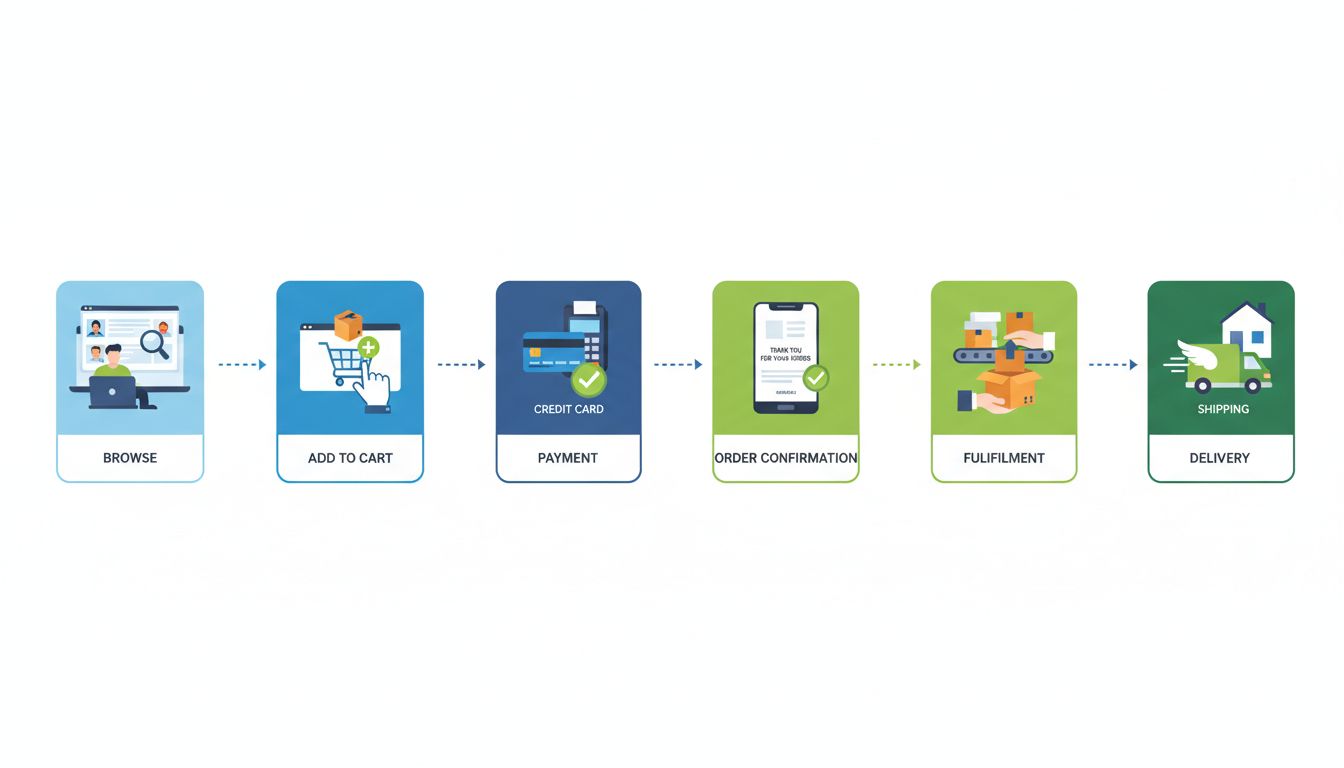
How Does E-Commerce Work?
Learn how e-commerce works in 2025. Discover the complete process from customer browsing to payment processing, order fulfillment, and delivery. Understand e-co...
