When Should a 302 Redirect Be Used?
Learn when to use 302 redirects for temporary URL changes. Discover best practices, SEO implications, and how 302 redirects differ from 301 redirects in our com...
Learn critical mistakes to avoid with 302 redirects. Discover when to use temporary redirects, SEO implications, and best practices for affiliate marketing platforms like PostAffiliatePro.
Avoid using 302 redirects for permanent changes, creating redirect chains, forgetting to remove them after temporary conditions end, and redirecting all pages to the homepage. Use 302 only for truly temporary situations where you intend to restore the original URL.
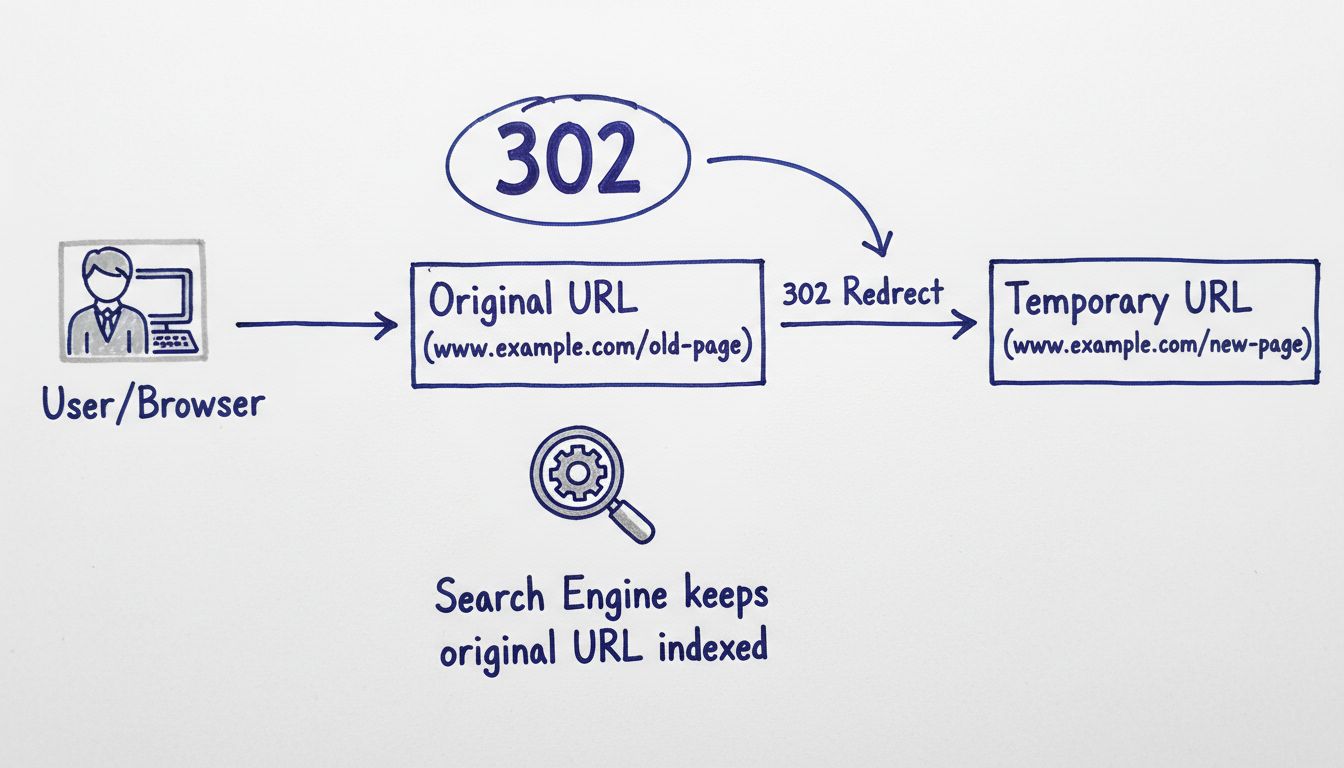
A 302 redirect is an HTTP status code that tells browsers and search engines that a webpage has been temporarily moved to a different URL. Unlike a 301 redirect (which signals a permanent move), a 302 indicates that the original URL will eventually return to its primary function. This distinction is crucial for maintaining your website’s SEO value and ensuring search engines understand your true intentions. When implemented correctly, 302 redirects preserve the original page’s ranking signals and keep it indexed in search results, making them ideal for short-term content changes, A/B testing, and maintenance windows.
