How to Check Your Website's Loading Time: Complete Guide to Speed Testing Tools
Learn how to check your website's loading time using free and paid tools like Pingdom, Google PageSpeed Insights, and GTmetrix. Discover key metrics, benchmarks...

proven methods to speed up your website including image optimization, caching, CDN, and Core Web Vitals optimization. Improve performance and conversions today.
In today’s digital landscape, website speed is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity. Studies show that users expect pages to load in under 3 seconds, with mobile users becoming increasingly impatient at even longer delays. A mere one-second delay in page load time can result in a 7% reduction in conversions, while 53% of mobile users abandon sites that take longer than 3 seconds to load. Beyond user experience, search engine optimization heavily favors faster websites, as Google has made page speed a critical ranking factor, making speed optimization essential for both user satisfaction and SEO success.
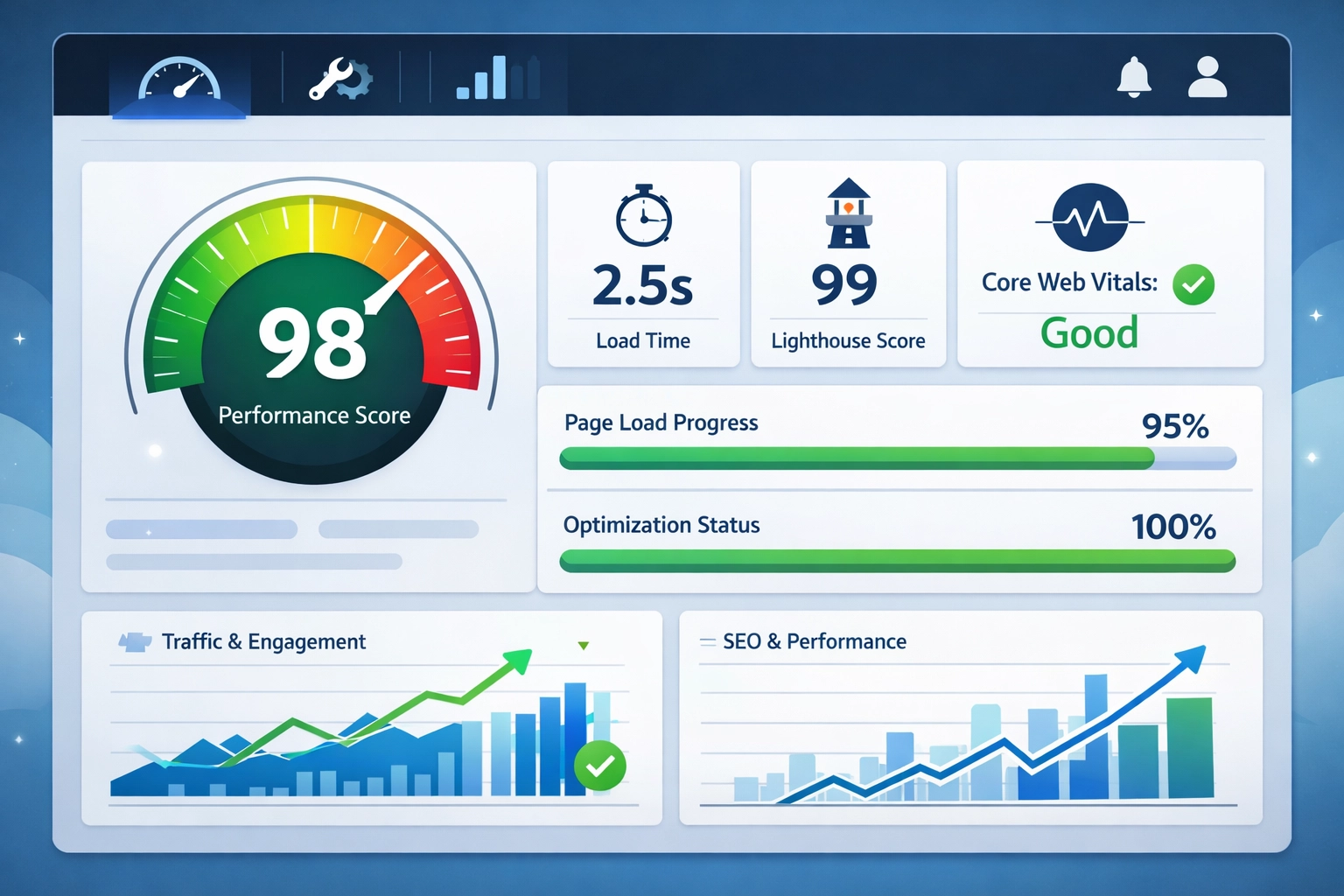
Core Web Vitals represent Google’s standardized metrics for measuring website performance and user experience. These three key metrics are Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), which measures when the largest visible element loads; First Input Delay (FID), which tracks the responsiveness to user interactions; and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), which quantifies unexpected layout changes during page load. Google prioritizes