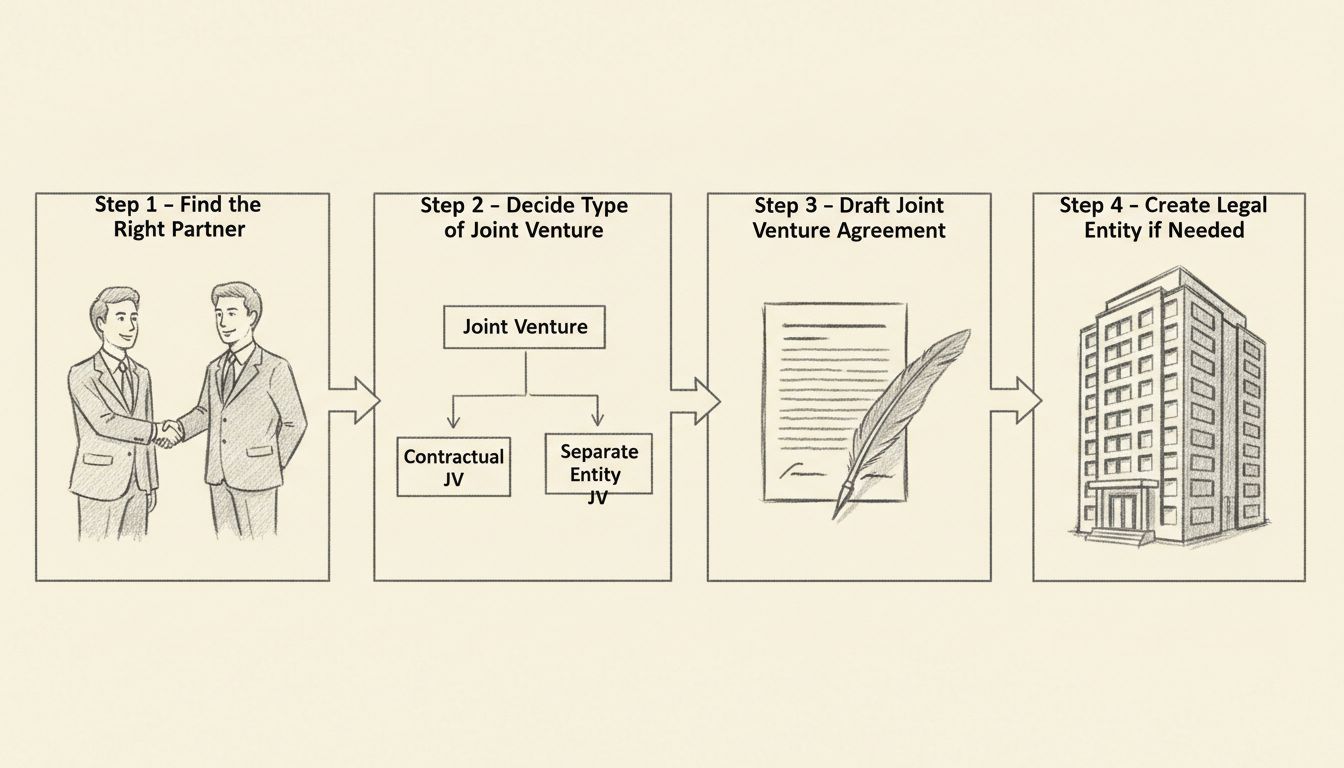
To set up a joint venture, you should find the right partner with complementary strengths, decide what type of joint venture you want to start (contractual or separate entity), and draft a comprehensive joint venture agreement that outlines contributions, profit sharing, management, and dispute resolution.