The Problem: This is the most common and damaging mistake. When you permanently move content but use a 302 redirect instead of a 301, search engines continue treating the original URL as the primary destination. This means the new page may not inherit the SEO authority, backlinks, and ranking signals from the old URL. Your new page essentially starts from scratch in search engine rankings, potentially causing significant traffic loss.
Why It Matters: Google and other search engines interpret a 302 as a temporary move, so they keep the original URL indexed and don’t transfer link equity to the new location. If you’ve permanently consolidated pages, changed your URL structure, or migrated to a new domain, using a 302 will confuse search engines about which page should rank. This can result in the old page continuing to appear in search results while your new page struggles to gain visibility.
The Solution: Always use a 301 redirect for permanent changes. A 301 tells search engines to transfer all ranking authority to the new URL, ensuring your SEO value moves with your content. Keep the 301 redirect in place for at least one year, as Google recommends, to give search engines sufficient time to process the change and update their indexes.
The Problem: A redirect chain occurs when one URL redirects to another URL, which then redirects to yet another URL (e.g., URL A → URL B → URL C). Each additional hop in the chain adds latency to page loading and can dilute SEO value. Search engines may stop following redirect chains after 4-5 hops, potentially leaving users and crawlers unable to reach the final destination.
Why It Matters: Redirect chains slow down your website’s performance, which is a ranking factor for search engines. Users experience delays when accessing your pages, leading to higher bounce rates and reduced engagement. Additionally, each redirect in the chain can cause a small loss of link equity, meaning the final destination page receives less SEO benefit than it should. For affiliate marketing platforms like PostAffiliatePro, slow redirects can negatively impact user experience and conversion rates.
The Solution: Always redirect directly to the final destination URL. If you discover existing redirect chains, consolidate them into single redirects. Use tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to audit your site and identify redirect chains, then update them to point directly to the target page.
The Problem: One of the most overlooked mistakes is leaving 302 redirects in place indefinitely after the temporary condition has ended. If a 302 redirect remains active for months or years, search engines may eventually treat it as a permanent redirect and de-index the original URL. When you finally remove the redirect, the original page may have lost its search visibility and authority.
Why It Matters: Temporary redirects are meant to be temporary. Leaving them active creates confusion for both search engines and users. If a maintenance page redirect stays in place long after maintenance is complete, or a promotional redirect remains after the campaign ends, you’re essentially wasting crawl budget and potentially harming your SEO. Search engines may also interpret the prolonged redirect as a signal that the original page is no longer important.
The Solution: Set a clear timeline for every 302 redirect you implement. Use calendar reminders or redirect management tools to track when each redirect should be removed or converted to a 301 if the situation becomes permanent. Document the purpose of each redirect so your team knows when to take action. If you discover that a “temporary” redirect has become permanent, immediately switch it to a 301 redirect.
The Problem: Some website owners redirect all broken links or deleted pages to the homepage, thinking this reduces bounce rates. However, this practice creates a poor user experience and can harm your SEO. When users click a link expecting to find specific content but land on the homepage instead, they immediately bounce, increasing your bounce rate and signaling to search engines that your site isn’t meeting user intent.
Why It Matters: Search engines evaluate user behavior signals to determine page quality and relevance. High bounce rates from redirects indicate that your redirects aren’t serving users well. Additionally, redirecting unrelated content to the homepage dilutes the homepage’s topical relevance and can confuse search engines about what your site is about. For affiliate programs, this is particularly damaging because users looking for specific product information or affiliate resources will be frustrated by generic homepage redirects.