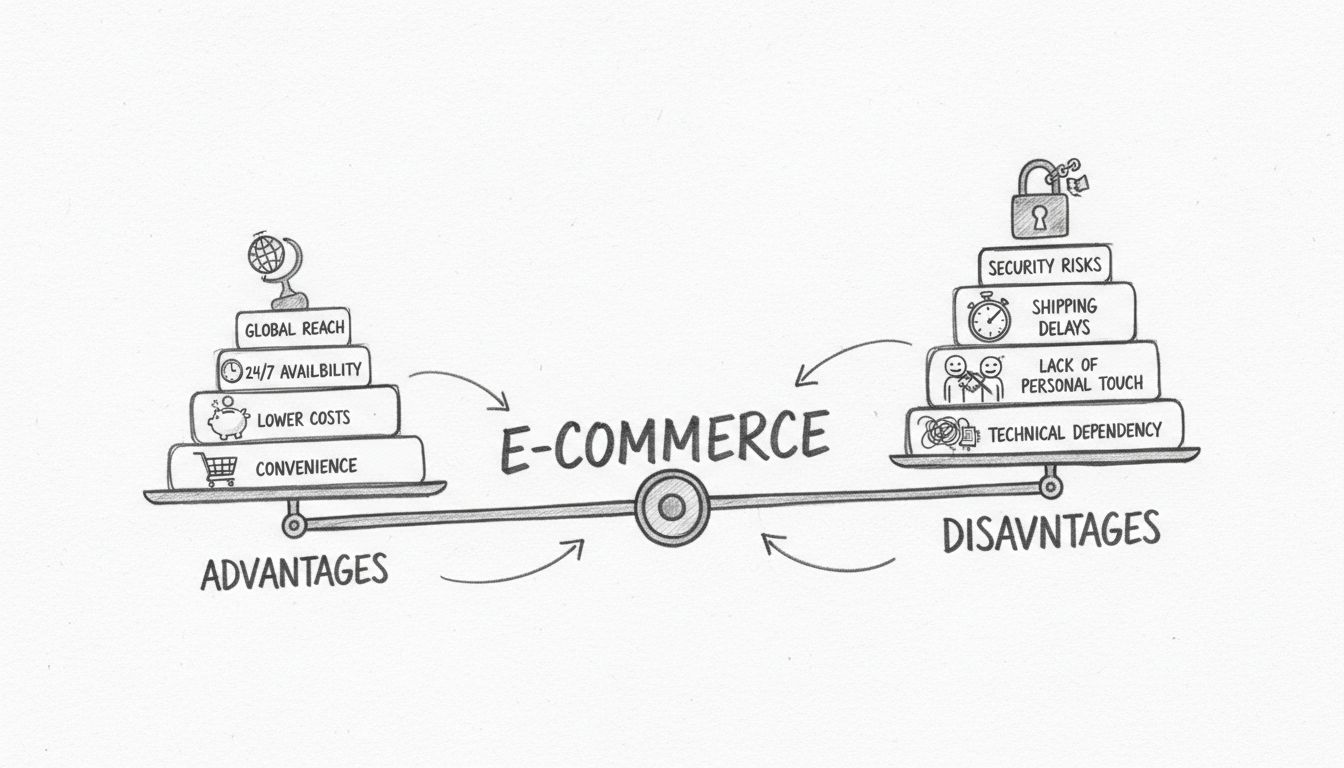
Explore the key advantages and disadvantages of e-commerce in 2025. Learn how online retail impacts businesses and consumers, from global reach to security challenges.
E-commerce offers significant advantages including convenience, global reach, lower operating costs, and 24/7 availability. However, it presents challenges such as security risks, shipping complexities, lack of personal customer interaction, and intense competition. Success requires balancing these factors with robust technology infrastructure and customer-centric strategies.
E-commerce has fundamentally transformed how businesses operate and consumers shop. As we move through 2025, the digital commerce landscape continues to evolve with new technologies, changing consumer expectations, and emerging market dynamics. Understanding both the advantages and disadvantages of e-commerce is essential for businesses looking to succeed in the online marketplace and for consumers making informed purchasing decisions.
One of the most compelling advantages of e-commerce is the ability to reach customers worldwide without geographical limitations. Traditional brick-and-mortar stores are constrained by their physical location, serving only customers within a reasonable distance. E-commerce eliminates these boundaries entirely, allowing businesses to sell products to customers across continents and time zones. This global accessibility opens unprecedented market opportunities, particularly for niche products that may have limited local demand but significant international appeal. Businesses can now establish themselves in multiple markets simultaneously without the substantial capital investment required for physical store expansion. The ability to serve international customers also provides revenue diversification, reducing dependence on any single market and creating more stable, predictable income streams.