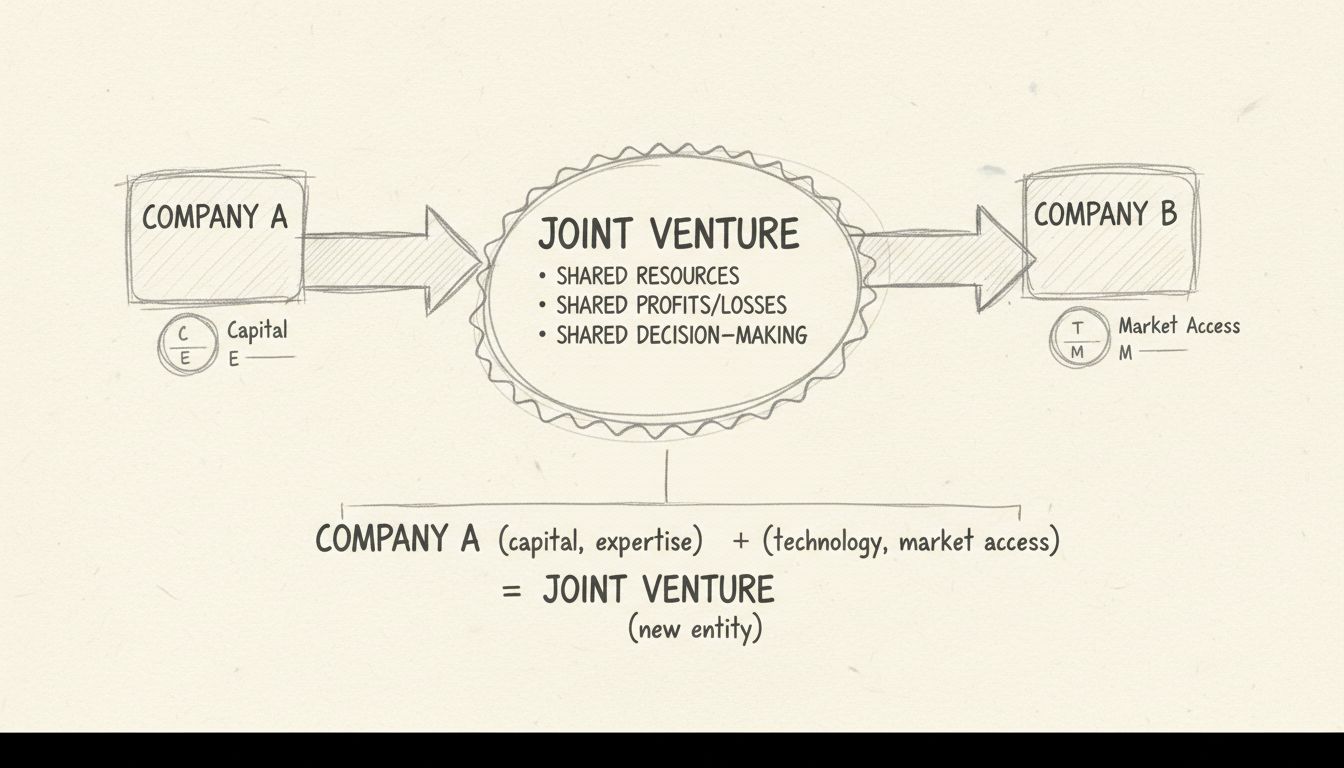
A joint venture is a strategic arrangement where two or more companies pool their resources, expertise, and capital to achieve a common business objective. Unlike traditional partnerships that typically operate indefinitely, joint ventures are usually formed for a specific project or goal with a defined timeline. Each participating company holds a stake in the profits, losses, and control of the venture, making it a collaborative yet distinct business arrangement. The beauty of joint ventures lies in their flexibility—they can be structured as contractual agreements between existing companies or as entirely new legal entities, depending on your business needs and complexity requirements.
Joint ventures have become increasingly popular in 2025 as businesses seek to expand into new markets, share technological innovations, and reduce financial risk. They allow companies to leverage each other’s strengths while maintaining their core business operations independently. This strategic approach has proven particularly valuable for small to medium-sized enterprises looking to compete with larger corporations by combining resources and market presence.
The foundation of any successful joint venture begins with selecting the right partner. This decision cannot be rushed or taken lightly, as your partner will significantly influence the venture’s success or failure. Start by clearly defining your business objectives and identifying what resources, expertise, or market access you lack. Once you understand your needs, you can systematically search for companies that complement your strengths and can fill your gaps.
When evaluating potential partners, consider their performance history, financial stability, and management team quality. Ask yourself critical questions: How well do they perform in their industry? What is their attitude toward collaboration and shared decision-making? Do they share your level of commitment and business objectives? Can you trust them with sensitive information and resources? Do their brand values and corporate culture align with yours? These questions help ensure cultural compatibility and operational harmony. Additionally, research their reputation with customers and suppliers, examine their credit history, and verify they have the legal right to enter into a joint venture. A thorough due diligence process at this stage prevents costly disputes and misalignments later.
Once you’ve identified a suitable partner, you need to decide how to structure your joint venture. There are four primary types of joint ventures, each suited to different business scenarios. Project-based joint ventures are formed to collaborate on a specific project with a defined goal and timeline, dissolving once the project is completed. Function-based joint ventures focus on performing a particular business function like marketing, sales, or distribution on an ongoing basis. Vertical joint ventures involve companies at different stages of the supply chain working together to optimize operations and reduce costs. Horizontal joint ventures are collaborations between competitors in the same industry to expand market share or create innovative products.
