
Prevent Plagiarism of Affiliate Content: Protection Guide
effective strategies to prevent plagiarism of affiliate content including security hosting, DMCA registration, monitoring tools like Copyscape, watermarks

Learn how to find uncredited images using Google Image Search, request proper attribution, and recover valuable backlinks to boost your SEO and brand authority.
Image theft is a pervasive issue affecting millions of content creators, photographers, and website owners worldwide. When your images are used without permission or proper attribution, you lose valuable SEO signals, brand authority, and potential backlink opportunities that could drive traffic to your website. Studies show that approximately 40% of images found on the internet lack proper attribution or licensing information, creating a significant gap between content creators and those who benefit from their work. This problem is particularly damaging for affiliate marketers and content creators who rely on organic search visibility and brand recognition to generate revenue.

Google Image Search’s reverse image search feature is one of the most powerful tools available for tracking down where your images have been used across the web. Here’s how to systematically find uncredited images:
Access Google Images - Navigate to images.google.com and click the camera icon in the search bar to activate reverse image search functionality.
Upload Your Image - Select “Upload an image” and choose the photo you want to track from your computer, or paste the image URL directly if it’s already hosted online.
Review Search Results - Google will display all instances where that image appears across the web, organized by relevance and size variations.
Filter and Analyze Results - Use the “Tools” menu to filter by size, color, type, and usage rights to identify unauthorized uses more efficiently.
Document Findings - Create a spreadsheet noting the website URL, date discovered, context of use, and whether attribution is present for each instance you find.
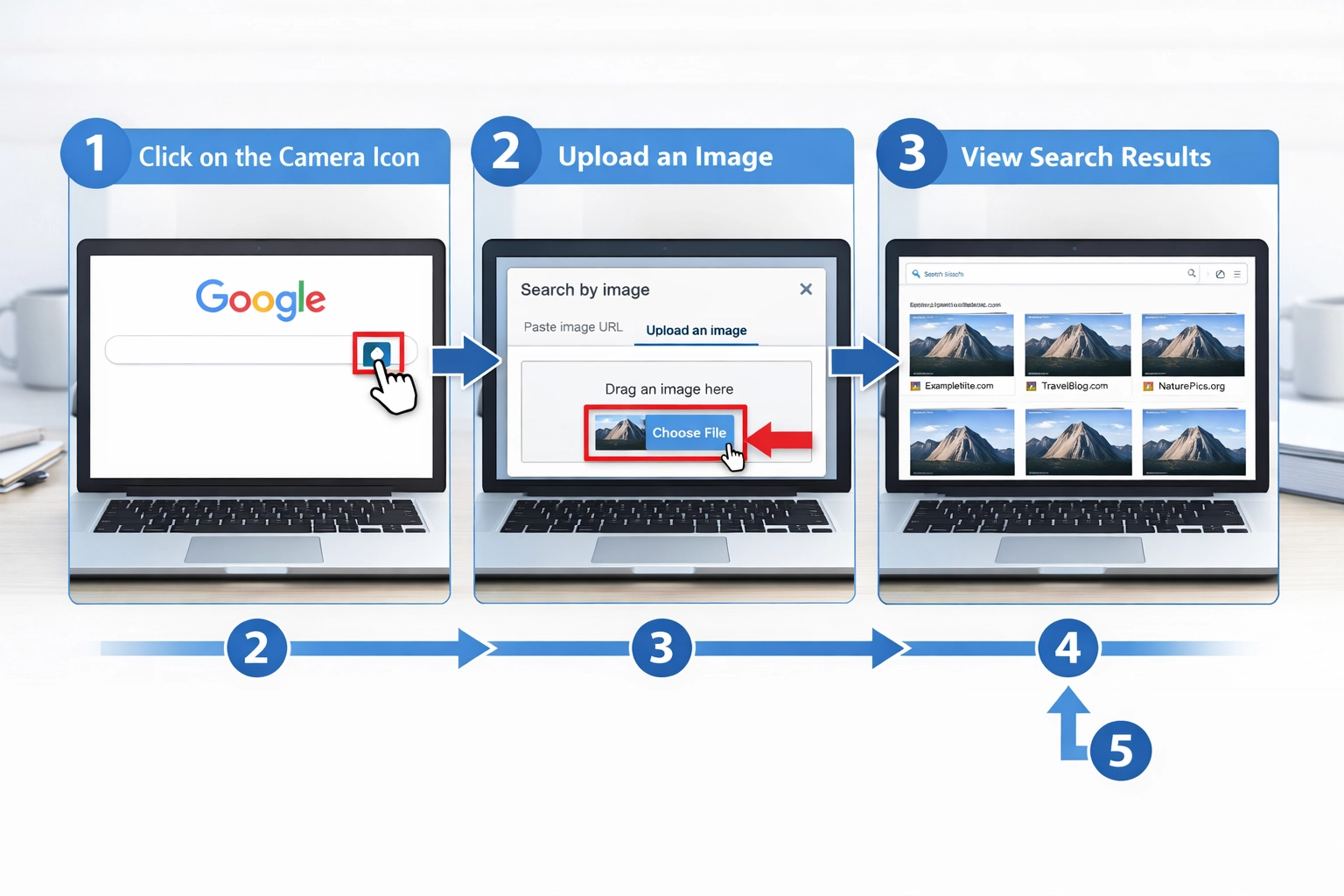
Image theft occurs across multiple platforms and contexts, each requiring different detection and recovery strategies. Here are the most common sources where your images are stolen:
Blog Posts and Content Websites - Bloggers and content aggregators frequently republish images without permission, often stripping metadata and attribution in the process.
Social Media Platforms - Facebook, Pinterest, and Instagram are hotspots for image theft, where users share content without crediting original creators or linking back to source material.
E-commerce and Product Listings - Sellers on Amazon, eBay, and Shopify sometimes use product photography without authorization or proper licensing agreements.
News Aggregators and Content Curation Sites - Platforms that automatically pull content from RSS feeds or scrape websites often include images without maintaining original attribution or backlinks.