these metrics in its ranking algorithm because they directly correlate with user satisfaction and engagement. Understanding and optimizing for these metrics is crucial for maintaining competitive search rankings and providing an excellent user experience.
| Metric | Good | Poor | Percentile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Largest Contentful Paint | ≤2500ms | >4000ms | 75th |
| First Input Delay | ≤100ms | >300ms | 75th |
| Cumulative Layout Shift | ≤0.1 | >0.25 | 75th |

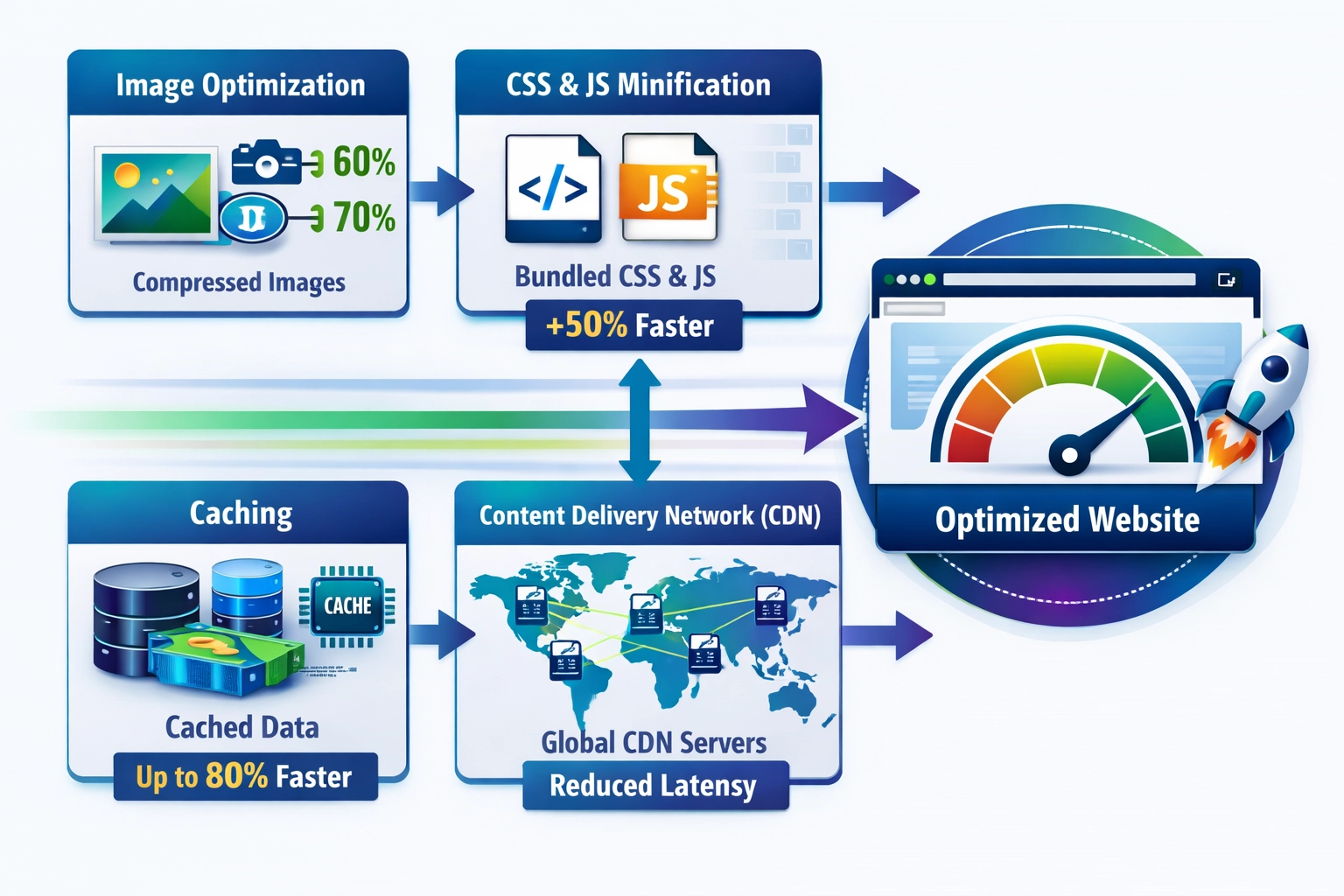
Image optimization is one of the most impactful yet often overlooked aspects of website speed improvement. Images typically account for 50-60% of a website’s total page weight, making them the primary culprit in slow load times. Implementing proper compression techniques, selecting appropriate file formats, and utilizing responsive images can dramatically reduce file sizes without sacrificing visual quality. Lazy loading—a technique that defers image loading until they’re needed—further enhances performance by reducing initial page load burden. Consider these image optimization strategies:
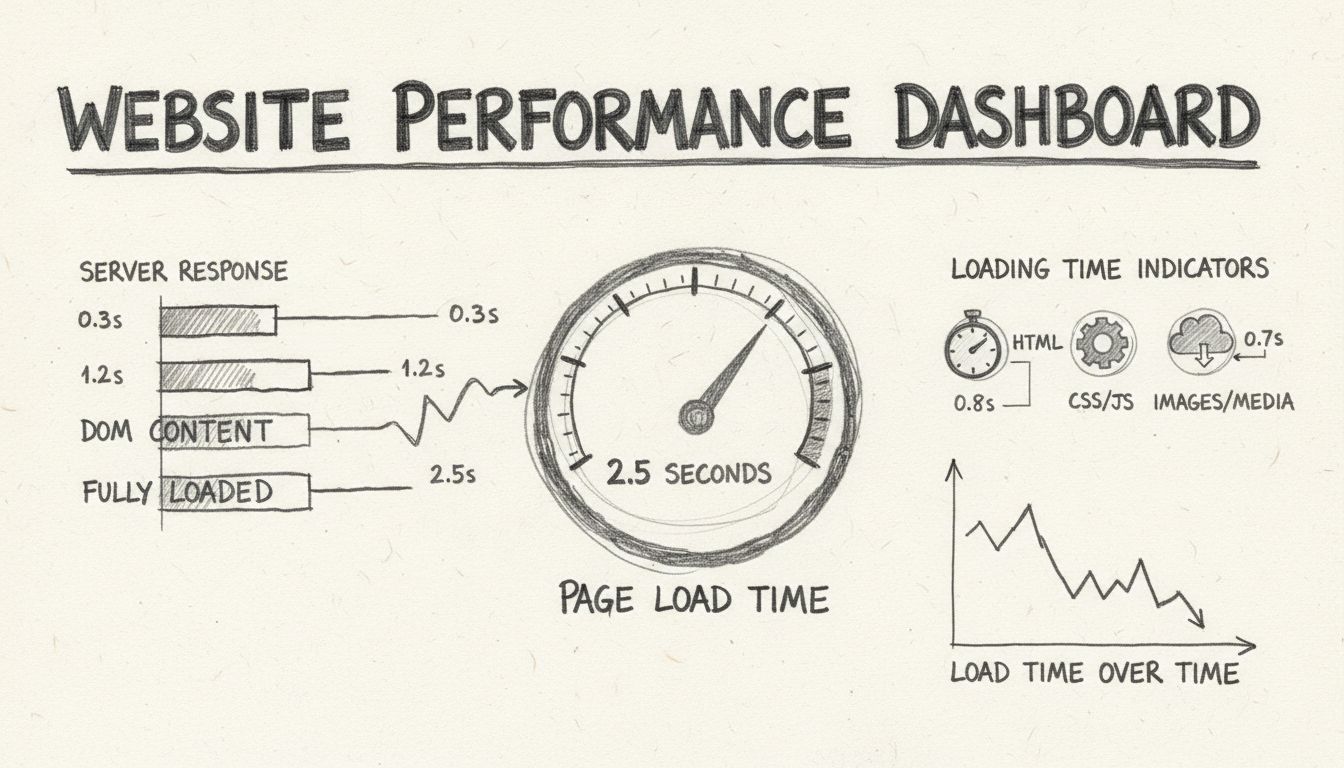
HTTP requests represent a significant overhead in page load times, with each request adding latency and consuming bandwidth. Modern websites often make 50-100+ HTTP requests per page, each adding milliseconds to load time. Minification of CSS and JavaScript files removes unnecessary characters without affecting functionality, reducing file sizes by 20-30%. Bundling