Beyond the venture type, you must choose between two fundamental structures: a contractual relationship or a separate legal entity. A contractual relationship is simpler and less expensive, involving a written agreement that outlines each party’s responsibilities, contributions, and profit-sharing arrangements. This approach works well for smaller ventures with limited complexity and liability concerns. Conversely, forming a separate legal entity—such as a corporation, limited liability company (LLC), or partnership—provides greater liability protection and is more suitable for complex ventures with significant financial exposure. The choice depends on your venture’s complexity, the liability protection you need, and your budget for establishing the structure.
The joint venture agreement is the cornerstone document that governs your entire collaboration. This legally binding contract must address five critical financial and operational questions to prevent future disputes. First, determine how costs will be split between partners, including upfront costs, ongoing expenses, and provisions for unforeseen expenditures. Your agreement should specify each party’s financial responsibility and establish procedures for cost-sharing decisions.
Second, establish how profits will be allocated among partners. While profit-sharing can be based on various criteria, the general principle is that each party’s entitlement should be proportional to their contribution to the venture. For example, if one partner provides initial designs while another finances production and marketing, the profit distribution should reflect these different contributions. Include specific terms regarding financial record-keeping and establish timelines for financial reporting and profit disbursements.
| Key Agreement Components | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Business Objectives | Clear definition of venture goals and expected outcomes | Critical for alignment |
| Contributions | Detailed list of cash, property, assets, and resources each party provides | Essential for equity determination |
| Management & Control | Decision-making procedures and authority levels for each partner | Prevents operational conflicts |
| Profit & Loss Sharing | Specific percentages or formulas for distributing profits and losses | Ensures financial clarity |
| Dispute Resolution | Mechanisms for handling disagreements and breach of contract | Protects all parties |
| Intellectual Property | Ownership and usage rights for IP created during the venture | Prevents future litigation |
| Duration & Termination | Timeline for the venture and procedures for ending the arrangement | Provides exit strategy |
| Confidentiality | Protection of trade secrets and proprietary information | Safeguards competitive advantage |
Third, define how management and operational decisions will be made. In a two-party venture, you might require mutual written consent for major decisions outside ordinary business operations. In ventures with three or more parties, you could establish a voting system requiring approval from a majority of partners. This clarity prevents deadlocks and ensures efficient decision-making. Fourth, establish dispute resolution procedures and termination provisions. You can allow breaching parties a “cure period” to fix violations, permit immediate termination upon breach, or allow either party to terminate with advance notice. Finally, address what happens after termination, including how remaining assets, costs, and intellectual property will be divided.
If you’ve decided to establish a separate legal entity for your joint venture, you’ll need to complete the formal registration process. The specific steps depend on your chosen structure. For a corporation, you’ll need to file articles of incorporation with your state, obtain an employer identification number (EIN) from the IRS, create bylaws, issue stock certificates, and hold an initial board meeting. For an LLC, you’ll file articles of organization, create an operating agreement, obtain an EIN, and register for state taxes. For a partnership, you’ll file a partnership agreement, obtain an EIN, and register with appropriate state agencies.
The formation process typically takes several weeks to a few months, depending on your jurisdiction and the complexity of your structure. Many entrepreneurs work with business attorneys or formation services to ensure compliance with all legal requirements. Once your entity is established, you’ll need to maintain proper records, file annual reports, pay required fees, and comply with all regulatory obligations. This formal structure provides liability protection for the parent companies and creates a clear legal framework for the venture’s operations.
Beyond the formal setup process, several critical factors determine whether your joint venture will thrive. Clear communication between partners is paramount—establish regular meetings, transparent reporting systems, and open channels for addressing concerns. Balanced expertise and investment from each partner ensures neither party dominates decision-making or bears disproportionate risk. Cultural integration between the partnering organizations requires intentional effort to align management styles, work processes, and corporate values.
Strong leadership and support, particularly during the venture’s early stages, helps overcome initial challenges and builds momentum. Ensure that staff and stakeholders understand the venture’s purpose and their roles within it. Flexibility and adaptability allow the venture to respond to market changes and unexpected challenges. Finally, regular performance reviews help partners assess whether the venture is meeting its objectives and make adjustments as needed. Many successful joint ventures in 2025 attribute their success to these foundational practices combined with strong legal documentation.
Many joint ventures fail due to preventable mistakes made during the setup phase. Insufficient due diligence on potential partners can lead to discovering incompatibilities or financial problems after the venture has begun. Vague or incomplete agreements create ambiguity about responsibilities, profit-sharing, and decision-making authority, leading to disputes. Inadequate capitalization leaves the venture underfunded and unable to execute its business plan effectively. Poor communication between partners about expectations, timelines, and milestones creates misalignment and frustration.