Different platforms and contexts have varying requirements for proper image attribution, and understanding these standards is crucial for enforcing your rights. The table below outlines attribution requirements across major platforms:
| Platform | Attribution Format | License Type | Backlink Required | Metadata Preservation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WordPress | Caption or alt text with creator name | Creative Commons or custom | Recommended | Optional |
| Photo credit in caption or comments | Fair use/personal use | Not required | Stripped by platform | |
| Credit in post caption or comments | Fair use/personal use | Not required | Removed automatically | |
| Flickr | Creator name and license displayed | CC, copyright, or custom | Depends on license | Preserved in EXIF |
| Unsplash | Creator name in image details | CC0 (public domain) | Recommended | Maintained in metadata |
Creative Commons licenses require specific attribution formats depending on the license type (CC-BY requires name and link, CC-BY-SA requires same license adoption). Copyright notices should include the copyright symbol (©), year, and creator name, and should be prominently displayed near the image. Understanding these standards helps you craft stronger attribution requests and provides legal backing when pursuing DMCA claims or cease-and-desist letters.
When you discover uncredited image usage, your first step should be a professional, courteous email requesting proper attribution and a backlink to your original content. The tone should be firm yet collaborative, positioning the website owner as someone who simply may not have realized the attribution requirement.
| Element | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Subject Line | Clear and specific | “Attribution Request for Image in Your [Article Title]” |
| Opening | Personalized greeting | “Hi [Name], I noticed your article…” |
| Image Reference | Specific identification | “The image showing [description] in your article…” |
| Ownership Proof | Evidence of creation | “This image was originally published on [date] at [URL]” |
| Request | Clear call-to-action | “Would you be willing to add a credit line with a link?” |
| Benefit | Why they should comply | “This helps readers find more quality content on the topic” |
| Closing | Professional sign-off | “Thank you for considering this request” |
Here’s an effective template you can customize:
Subject: Image Attribution Request - [Your Website Name]
Dear [Website Owner/Editor],
I noticed that your article “[Article Title]” features an image that was originally created and published by [Your Name/Company] on [Your Website]. While I appreciate the use of my work, I noticed the image lacks proper attribution and a link back to the original source.
To comply with standard attribution practices and copyright standards, I’d appreciate it if you could add a caption crediting my work with a link to [Original URL]. This helps maintain proper attribution across the web and supports original content creators.