E-commerce operates continuously, allowing customers to browse, compare, and purchase products at any time that suits them, regardless of time zones or business hours. This round-the-clock availability represents a fundamental shift from traditional retail, where customers must adapt their schedules to store operating hours. Consumers can shop from their homes, offices, or while traveling, eliminating the need to visit physical locations. This convenience factor has become increasingly important as consumer lifestyles have become more demanding and time-constrained. The ability to shop at 3 AM or on holidays has made e-commerce the preferred shopping method for millions of people worldwide. For businesses, this means capturing sales opportunities that would be impossible in a traditional retail environment, effectively multiplying revenue potential across all hours of the day and night.
Operating an e-commerce business typically requires substantially lower overhead costs compared to maintaining physical retail locations. Businesses eliminate expenses such as store rent, utilities, property maintenance, and in-store staffing requirements. According to industry data, e-commerce businesses can operate with overhead costs 40-60% lower than comparable brick-and-mortar operations. This cost advantage translates directly to improved profit margins and allows businesses to offer more competitive pricing to customers. The savings extend beyond physical space costs to include reduced inventory carrying costs through just-in-time fulfillment models and dropshipping arrangements. These financial advantages make e-commerce particularly attractive for startups and small businesses that lack the capital for traditional retail expansion, democratizing access to market opportunities.
E-commerce platforms generate rich, detailed data about customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns. Every click, search query, product view, and purchase creates valuable insights that businesses can leverage to improve their operations and customer experiences. This data enables sophisticated personalization strategies, including targeted product recommendations, customized marketing messages, and individualized pricing strategies. Advanced analytics platforms can predict customer behavior with remarkable accuracy, allowing businesses to anticipate needs and present relevant products at optimal moments in the customer journey. The ability to segment customers into precise groups based on behavior, demographics, and preferences enables marketing efficiency that traditional retail cannot match. This data-driven approach has become a competitive necessity, with businesses using machine learning and artificial intelligence to continuously refine their understanding of customer needs and preferences.
E-commerce businesses can scale operations dramatically without the physical limitations that constrain traditional retail. Adding new products, expanding to new markets, or increasing sales volume requires minimal infrastructure changes compared to opening new physical locations. A successful e-commerce business can grow from serving hundreds to millions of customers by simply increasing server capacity and adjusting inventory management systems. This scalability advantage has enabled numerous companies to achieve unicorn status (billion-dollar valuations) in remarkably short timeframes. The ability to test new markets, products, and business models with minimal capital investment allows for rapid experimentation and iteration. This flexibility has become increasingly important in fast-moving markets where the ability to adapt quickly often determines success or failure.