multiple files into single requests further decreases overhead. By combining CSS files, consolidating JavaScript, and removing unused code, developers can substantially improve load times while maintaining full functionality and maintainability.
Browser caching stores static assets locally on users’ devices, eliminating the need to re-download unchanged files on subsequent visits. Server-side caching stores frequently accessed data in memory, reducing database queries and server processing time. Setting appropriate cache expiration headers ensures that returning visitors experience dramatically faster load times while still receiving updated content when necessary. For websites with significant repeat traffic, caching can reduce load times by 50-70% for returning visitors. Implementing both browser and server-side caching strategies creates a multi-layered approach that benefits both new and returning users.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) distribute your website’s content across geographically dispersed servers worldwide, ensuring users download from locations nearest to them. By reducing the physical distance between users and servers, CDNs dramatically decrease latency and improve load times, particularly for international audiences. A CDN can reduce latency by 30-50% depending on geographic distribution and server density. Major CDNs like Cloudflare, Akamai, and AWS CloudFront provide global infrastructure that automatically routes user requests to optimal servers. For websites serving global audiences, CDN implementation is one of the most effective speed optimization strategies available.
Render-blocking resources—CSS and JavaScript files that prevent page rendering until fully loaded—significantly impact perceived performance and Core Web Vitals. Using the async attribute allows JavaScript to load without blocking HTML parsing, while the defer attribute loads scripts after page rendering completes. Critical CSS identifies and inlines essential styles needed for above-the-fold content, allowing the page to render faster while deferring non-critical styles. Tools like PurgeCSS and UnCSS automatically remove unused CSS rules, reducing file sizes and improving load times. Strategic optimization of JavaScript and CSS loading patterns can improve LCP by 20-40% and significantly enhance overall page responsiveness.
Time to First Byte (TTFB) measures the time between requesting a page and receiving the first byte of response, directly reflecting server performance. Server response time depends heavily on hosting quality, server-side code efficiency, and database optimization. Upgrading to managed hosting or dedicated servers can reduce TTFB by 30-50% compared to shared hosting. Database optimization—including proper indexing, query optimization, and connection pooling—reduces server processing time significantly. Implementing server-side caching and content compression further improves TTFB. A fast server response time is foundational to overall website speed, as it directly impacts all other performance metrics.