Please let me know if you have any questions, and thank you for your cooperation in crediting original creators.
Best regards, [Your Name]
Most website owners respond positively to polite requests, especially when you provide them with the exact attribution format you’d like them to use. Keep your email concise, provide specific details about the image and article, and make it easy for them to comply by suggesting the exact text and link format. If you don’t receive a response within 7-10 days, follow up with a second email before escalating to DMCA procedures.
When polite requests fail, the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) provides legal recourse for protecting your copyrighted images. DMCA takedown notices are formal legal documents that require website hosts to remove infringing content or face liability. Follow these steps to file an effective DMCA claim:
Identify the Hosting Provider - Use WHOIS lookup tools or services like BuiltWith to determine which company hosts the infringing website, as DMCA notices must be sent to the hosting provider, not the website owner.
Locate the Abuse Contact - Visit the hosting provider’s website and find their DMCA/abuse contact information, typically listed in their legal or support section, or search for “[Hosting Provider] DMCA agent.”
Document Your Ownership - Gather evidence proving you created the image, including original files with metadata, publication dates on your website, and any copyright registrations (which strengthen your claim significantly).
Draft the DMCA Notice - Include your contact information, the copyrighted work description, the infringing URL, a statement under penalty of perjury that you own the copyright, and your signature (digital signatures are acceptable).
Include Required Elements - Ensure your notice contains all legally required information: identification of the copyrighted work, identification of the infringing material, your contact information, a statement of good faith belief, and a statement that the information is accurate under penalty of perjury.
Send to Hosting Provider - Email or mail the DMCA notice to the hosting provider’s designated agent, keeping detailed records of when and how you submitted it, as most providers must respond within 10-14 business days.
Rather than manually searching for your images repeatedly, automated tools can continuously monitor the web for unauthorized usage and help you recover lost attribution and backlinks. Pixsy is one of the most comprehensive image protection services, automatically scanning the internet for your images and providing one-click DMCA filing capabilities. Google Alerts can be configured to notify you when specific image filenames or your website URL appears in new web content, helping you catch theft early. TinEye offers reverse image search with monitoring features, allowing you to track image usage over time and receive notifications when new instances appear. Copyscape specializes in detecting content theft and can be configured to monitor for image usage alongside text content. These tools save countless hours compared to manual searching and provide documented evidence of unauthorized use, which strengthens DMCA claims and attribution requests.
The best approach to image theft is prevention through proactive protection measures that discourage unauthorized use and make your images less attractive to thieves. Implement these strategies to safeguard your visual content:
Add Watermarks - Place visible watermarks containing your brand name, website URL, or copyright symbol directly on images, making them less useful for thieves while maintaining visibility for legitimate users.
Embed Metadata and EXIF Data - Include copyright information, creator name, and licensing terms in image metadata using tools like Adobe Lightroom or online EXIF editors, which persists even when images are downloaded.
Optimize Image Sizes - Serve images at web-optimized resolutions (72 DPI, appropriate dimensions) rather than high-resolution files, reducing their value for commercial reuse while maintaining quality for web display.
Use Creative Commons Licenses - Clearly specify your licensing terms (CC-BY, CC-BY-SA, or copyright) on your website and in image metadata, setting clear expectations for how your images can be used.
Disable Right-Click Downloads - Implement JavaScript solutions that disable right-click image saving on your website, adding friction to casual image theft (though determined thieves can still access images through browser developer tools).
Recovered image attribution creates valuable backlinks that improve your SEO authority and drive referral traffic to your website, making image protection a critical component of your link-building strategy. Each properly attributed image represents a potential backlink from an established website, and these links carry significant SEO weight because they’re contextually relevant to your content. For affiliate marketers, these recovered backlinks are particularly valuable because they drive qualified traffic from readers already interested in your niche and content. When you successfully recover attribution and backlinks, you’re not just protecting your copyright—you’re building your domain authority and improving your search rankings for competitive keywords. Document all recovered backlinks in your SEO tools and monitor their impact on your organic traffic, as this data demonstrates the ROI of your image protection efforts and justifies continued investment in monitoring and enforcement.
