What Security Improvements Were Made in This Update? | PostAffiliatePro FAQ
Learn about the XSS vulnerability patch in PostAffiliatePro's latest update. Discover how stricter input validation and output encoding protect your affiliate d...

how Post Affiliate Pro eliminates cross-site scripting vulnerabilities through input validation, output encoding, and Content Security Policy to protect

Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is a security vulnerability that occurs when attackers inject malicious code (typically JavaScript) into web applications, allowing them to execute unauthorized scripts in users’ browsers—a particularly critical threat for affiliate platforms where user data and financial transactions are constantly flowing between networks. XSS attacks come in three primary forms: Stored XSS (where malicious code is permanently saved in a database and executed whenever users access affected pages), Reflected XSS (where attackers trick users into clicking links containing malicious code that executes immediately but isn’t stored), and DOM-based XSS (where vulnerabilities exist in client-side JavaScript code that processes user input unsafely). For affiliate software like Post Affiliate Pro, XSS vulnerabilities pose severe risks including session hijacking (where attackers steal authentication cookies to impersonate users and access sensitive affiliate accounts), credential theft (capturing login information and payment details from affiliates and merchants), and malware distribution (injecting code that redirects users to malicious sites or installs unwanted software)—consequences that can compromise entire affiliate networks, destroy user trust, and result in significant financial and reputational damage. Understanding and preventing XSS is essential for affiliate platforms because they handle sensitive data across multiple user roles (affiliates, merchants, administrators) and serve as bridges between different websites, making them attractive targets for attackers seeking to exploit trust relationships and gain access to valuable customer information.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities pose particularly severe risks to affiliate software platforms because they directly threaten the integrity of commission tracking, payment processing, and sensitive merchant-affiliate relationships; an attacker exploiting XSS could inject malicious scripts to redirect affiliate commissions to fraudulent accounts, impersonate legitimate affiliates to claim unearned commissions, or steal authentication credentials and personal data from both merchants and publishers, fundamentally undermining the trust that underpins the entire affiliate ecosystem. Beyond financial fraud, XSS attacks can compromise the accuracy and reliability of affiliate tracking and reporting systems—attackers could manipulate conversion data, inflate or deflate performance metrics, and generate false attribution records that distort commission calculations and create disputes between merchants and affiliates, while also potentially exposing sensitive payment information and customer data that violates PCI DSS compliance requirements and triggers GDPR violations with significant regulatory penalties.
| XSS Attack Impact | Affiliate Platform Risk | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Session Hijacking | Unauthorized access to affiliate accounts | Critical |
| Commission Fraud | Stolen or redirected commissions | Critical |
| Data Breach | Exposure of merchant and affiliate data | Critical |
| Tracking Manipulation | Inaccurate conversion and performance data | High |
| Credential Theft | Compromised login credentials | Critical |
| Malware Distribution | Malicious redirects and software installation | High |
| Reputation Damage | Loss of trust and partner exodus | Critical |
The reputational damage from XSS-enabled breaches extends far beyond immediate financial losses; when merchants and affiliates discover that their data has been compromised or that commission fraud has occurred through platform vulnerabilities, confidence in the platform collapses, leading to mass exodus of partners, loss of transaction volume, and permanent damage to brand credibility that can take years to recover. From a compliance perspective, affiliate platforms handling payment data and personal information must maintain PCI DSS Level 1 certification and GDPR compliance, and XSS vulnerabilities that expose cardholder data or customer information create audit failures, mandatory breach notifications, and potential fines ranging from thousands to millions of dollars depending on the scale and nature of the exposure. Therefore, implementing robust XSS prevention measures—including input validation, output encoding, Content Security Policy (CSP) headers, and regular security testing—is not merely a technical best practice but a critical business imperative that directly protects revenue streams, maintains regulatory compliance, preserves platform reputation, and ensures the long-term viability of the affiliate software business.