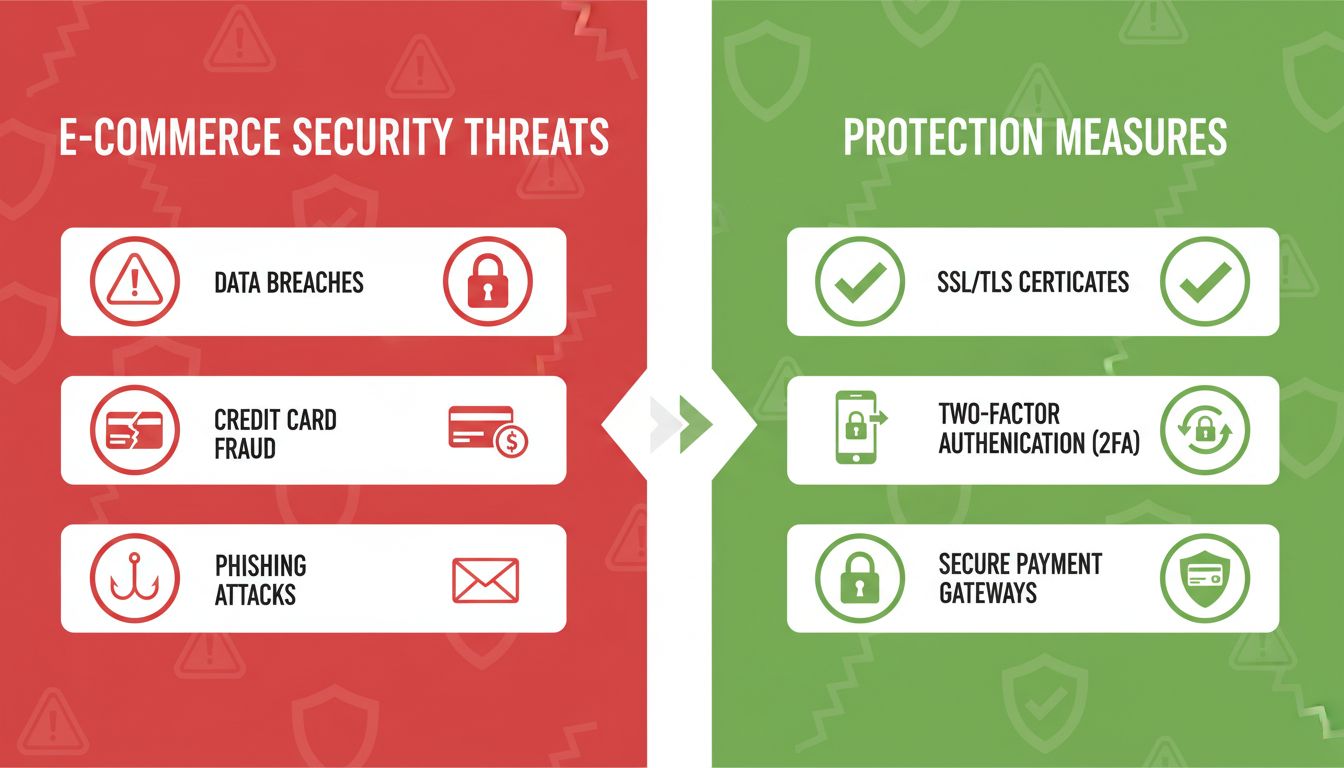
Security represents one of the most significant challenges in e-commerce, with cybercriminals continuously developing sophisticated methods to compromise customer data and financial information. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime damages are projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, with e-commerce businesses representing prime targets. Data breaches can expose sensitive customer information including credit card numbers, personal addresses, and purchase histories, leading to identity theft and financial fraud. The regulatory landscape has become increasingly stringent, with regulations like GDPR and CCPA imposing substantial fines for data breaches and privacy violations. Businesses must invest heavily in security infrastructure including SSL certificates, encryption protocols, two-factor authentication, and continuous security monitoring. The reputational damage from security breaches can be devastating, with customers losing trust and switching to competitors. Building and maintaining customer confidence in the security of their personal and financial information requires ongoing investment and vigilance.
While e-commerce eliminates the need for physical stores, it creates substantial challenges in shipping and fulfillment operations. Customers expect fast, reliable delivery with transparent tracking information, creating pressure on logistics networks. Late deliveries, damaged products, and lost shipments directly impact customer satisfaction and generate negative reviews that harm business reputation. The complexity increases significantly for businesses operating internationally, where customs regulations, import duties, and varying shipping standards create additional complications. Shipping costs represent a substantial portion of e-commerce expenses, often consuming 5-15% of revenue depending on product type and delivery distance. Returns management adds another layer of complexity, requiring businesses to manage reverse logistics, restocking, and refund processing. The rise of customer expectations for free or low-cost shipping has compressed profit margins, forcing businesses to optimize logistics operations continuously or absorb costs that reduce profitability.