A sustainable image reclamation strategy requires ongoing monitoring and systematic processes. Rather than conducting one-time searches, establish a regular schedule—monthly or quarterly—to check for new instances of your images across the web. This proactive approach catches unauthorized uses early, before they become deeply embedded in search results and harder to address.
Consider implementing a formal image attribution policy on your website that clearly states your images are original content and explains how others should credit and link to your work. Include this policy in your website footer, in your image metadata, and in your content management system.
Develop a tiered response strategy based on the value of each opportunity:
This tiered approach ensures you’re allocating your resources efficiently and focusing on opportunities that will have the greatest impact on your search rankings. Document all your outreach efforts, including dates, contact information, and responses received. This documentation serves multiple purposes: it helps you avoid duplicate outreach, provides evidence if you need to pursue legal action, and allows you to measure the success rate of your campaigns.
Understanding the limitations of copyright protection and fair use doctrine is essential before pursuing aggressive enforcement actions against image users. Fair use permits limited use of copyrighted images for purposes like criticism, commentary, news reporting, teaching, scholarship, and parody, meaning not all unauthorized image use constitutes infringement. The fair use analysis considers four factors: the purpose and character of use, the nature of the copyrighted work, the amount and substantiality of the portion used, and the effect on the market value of the original work. DMCA notices should only be filed when you have a strong copyright claim and the use doesn’t qualify as fair use; filing false DMCA claims can result in legal liability and damages. International considerations are important if your images are used on foreign websites, as copyright protection varies significantly by country and DMCA only applies to U.S.-based hosting providers. When facing complex situations involving fair use questions, international disputes, or commercial infringement, consult with an intellectual property attorney who can evaluate your specific circumstances and recommend the most effective legal strategy.
Using Google Image Search, you can find most instances of your images within 30 minutes to an hour. However, automated monitoring tools like Pixsy continuously scan the web and can identify new instances within 24-48 hours. The time depends on how widely your images have been distributed and how frequently you search.
An attribution request is a polite, informal request asking for proper credit and a backlink. A DMCA takedown is a formal legal notice that requires hosting providers to remove content or face liability. Use attribution requests first; escalate to DMCA only if the website owner ignores your requests or refuses to comply.
Yes, when you successfully recover attribution and get a backlink added to the website using your image, you gain a valuable SEO backlink. These recovered backlinks are particularly valuable because they're contextually relevant to your content and come from established websites already interested in your niche.
DMCA takedown notices only apply to U.S.-based hosting providers. For international websites, you can still send polite attribution requests, but legal enforcement is more difficult. Consider using international copyright laws or consulting with an intellectual property attorney familiar with the country where the website is hosted.
Implement multiple prevention strategies: add visible watermarks to your images, embed copyright metadata and EXIF data, serve web-optimized image sizes rather than high-resolution files, clearly specify your licensing terms, and use automated monitoring tools to catch theft early. No single method is foolproof, but combining multiple approaches significantly reduces theft.
Watermarking is effective as a deterrent and makes your images less attractive to thieves, but determined bad actors can remove watermarks using image editing software. However, watermarks serve as a clear copyright notice and make it obvious that the image is protected, which discourages casual theft and strengthens your legal position if you need to pursue DMCA claims.
You can pursue compensation for unauthorized commercial use of your images, but this requires proving damages or negotiating a licensing fee. Many photographers use services like Pixsy that help recover compensation from image theft. For non-commercial use, requesting attribution and a backlink is typically more practical than pursuing monetary damages.
DMCA takedown notices have a high success rate (typically 85-95%) when filed correctly against U.S.-based hosting providers. Most hosting providers comply within 10-14 business days to avoid liability. Success depends on having clear evidence of copyright ownership, filing the notice with the correct hosting provider, and ensuring your notice includes all legally required information.
PostAffiliatePro helps you track and manage your affiliate content across the web, ensuring proper attribution and maximizing your backlink profile for better SEO results.

effective strategies to prevent plagiarism of affiliate content including security hosting, DMCA registration, monitoring tools like Copyscape, watermarks
why direct upload is essential for profile image security. how direct upload prevents malware, protects against vulnerabilities

How affiliate management systems detect and prevent fraud in real-time. Fraud detection tools, prevention strategies, and PostAffiliatePro protection.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.