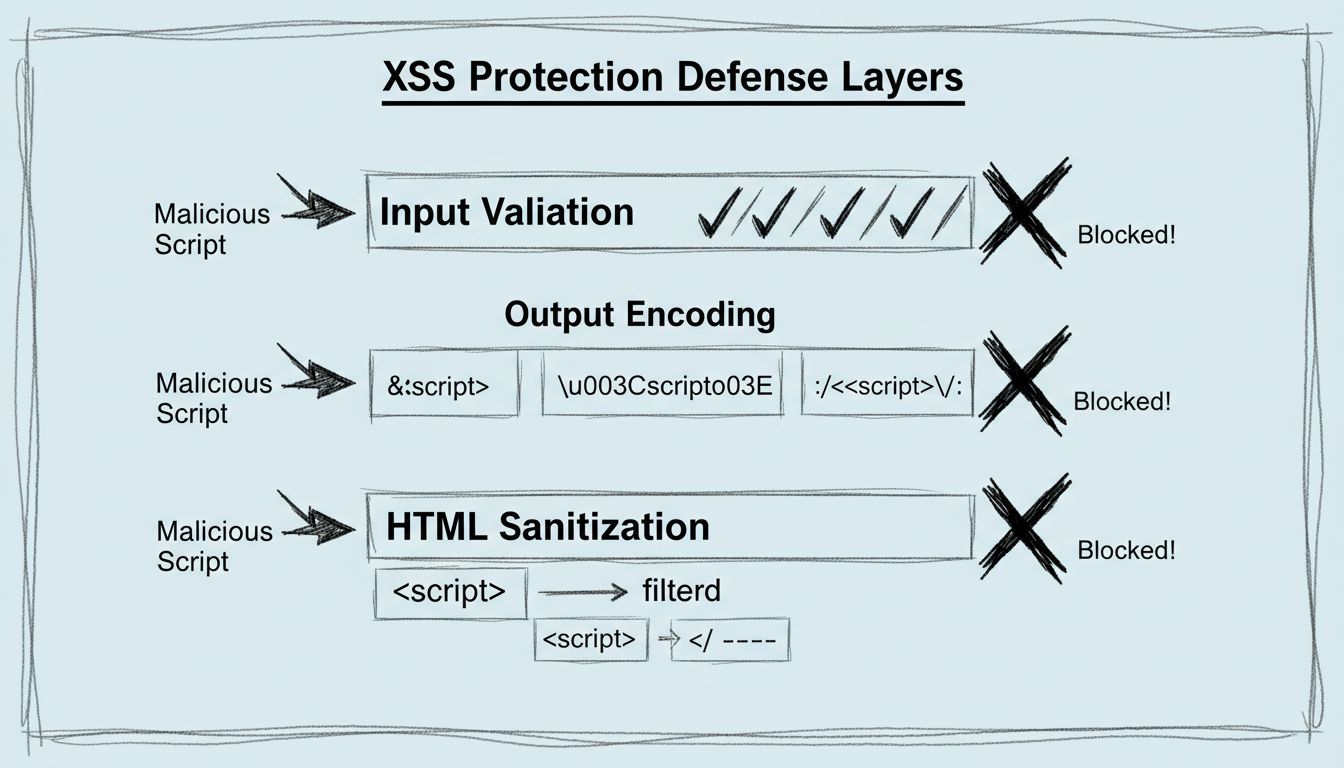
Input validation and sanitization are complementary defense mechanisms that work together to prevent Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks by controlling what data enters an application and how it is processed. Allowlisting (accepting only known-good input patterns) is significantly more secure than denylisting (rejecting known-bad patterns), as the latter can be bypassed through encoding variations, Unicode normalization, or novel attack vectors; for example, allowlisting email inputs to match ^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$ prevents injection attempts while denylisting <script> tags fails against alternatives like <img src=x onerror=alert(1)> or HTML entity-encoded variants. Input validation should enforce strict type checking, length limits, and format constraints at the application boundary, while sanitization libraries like DOMPurify remove potentially dangerous HTML elements and attributes by parsing the DOM tree and reconstructing only safe content—a technique superior to regex-based filtering which cannot reliably parse nested HTML structures. Context-specific encoding is essential because different output contexts require different escaping strategies: HTML context requires entity encoding (< becomes <), JavaScript context requires Unicode escaping (' becomes \x27), URL context requires percent-encoding, and CSS context requires hex escaping, as demonstrated by the principle that <div> + HTML encoding = <div> (safe), but the same string in a JavaScript string context without proper escaping could still execute code. Input validation alone is insufficient because it cannot account for all legitimate use cases—a user might legitimately need to store <b>important</b> in a rich text field—making output encoding the critical final layer that ensures data is rendered safely regardless of its origin. These techniques form a defense-in-depth strategy where validation reduces attack surface, sanitization removes malicious markup, and context-aware encoding prevents interpretation of user data as executable code, with each layer compensating for potential weaknesses in the others.