E-commerce transactions are inherently impersonal, lacking the human interaction that characterizes traditional retail experiences. Customers cannot physically examine products before purchase, cannot receive personalized recommendations from knowledgeable sales staff, and cannot resolve issues through face-to-face conversations. This impersonality creates friction in the customer journey, particularly for complex products requiring detailed explanation or for customers who value personal service. The absence of immediate gratification—customers must wait for delivery rather than leaving the store with their purchase—creates a different psychological dynamic that some customers find unsatisfying. Building customer loyalty becomes more challenging without the personal relationships that develop through repeated in-person interactions. While technology has improved customer service capabilities through chatbots and video support, these solutions cannot fully replicate the human connection that many customers value. The challenge of creating emotional connections with customers in a digital environment requires sophisticated marketing and customer experience strategies.
The low barriers to entry in e-commerce have created an intensely competitive marketplace where businesses compete primarily on price, selection, and customer experience. Unlike traditional retail where geographic location provides natural competitive advantages, e-commerce businesses compete globally with every other business selling similar products. This competition has driven prices down significantly, compressing profit margins across most product categories. Large, well-capitalized competitors like Amazon have set customer expectations for fast shipping, low prices, and extensive selection that smaller businesses struggle to match. The ease of price comparison online has eliminated information asymmetries that traditionally allowed retailers to maintain price premiums. Businesses must continuously innovate in product offerings, customer experience, and marketing to differentiate themselves from competitors. The competitive pressure has forced many businesses to operate on razor-thin margins, making profitability challenging and leaving little room for operational inefficiencies or market downturns.
E-commerce businesses are entirely dependent on technology infrastructure, creating vulnerability to system failures that can completely halt operations. Website crashes, server outages, payment processing failures, or database corruption can instantly eliminate revenue generation and damage customer relationships. The complexity of modern e-commerce systems—involving multiple integrated platforms for inventory management, payment processing, shipping, and customer relationship management—creates numerous potential failure points. Businesses must invest substantially in redundant systems, backup infrastructure, and disaster recovery planning to ensure business continuity. The rapid evolution of technology creates ongoing challenges in maintaining systems, updating security protocols, and integrating new capabilities. Technical expertise requirements have increased substantially, forcing businesses to hire specialized talent or outsource to expensive service providers. The cost of maintaining reliable, secure, scalable technology infrastructure represents a significant ongoing expense that traditional retailers do not face to the same degree.
| Factor | E-Commerce | Traditional Retail | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Costs | 40-60% lower overhead | High rent, utilities, staffing | E-Commerce |
| Geographic Reach | Global, unlimited | Local/regional only | E-Commerce |
| Availability | 24/7/365 | Limited business hours | E-Commerce |
| Customer Experience | Digital, impersonal | In-person, personal | Traditional Retail |
| Product Examination | Limited (photos/descriptions) | Full hands-on evaluation | Traditional Retail |
| Shipping Costs | 5-15% of revenue | Eliminated (customer takes product) | Traditional Retail |
| Scalability | Rapid, minimal investment | Slow, capital intensive | E-Commerce |
| Data Collection | Extensive, detailed | Limited | E-Commerce |
| Security Risks | High (data breaches) | Lower (physical security) | Traditional Retail |
| Competition Level | Intense, global | Moderate, local | Traditional Retail |
| Customer Loyalty | Challenging to build | Easier through relationships | Traditional Retail |
| Return Management | Complex, costly | Simple (in-store returns) | Traditional Retail |
Mobile commerce has become the dominant e-commerce channel, with mobile devices accounting for approximately 72.9% of all e-commerce sales in 2025. This shift has fundamentally changed how businesses must approach e-commerce strategy, requiring mobile-first design, fast-loading pages, and simplified checkout processes. The advantage of mobile commerce is its accessibility and convenience, allowing customers to shop from anywhere at any time. However, this trend also creates challenges for businesses that must optimize their entire digital infrastructure for mobile devices while maintaining desktop functionality. The rise of mobile wallets and one-click purchasing has reduced friction in the buying process, increasing conversion rates and customer satisfaction. Businesses that fail to optimize for mobile are losing significant market share to competitors who provide superior mobile experiences.