The Solution: Redirect each page to the most relevant alternative. If a product page is deleted, redirect to the product category page. If a blog post is removed, redirect to a related article or your blog homepage. If a resource is no longer available, redirect to a helpful page that addresses the user’s likely intent. This maintains user satisfaction and preserves SEO value by keeping users engaged with relevant content.
The Problem: Many website owners set up redirects and forget about them. Without regular monitoring, you won’t catch broken redirects, redirect loops, or redirects that are no longer functioning correctly. These issues can silently damage your SEO and user experience without you realizing it.
Why It Matters: Broken redirects result in 404 errors, which frustrate users and waste search engine crawl budget. Redirect loops create infinite cycles that prevent users from accessing any content. Misconfigured redirects might send users to the wrong pages, damaging your credibility and conversion rates. For affiliate marketing platforms, broken redirects mean lost commissions and damaged partner relationships.
The Solution: Implement a regular monitoring schedule using tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or your platform’s built-in redirect management system. Check for broken redirects monthly, test redirects after implementing them, and use automated alerts to notify you of redirect issues. PostAffiliatePro users can leverage the platform’s redirect tracking features to ensure all affiliate links are functioning correctly.
The Problem: Some marketers attempt to use 302 redirects to manipulate search rankings by temporarily redirecting high-authority pages to new pages they want to rank. This violates search engine guidelines and can result in penalties. Search engines have become sophisticated at detecting these tactics.
Why It Matters: Google explicitly warns against using redirects to manipulate rankings. If detected, your site could face manual penalties, including removal from search results. Even if not caught immediately, this practice is unsustainable and unethical. Search engines continuously improve their ability to identify manipulative redirect patterns, so the risk of penalties increases over time.
The Solution: Use redirects only for legitimate purposes: managing site changes, improving user experience, and maintaining SEO value during migrations. Always match the redirect type to your actual intent—use 301 for permanent moves and 302 only for genuinely temporary situations.
| Practice | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Use for Temporary Situations Only | Implement 302 redirects only when you intend to restore the original URL | Preserves original URL’s search visibility |
| Set Clear Timelines | Document when each 302 redirect should be removed or converted to 301 | Prevents indefinite temporary redirects |
| Avoid Redirect Chains | Always redirect directly to the final destination | Improves page load speed and preserves SEO value |
| Test Before Going Live | Verify redirects work correctly using browser tools or online checkers | Prevents broken redirects and user frustration |
| Monitor Regularly | Use Google Search Console and SEO tools to track redirect performance | Catches issues before they damage SEO |
| Update Internal Links | Change internal links to point directly to new URLs instead of relying on redirects | Reduces server load and improves crawl efficiency |
| Document All Redirects | Keep records of why each redirect was implemented and when it should end | Helps your team manage redirects effectively |
Scenario 1: A/B Testing When running A/B tests, use a 302 redirect to temporarily send a portion of traffic to a test page. This tells search engines not to index the test page or transfer ranking signals to it. Once testing is complete, remove the redirect so all traffic returns to the original page. This approach ensures your test doesn’t interfere with your search rankings while allowing you to gather valuable performance data.
Scenario 2: Site Maintenance During scheduled maintenance, redirect users to a maintenance page using a 302. This informs users that the service is temporarily unavailable while preserving the original page’s search visibility. Remove the redirect as soon as maintenance is complete. Consider using a 503 Service Unavailable status code with a Retry-After header for even better search engine handling during maintenance windows.
Scenario 3: Temporary Promotions For limited-time campaigns, use a 302 redirect to send traffic from a standard page to a promotional page. When the promotion ends, remove the redirect to restore normal traffic flow. This approach prevents search engines from permanently associating your brand with the promotional content. It’s particularly useful for seasonal sales, flash promotions, or limited-time offers.
Scenario 4: Temporary Unavailability If a product is temporarily out of stock or a service is temporarily unavailable, use a 302 redirect to an informational page or alternative product. This keeps users engaged without signaling to search engines that the original page is gone forever. When the product or service becomes available again, remove the redirect to restore normal traffic patterns.