Output encoding is a critical defense layer against Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks that operates on the principle of context-aware encoding, where the specific output context determines the appropriate encoding strategy—HTML context requires entity encoding (e.g., converting < to <), JavaScript context demands JavaScript string escaping, URL context necessitates percent-encoding, and CSS context requires CSS-specific escaping to prevent injection through style attributes or property values. The concept of safe sinks refers to DOM APIs and template functions that automatically apply context-appropriate encoding (such as textContent in JavaScript or parameterized template engines), contrasting with dangerous sinks like innerHTML or eval() that bypass encoding protections entirely. However, certain contexts present encoding-resistant vulnerabilities where encoding alone proves insufficient—notably JavaScript event handlers, CSS expressions, and data URIs—requiring additional controls such as Content Security Policy (CSP) headers, input validation, and architectural constraints to prevent exploitation. Modern web frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue implement automatic output encoding by default, encoding all interpolated values in templates and providing explicit APIs for raw HTML insertion only when developers consciously opt-in, significantly reducing the attack surface compared to legacy server-side templating engines that required manual encoding at each output point. The effectiveness of output encoding as a defense mechanism depends critically on consistent application across all user-controlled data flows, comprehensive understanding of context-specific encoding requirements, and recognition that encoding represents one layer in a defense-in-depth strategy that must be complemented by input validation, CSP policies, and secure coding practices to achieve robust XSS prevention.
Content Security Policy (CSP) is an HTTP response header mechanism that enforces a whitelist of trusted sources for various content types (scripts, stylesheets, images, fonts, etc.), effectively mitigating Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks by preventing the execution of unauthorized or inline scripts unless explicitly permitted through directives such as script-src and default-src. CSP works by instructing the browser to reject any script execution from sources not explicitly listed in the policy, and when combined with the script-src 'none' or script-src 'self' directives, it eliminates the attack surface for inline script injection and third-party script exploitation. Complementary to CSP, HTTPOnly and Secure cookie flags provide additional layers of defense by preventing JavaScript from accessing sensitive session cookies (HTTPOnly) and ensuring cookies are only transmitted over encrypted HTTPS connections (Secure), thereby reducing the impact of successful XSS exploitation even if an attacker manages to execute malicious code. Additional security headers such as X-Frame-Options (preventing clickjacking and framing attacks) and X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff (preventing MIME-type sniffing) work synergistically with CSP to create a comprehensive defense-in-depth strategy that addresses multiple attack vectors beyond XSS alone. While CSP is a powerful protective mechanism, it should be implemented as a secondary or tertiary defense layer rather than the primary mitigation strategy, as it cannot protect against all XSS vectors (such as DOM-based XSS in certain contexts) and should be paired with robust input validation, output encoding, and secure coding practices to establish a resilient security posture against modern web application threats.