Artificial intelligence has become increasingly central to e-commerce operations, enabling sophisticated personalization at scale that was previously impossible. AI-powered recommendation engines can predict customer preferences with remarkable accuracy, increasing average order value and customer satisfaction simultaneously. Chatbots powered by large language models can handle complex customer service inquiries, reducing support costs while improving response times. Generative AI tools are automating content creation, product descriptions, and marketing copy, allowing businesses to scale operations without proportional increases in staffing costs. However, the implementation of AI systems requires substantial investment in technology infrastructure and specialized talent. The ethical implications of AI-driven personalization and data collection are creating new regulatory challenges and customer privacy concerns that businesses must navigate carefully.
Environmental sustainability has emerged as a significant factor in e-commerce operations and customer decision-making. The packaging waste, transportation emissions, and energy consumption associated with e-commerce operations are creating pressure for more sustainable practices. Customers increasingly prefer businesses that demonstrate environmental responsibility, with 73% of consumers willing to pay premium prices for sustainable products. However, achieving sustainability in e-commerce operations requires substantial investment in eco-friendly packaging, carbon-neutral shipping options, and supply chain optimization. The tension between customer expectations for fast, free shipping and environmental sustainability goals creates ongoing operational challenges. Businesses that successfully balance sustainability with operational efficiency are gaining competitive advantages and building stronger customer loyalty.
Businesses can mitigate security concerns by implementing industry-leading security measures and communicating these efforts clearly to customers. Displaying security certifications, SSL badges, and privacy policies prominently builds customer confidence. Transparent communication about data collection practices and how customer information is protected helps address privacy concerns. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and compliance with regulatory requirements demonstrate commitment to customer protection. Offering multiple payment options, including secure digital wallets and buy-now-pay-later services, provides customers with choices that match their comfort levels. Businesses that prioritize security and communicate these efforts effectively gain competitive advantages through increased customer trust and loyalty.
Successful e-commerce businesses invest heavily in logistics optimization to overcome shipping challenges. Partnering with reliable fulfillment providers, implementing inventory management systems that minimize stockouts and overstock situations, and offering multiple shipping options help manage customer expectations. Providing real-time tracking information, proactive communication about delays, and hassle-free return processes improve customer satisfaction despite shipping complexities. Businesses that can offer fast, affordable shipping gain significant competitive advantages. The rise of same-day and next-day delivery options in major markets has created new customer expectations that businesses must meet to remain competitive.
While e-commerce lacks the personal touch of traditional retail, businesses can create meaningful customer experiences through sophisticated personalization strategies. Personalized product recommendations, customized email communications, and targeted promotions based on customer behavior create a sense of individual attention. Implementing live chat support, video consultations, and responsive customer service channels help bridge the gap created by the absence of in-person interaction. Building community through social media engagement, user-generated content, and customer forums creates emotional connections that transcend the transactional nature of e-commerce. Businesses that successfully create personalized, engaging customer experiences build loyalty that insulates them from price-based competition.
E-commerce presents a complex landscape of significant advantages and meaningful disadvantages that businesses and consumers must carefully navigate. The advantages—including global reach, lower operating costs, 24/7 availability, and data-driven personalization—have fundamentally transformed commerce and created unprecedented opportunities for businesses of all sizes. However, these advantages come with substantial challenges including security risks, logistics complexity, intense competition, and the inherent impersonality of digital transactions.
Success in e-commerce requires acknowledging and actively addressing these disadvantages rather than ignoring them. Businesses that invest in security infrastructure, optimize logistics operations, create personalized customer experiences, and differentiate through superior service and product quality can overcome the inherent challenges of e-commerce. The most successful e-commerce businesses combine the efficiency and reach advantages of digital commerce with customer-centric strategies that create loyalty and competitive differentiation.
As e-commerce continues to evolve in 2025 and beyond, the businesses that thrive will be those that balance the pursuit of scale and efficiency with genuine commitment to customer satisfaction, security, and sustainability. The future of commerce belongs to businesses that leverage the advantages of e-commerce while thoughtfully addressing its disadvantages through innovation, investment, and customer-focused strategy.