Modern search engines, including Google, have clarified that 302 redirects do pass PageRank and link equity similarly to 301 redirects. However, the key difference lies in indexing behavior. With a 302 redirect, search engines typically keep the original URL indexed as the primary version and may not index the destination URL at all. This is beneficial if you truly intend the redirect to be temporary, but problematic if you’ve actually made a permanent change.
The critical factor is intent alignment. If you use a 302 for a permanent change, search engines may eventually treat it as a 301 anyway after observing it for an extended period. However, this creates uncertainty and can lead to indexing issues during the transition period. The safest approach is to always use the redirect type that matches your actual intent: 301 for permanent, 302 for temporary. According to Google’s John Mueller, both redirect types now pass link equity effectively, so the choice should be based purely on whether the change is temporary or permanent.
Server-Side Implementation (Recommended): The most reliable method is implementing 302 redirects at the server level using .htaccess (Apache), Nginx configuration, or your hosting control panel. This ensures the redirect happens before any page content loads, providing the fastest and most reliable experience for users and search engines. Server-side redirects are processed immediately and consistently, making them the gold standard for redirect implementation.
CMS and Plugin Solutions: If you’re using WordPress or another CMS, plugins like Yoast SEO, Rank Math, or All in One SEO provide user-friendly redirect managers. These tools handle the technical implementation while allowing you to manage redirects through a simple interface. PostAffiliatePro users benefit from built-in redirect management features designed specifically for affiliate marketing, allowing you to track and manage affiliate redirects without technical expertise.
Avoid Client-Side Methods: JavaScript redirects and meta refresh tags are slower and less reliable than server-side redirects. Search engines may struggle to process them, and they can negatively impact user experience. Use these methods only as a last resort when server-side options aren’t available. Meta refresh redirects, in particular, are often associated with spammy practices and should be avoided whenever possible.
Use Google Search Console: The URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console shows whether Google has indexed your redirected URLs and how it’s handling the redirects. The Links section reveals whether backlinks pointing to old URLs are being counted toward the new URL, indicating successful redirect implementation. Check the Pages section to see which URLs have been redirected and removed from Google’s index.
Audit with Screaming Frog: This SEO tool crawls your entire website and identifies redirect chains, loops, and broken redirects. Run audits monthly to catch issues before they impact your SEO. The tool provides detailed reports on redirect types, destinations, and any problems it discovers. You can filter results to show only redirects and quickly identify problematic patterns.
Track with Analytics: Monitor traffic patterns in Google Analytics to ensure redirects aren’t causing unexpected drops in traffic or increases in bounce rates. If you notice anomalies, investigate whether your redirects are functioning correctly or if users are having trouble finding content. Set up alerts for significant traffic changes to catch redirect issues quickly.
Using 302 redirects correctly is essential for maintaining your website’s SEO value while providing a smooth user experience. The key is remembering that 302 redirects are only for temporary situations. Avoid the common mistakes of using 302 for permanent changes, creating redirect chains, forgetting to remove redirects, and redirecting everything to the homepage. Instead, implement redirects that match your actual intent, monitor them regularly, and remove or update them when the temporary condition ends.
For affiliate marketing platforms like PostAffiliatePro, proper redirect management is particularly important because it directly impacts affiliate link performance, user experience, and commission tracking. By following these best practices, you’ll maintain strong SEO performance while ensuring your affiliate program runs smoothly and efficiently. PostAffiliatePro’s advanced redirect tracking and management capabilities make it easier than ever to maintain clean, efficient affiliate links that preserve SEO value and maximize conversions.
PostAffiliatePro provides advanced URL management and redirect tracking capabilities to help you maintain clean affiliate links and preserve SEO value. Manage your affiliate redirects efficiently with our industry-leading platform.

Learn when to use 302 redirects for temporary URL changes. Discover best practices, SEO implications, and how 302 redirects differ from 301 redirects in our com...
Learn about 302 redirects—what they are, when to use them, how they impact SEO, and best practices for temporary URL redirection in affiliate marketing.

Learn how 302 redirects work, their SEO impact, and best practices for implementation. Understand temporary redirects vs permanent 301 redirects with technical ...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.