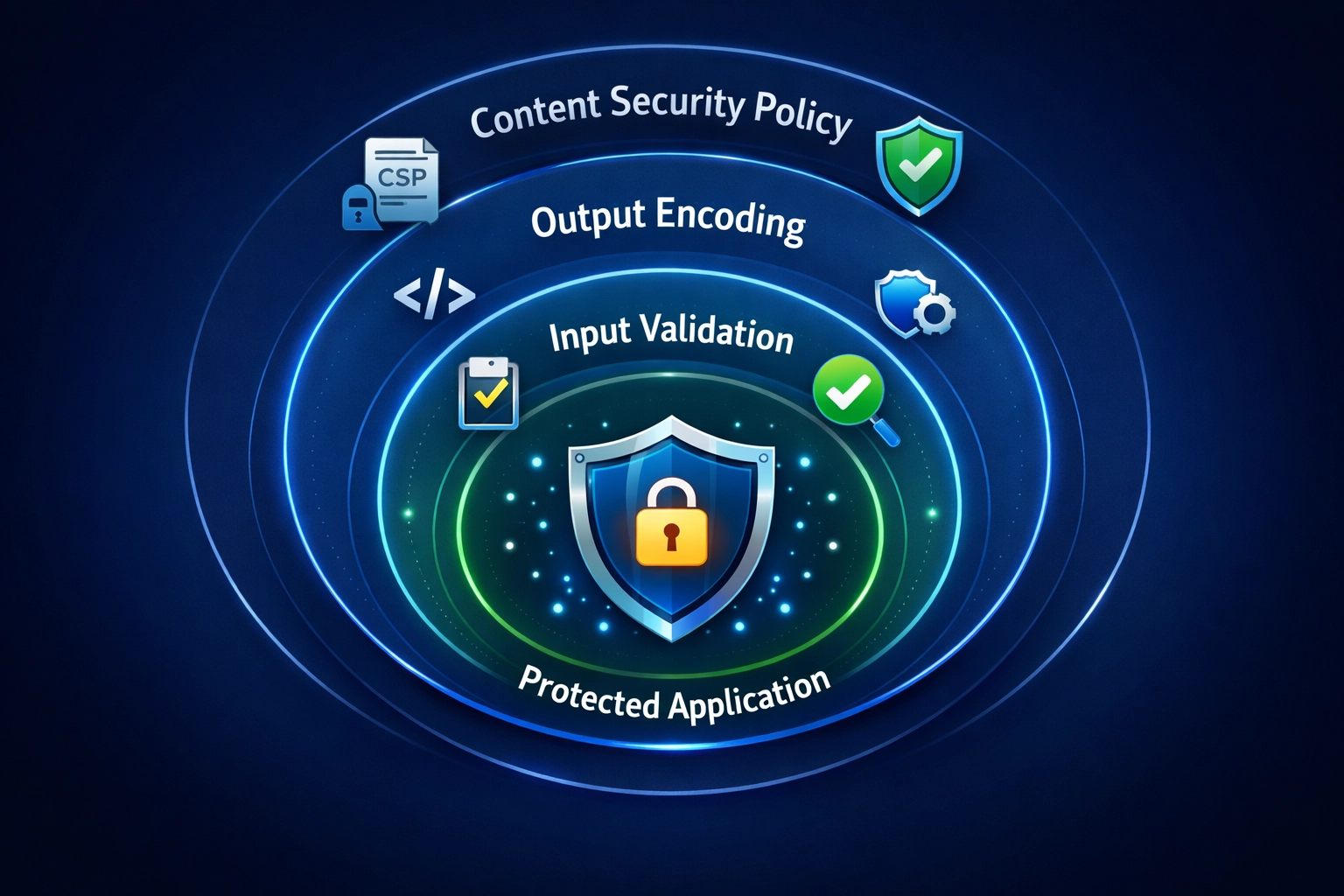
Post Affiliate Pro has demonstrated exceptional commitment to eliminating Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities through a multi-layered security architecture that implements stricter input validation, output encoding, and HTML sanitization across its platform, particularly in critical areas such as user profile sections where attackers could previously inject malicious scripts. The platform’s security improvements employ whitelist-based validation that accepts only data matching predefined safe patterns, combined with comprehensive HTML entity encoding (converting characters like <, >, &, and quotes to their encoded equivalents) to prevent browsers from interpreting user input as executable code, while also implementing Content Security Policy (CSP) headers that restrict script execution to trusted domains only. Post Affiliate Pro’s security framework adheres to industry best practices established by OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project), ensuring that the platform meets the same security standards used by Fortune 500 companies, and the platform reinforces this commitment through a formal Bug Bounty Program that rewards security researchers for responsible vulnerability disclosure, with regular penetration testing, automated vulnerability scanning, and rigorous code review procedures conducted by a dedicated security team. These comprehensive security measures protect affiliate networks and merchants from stored XSS attacks that could compromise affiliate credentials, manipulate commission data, or redirect traffic to fraudulent destinations, while also preventing reflected XSS and DOM-based XSS attack vectors that could steal session cookies or perform unauthorized actions. By combining enterprise-grade security infrastructure with proactive vulnerability management and continuous security monitoring, Post Affiliate Pro has established itself as a leader in affiliate software security, offering merchants and affiliates the confidence that their sensitive data, transaction records, and user sessions are protected by industry-leading security practices that go beyond reactive patching to implement preventive security measures before vulnerabilities can be exploited.
Implementing comprehensive XSS prevention requires a multi-faceted approach that extends beyond the platform itself. Here are essential security practices that affiliate network operators should adopt:
Implement Input Validation and Output Encoding: Use established security libraries like OWASP ESAPI or DOMPurify to validate all user inputs against strict allowlists and encode output based on context (HTML, JavaScript, URL, CSS). This foundational practice prevents the vast majority of XSS attacks by ensuring malicious code cannot be injected or executed.
Leverage Secure Coding Frameworks: Adopt modern web frameworks (React, Angular, Vue) that provide automatic output encoding by default, implement Content Security Policy headers, and follow OWASP guidelines. These frameworks significantly reduce the attack surface compared to legacy systems that require manual security implementation at every output point.
Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Schedule quarterly security audits and annual third-party penetration tests to identify vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. Automated vulnerability scanning tools should continuously monitor for known vulnerabilities in dependencies and custom code.
Invest in Developer Security Training: Provide mandatory training on OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities, secure coding practices, and XSS-specific attack vectors. Security-aware developers are the first line of defense against vulnerabilities, and ongoing education ensures teams stay current with evolving threats.
Maintain Updated Dependencies and Security Patches: Use automated dependency scanning tools (Snyk, Dependabot) to identify vulnerable libraries and establish a 30-day remediation timeline for critical vulnerabilities. Outdated frameworks and libraries are common attack vectors that can be easily exploited.
Deploy Comprehensive Monitoring and Incident Detection: Implement Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems with real-time alerting for suspicious activities, unusual data access patterns, and potential XSS exploitation attempts. Rapid detection and response minimize the impact of successful attacks.
Compliance with industry standards and best practices is paramount in affiliate software development, particularly regarding Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) prevention. OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) provides comprehensive guidelines for XSS mitigation, including input validation, output encoding, and content security policies, which form the foundation of secure affiliate platforms. PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) mandates strict web application security controls, requiring organizations to implement robust defenses against XSS vulnerabilities to protect cardholder data and maintain compliance certification. Additionally, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) imposes stringent data protection requirements that necessitate secure handling of personal information, making XSS prevention a critical component of organizational accountability and user privacy safeguards. Post Affiliate Pro demonstrates commitment to these standards by implementing input sanitization, output encoding, Content Security Policy (CSP) headers, and regular security audits that exceed baseline requirements, ensuring protection against evolving XSS threats. The platform’s adherence to these compliance frameworks protects both the business from regulatory penalties and reputational damage while simultaneously safeguarding users’ sensitive data and maintaining trust in the affiliate ecosystem. Regular third-party security assessments, penetration testing, and vulnerability management programs further reinforce the platform’s security posture, demonstrating that comprehensive compliance is not merely a checkbox requirement but a fundamental commitment to operational excellence and stakeholder protection.