PostAffiliatePro is the leading affiliate management software that helps businesses build profitable e-commerce partnerships. Manage commissions, track performance, and scale your affiliate network with industry-leading security and reliability.

Learn how e-commerce works in 2025. Discover the complete process from customer browsing to payment processing, order fulfillment, and delivery. Understand e-co...

Learn what eCommerce affiliate marketing is, how it works, and why it's the top customer acquisition channel for 40% of US merchants. Discover commission struct...
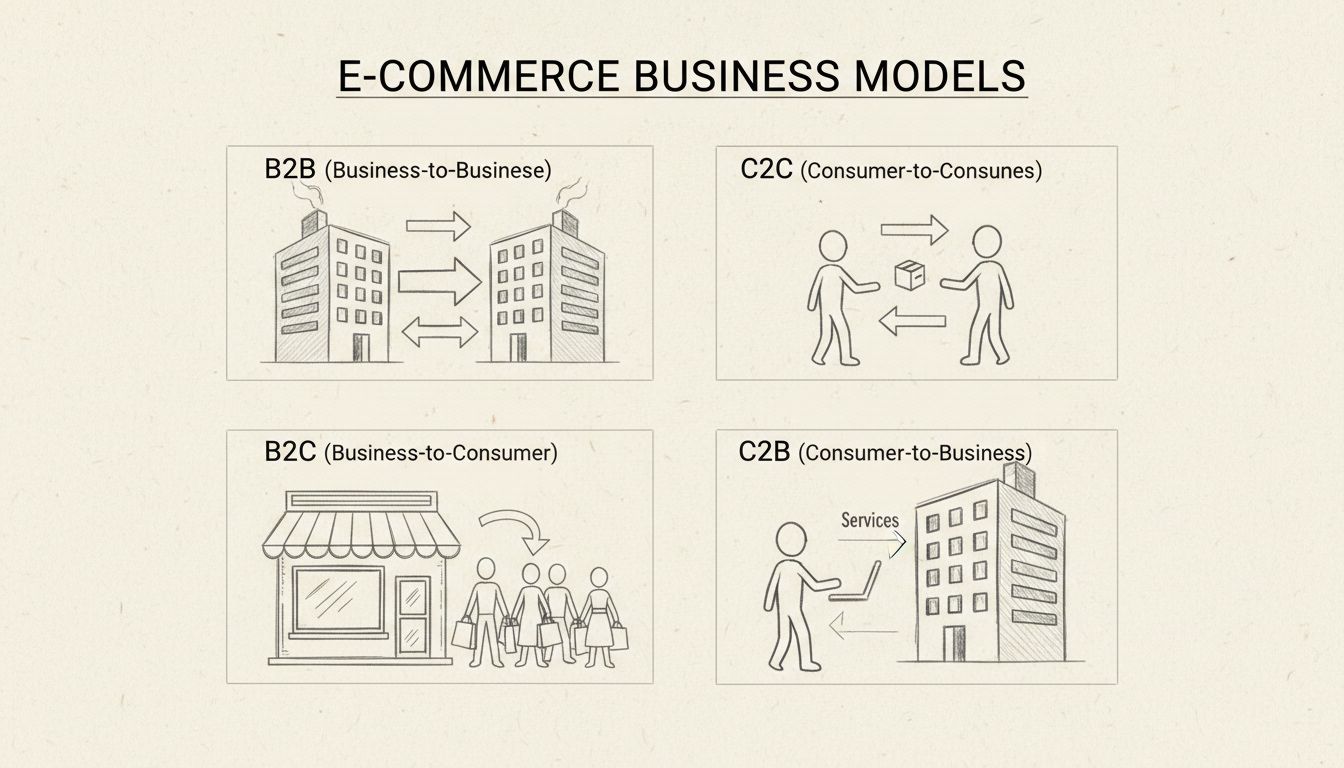
Discover the four main types of e-commerce: B2B, B2C, C2C, and C2B. Learn how each model works, their advantages, and which is best for your business with PostA...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.