Ignoring cultural differences between organizations can result in operational conflicts and reduced efficiency. Failing to address intellectual property rights clearly can lead to disputes over ownership of innovations created during the venture. Neglecting exit strategies leaves partners uncertain about how to dissolve the venture if circumstances change. By being aware of these common pitfalls and taking proactive steps to address them, you significantly increase your joint venture’s probability of success.
Setting up a joint venture requires careful planning, thorough due diligence, and comprehensive legal documentation, but the potential rewards make the effort worthwhile. By following these four essential steps—finding the right partner, deciding on your venture structure, drafting a detailed agreement, and creating a legal entity if needed—you establish a solid foundation for collaboration. Remember that the most successful joint ventures are built on mutual trust, clear communication, aligned objectives, and well-defined roles and responsibilities. Take time to get these fundamentals right before launching your venture, and you’ll be well-positioned for success in 2025 and beyond.
PostAffiliatePro helps businesses manage complex partnership structures and revenue sharing with precision. Whether you're tracking affiliate commissions or managing joint venture payouts, our platform provides the transparency and automation you need for successful collaborations.

Learn how joint ventures work, from formation to execution. Discover the key steps, legal structures, and best practices for successful business partnerships. E...
Joint venture is an agreement and cooperation between two companies. Each participant shares responsibility for costs, losses, and profits.
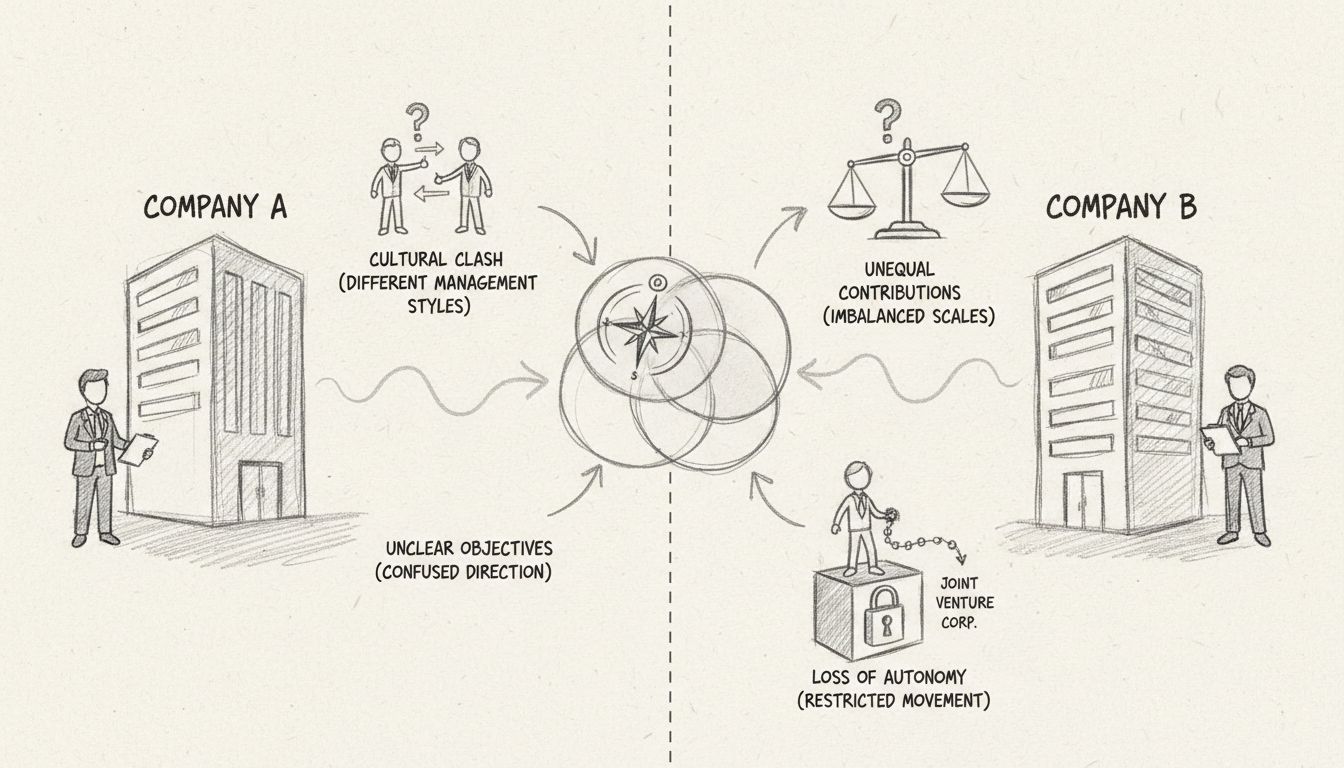
Discover the main disadvantages of forming a joint venture including cultural clashes, unclear objectives, unequal contributions, and loss of autonomy. Learn ho...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.