Mobile optimization requires a fundamentally different approach than desktop optimization, as mobile users face unique challenges including limited bandwidth, processing power, and screen real estate. A mobile-first design approach ensures that websites are optimized for mobile devices from the ground up, with desktop enhancements added progressively. Responsive design automatically adapts layouts to different screen sizes, ensuring usability across all devices. Mobile users are particularly sensitive to performance, with 64% of mobile users expecting pages to load in under 2 seconds. Regular testing on actual mobile devices and networks reveals performance bottlenecks that desktop testing might miss.
Monitoring and measuring website performance is essential for identifying bottlenecks and tracking improvement progress. Google PageSpeed Insights provides actionable recommendations and Core Web Vitals data directly from Google’s perspective. GTmetrix offers detailed waterfall charts and performance comparisons, while WebPageTest enables testing from multiple geographic locations and browsers. Establishing performance baselines and tracking metrics over time reveals the impact of optimization efforts. Regular monitoring—ideally weekly or monthly—ensures that performance remains optimal and alerts you to regressions before they impact users significantly.
Effective speed optimization requires a strategic approach that balances quick wins with long-term improvements. Prioritize your optimization efforts using this action plan:
Begin with high-impact, low-effort optimizations, then progress to more complex improvements. Establish a continuous monitoring schedule to catch performance regressions early and maintain optimal speed over time.
Website speed optimization is not a one-time project but an ongoing commitment to excellence. By implementing the strategies outlined—from image optimization and caching to CDN deployment and Core Web Vitals monitoring—you can dramatically improve user experience, increase conversions, and boost search rankings. The investment in speed optimization pays dividends through improved user satisfaction, higher engagement rates, and better business outcomes. Start implementing these methods today, monitor your progress consistently, and remember that every millisecond of improvement contributes to a better user experience and stronger business performance.
Ideally, your website should load in under 3 seconds. Research shows users lose focus after this threshold. For optimal performance, aim for a Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) of 2.5 seconds or less, which is Google's recommended benchmark for good user experience.
Browser caching stores website resources on a user's device, reducing the need to fetch them during subsequent visits. Server-side caching stores a static version of your website on the server, which can be served to users, reducing the need to generate a page dynamically for each visit.
Image optimization can reduce file sizes by 50-70% using compression techniques like Gzip. Since images typically make up the largest portion of a webpage's size, optimizing them is one of the quickest ways to improve overall page load time.
Google uses Core Web Vitals as ranking factors in its search algorithm. Websites that perform well on these metrics (LCP, FID, CLS) tend to rank higher in search results. Additionally, these metrics directly correlate with better user experience and higher conversion rates.
The quickest wins typically come from: enabling browser caching, optimizing images, reducing HTTP requests, and implementing a CDN for static assets. These changes can often be implemented quickly and yield significant performance improvements.
It's recommended to test your website speed monthly as a best practice. However, you should also test after any significant content updates, design changes, or when implementing new features to ensure performance hasn't degraded.
Yes, CDNs can significantly improve speed, especially for geographically distant users. By serving content from servers closest to the user, CDNs reduce latency and load times. Studies show CDNs can improve load times by 30-50% depending on your user distribution.
Research shows that for every second longer your site takes to load, you could lose nearly 5% of conversions. A site that loads in 1 second has a conversion rate 3x higher than one that loads in 5 seconds, making speed optimization directly tied to revenue.
Fast websites drive better conversions and affiliate engagement. PostAffiliatePro helps you track and optimize your affiliate program's performance metrics.

Learn how to check your website's loading time using free and paid tools like Pingdom, Google PageSpeed Insights, and GTmetrix. Discover key metrics, benchmarks...

how website speed directly impacts conversion rates, SEO rankings, and revenue. why fast-loading websites are essential for business success and get actionable

how page load time directly impacts affiliate conversions. why fast-loading pages reduce bounce rates, increase conversions
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.