The elimination of XSS vulnerabilities in Post Affiliate Pro represents a significant advancement in affiliate software security, protecting the integrity of commission tracking, merchant-affiliate relationships, and sensitive user data. By implementing a comprehensive security architecture that combines input validation, output encoding, Content Security Policy, and continuous security monitoring, Post Affiliate Pro ensures that affiliate networks and merchants can operate with confidence that their platforms are protected against modern XSS threats. As the affiliate industry continues to evolve and attackers develop more sophisticated techniques, platforms that prioritize security and maintain proactive vulnerability management will emerge as trusted partners for merchants and publishers seeking reliable, secure affiliate solutions. The investment in enterprise-grade security infrastructure is not just a technical requirement—it’s a business imperative that protects revenue, maintains regulatory compliance, and preserves the trust that underpins successful affiliate relationships.
XSS is a security vulnerability that allows attackers to inject malicious JavaScript code into web applications. When users visit the affected page, the malicious script executes in their browser, potentially stealing sensitive data, session cookies, or performing unauthorized actions. XSS vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous for affiliate platforms that handle financial transactions and sensitive user information.
The three main types are: Stored XSS (malicious code permanently saved in a database), Reflected XSS (code injected through URLs and executed immediately but not stored), and DOM-based XSS (vulnerabilities in client-side JavaScript that processes user input unsafely). Each type poses different risks and requires specific prevention strategies.
Input validation uses allowlisting to accept only known-good data patterns while rejecting anything that doesn't match expected formats. This prevents attackers from injecting malicious code through form fields, URLs, or other input vectors. However, input validation should be combined with output encoding for comprehensive protection.
Output encoding converts special characters into safe formats that browsers interpret as data rather than executable code. For example, '<' becomes '<' in HTML context. Context-aware encoding is critical because different contexts (HTML, JavaScript, URL, CSS) require different encoding strategies to prevent XSS exploitation.
CSP is an HTTP header that specifies which sources are trusted for loading scripts and other resources. By restricting script execution to trusted domains only and preventing inline scripts, CSP significantly reduces the attack surface for XSS vulnerabilities. However, CSP should be used as a defense-in-depth measure alongside input validation and output encoding.
Affiliate platforms handle sensitive data including commission information, merchant credentials, and customer data. XSS vulnerabilities could allow attackers to steal commissions, impersonate affiliates, manipulate tracking data, or compromise user accounts. Robust XSS prevention protects the integrity of the entire affiliate ecosystem and maintains trust between merchants and publishers.
Post Affiliate Pro implements a multi-layered security approach including strict input validation with allowlisting, comprehensive output encoding, HTML sanitization, Content Security Policy headers, HTTPOnly and Secure cookie flags, and regular security audits. The platform adheres to OWASP guidelines and conducts continuous penetration testing to identify and eliminate vulnerabilities.
Post Affiliate Pro complies with OWASP security guidelines, PCI DSS requirements for payment card data protection, and GDPR regulations for personal data handling. The platform undergoes regular third-party security assessments and maintains a bug bounty program to ensure ongoing security excellence and regulatory compliance.
Post Affiliate Pro's advanced security features eliminate XSS vulnerabilities and protect your affiliate data. Start your free trial today and experience the difference that professional security makes.

Learn about the XSS vulnerability patch in PostAffiliatePro's latest update. Discover how stricter input validation and output encoding protect your affiliate d...
Discover PostAffiliatePro's February 2024 updates including user profile variables in redirect URLs, improved email notifications, enhanced Samcart integration,...

Learn how CSP headers protect against XSS attacks, implement nonces and hashes, and secure your affiliate panel with Content-Security-Policy directives.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.