Cookies in Marketing: What They Do
Cookie is a data or code that is stored in a computer by a website. It stores login information or information about user’s interests. In affiliate marketing, c...

Learn why Post Affiliate Pro discontinued Flash cookies and moved to HTML5 for secure, compliant affiliate tracking. Discover modern alternatives.

Flash cookies, also known as Local Shared Objects (LSOs), were a form of persistent data storage technology developed by Adobe for Flash Player applications. These cookies emerged in the early 2000s as a powerful alternative to traditional HTTP cookies, offering significantly larger storage capacity and more sophisticated tracking capabilities. Flash cookies became particularly popular among advertisers and analytics platforms because they could store up to 100KB of data per domain, compared to the 4KB limit of standard HTTP cookies. Why they mattered: Flash cookies could persist across browser sessions, survive cookie deletion, and even be used to “respawn” deleted HTTP cookies—a practice known as cookie respawning. Their widespread adoption made them a critical component of the digital advertising ecosystem, though this power would eventually become their downfall as privacy concerns mounted.
Flash cookies are persistent data files stored locally on a user’s computer by Adobe Flash Player, operating independently of the browser’s cookie management system. Unlike HTTP cookies that are stored in a browser’s designated cookie folder and transmitted with every HTTP request, Flash cookies are stored in a separate directory structure on the user’s hard drive and are only accessed by Flash applications. The technical architecture of Flash cookies allowed them to store significantly more data and maintain persistence even when users cleared their browser cache or disabled cookies entirely. Flash Player maintained these files in platform-specific locations: on Windows in %APPDATA%\Macromedia\Flash Player\#SharedObjects, and on macOS in ~/Library/Preferences/Macromedia/Flash Player/#SharedObjects. This isolation from browser controls made Flash cookies particularly valuable for tracking purposes, but also made them difficult for users to manage or delete.
| Feature | Flash Cookies | HTTP Cookies |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Location | Local file system (Macromedia directory) | Browser cookie store |
| Capacity | Up to 100KB per domain | ~4KB per cookie |
| Persistence | Survives browser cache clearing | Can be deleted by users |
| Cross-browser Access | Limited to Flash Player | Accessible across browsers |
| User Control | Minimal, hidden from users | Visible and manageable in settings |
The power of Flash cookies came with significant privacy implications that eventually led to their downfall. Cookie respawning became a major concern when advertisers and tracking companies used Flash cookies to restore deleted HTTP cookies, effectively circumventing user privacy preferences and browser controls. This practice violated user expectations and trust, as individuals who deliberately cleared their cookies believed they were removing tracking mechanisms, only to have them silently restored. The emergence of privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA created legal complications for Flash cookie usage, as these laws required explicit user consent for tracking and gave users rights to access and delete their data. Security vulnerabilities in Flash Player made Flash cookies attractive targets for malware and unauthorized access, with attackers able to steal stored data or manipulate tracking information. The lack of transparency and user control over Flash cookies—they were hidden from most users and difficult to manage—made them increasingly incompatible with modern privacy standards and regulatory requirements.
Adobe announced the end of Flash Player support on July 25, 2017, with a firm discontinuation date of December 31, 2020. This decision was driven by multiple converging factors: the rise of open web standards like HTML5, WebGL, and WebAssembly that provided superior performance and security; widespread security vulnerabilities in Flash Player that made it a constant target for exploits; and major browser vendors’ decision to block Flash content by default. Browser blocking accelerated the timeline: Google Chrome began blocking Flash in 2015, Firefox followed suit, and Safari and Edge implemented similar restrictions, making Flash increasingly unusable across the web. The final nail in the coffin came when major websites and platforms—including YouTube, Facebook, and others—migrated away from Flash-based video and interactive content to HTML5 alternatives. By the end of 2020, Flash Player was completely removed from most systems, and websites attempting to use Flash were met with error messages rather than functional content.
As Flash cookies became obsolete, the digital marketing and analytics industries rapidly adopted alternative tracking technologies that offered similar functionality while addressing some privacy concerns. The modern tracking landscape is diverse and sophisticated, with multiple complementary approaches:
These alternatives collectively provide advertisers and analytics platforms with powerful tracking capabilities while offering better alignment with privacy regulations and user expectations. Server-side tracking has emerged as particularly important in the post-cookie era, as it reduces dependence on client-side storage and provides more reliable data collection that isn’t affected by browser privacy features or user cookie deletion.
Post Affiliate Pro (PAP) recognized early that Flash cookie dependence was unsustainable and proactively transitioned its tracking infrastructure to modern, privacy-compliant technologies. The platform moved away from Flash-based tracking well before the 2020 discontinuation deadline, implementing robust HTML5-based tracking mechanisms that maintain accuracy while respecting user privacy. PAP’s current tracking architecture leverages server-to-server communication, allowing affiliate networks to track conversions and user interactions without relying on persistent client-side storage. The platform implemented first-party cookie tracking that operates within the domain of the merchant’s website, providing better privacy compliance while maintaining reliable conversion attribution. PAP also integrated pixel-based tracking for scenarios where cookie-based tracking isn’t feasible, ensuring comprehensive coverage across different traffic sources and user scenarios. The evolution demonstrates PAP’s commitment to staying ahead of industry standards and regulatory requirements, providing affiliate marketers with tracking solutions that are both effective and compliant with GDPR, CCPA, and other privacy frameworks.
Each modern tracking method offers distinct advantages and trade-offs in terms of accuracy, reliability, and privacy compliance. Server-to-server tracking provides the highest accuracy and reliability because it operates independently of browser privacy features and user cookie deletion, making it ideal for high-value transactions where attribution accuracy is critical. HTML5 Local Storage offers a middle ground, providing persistent client-side storage with better user visibility and control compared to Flash cookies, though it remains subject to browser privacy features and user deletion. Pixel tracking excels in scenarios where cookies are blocked or unavailable, though it provides less detailed data and cannot track repeat visitors as effectively. Device fingerprinting offers persistent identification without relying on stored data, but raises significant privacy concerns and faces increasing regulatory scrutiny. First-party cookies provide good accuracy and privacy compliance when implemented correctly, though they’re limited to tracking within a single domain and cannot track users across multiple websites.
| Method | Accuracy | Browser Support | Privacy Compliance | Persistence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Server-to-Server | Very High | Universal | Excellent | N/A (server-side) |
| HTML5 Local Storage | High | Modern browsers | Good | Until user deletion |
| First-party Cookies | High | Universal | Excellent | Domain-specific |
| Pixel Tracking | Medium | Universal | Good | No persistence |
| Device Fingerprinting | Medium-High | Universal | Poor | Browser session |

HTML5 Local Storage represents a significant improvement over Flash cookies in terms of transparency, user control, and regulatory compliance. Unlike Flash cookies that were hidden from users and difficult to manage, HTML5 Local Storage data is accessible through browser developer tools, allowing technically-savvy users to inspect and delete stored data. The 5MB storage capacity provides ample space for tracking data while remaining reasonable enough to discourage excessive data collection, creating a natural balance between functionality and privacy. Better compliance with privacy regulations is a key advantage, as HTML5 Local Storage operates within the browser’s standard data management framework, making it easier for websites to implement proper consent mechanisms and honor user deletion requests. The technology integrates seamlessly with modern web standards and doesn’t require proprietary plugins, reducing security vulnerabilities and ensuring long-term compatibility as web technologies evolve. User empowerment is enhanced because individuals can easily clear Local Storage data alongside their browser cache and cookies, giving them genuine control over their digital footprint.
Implementing modern tracking methods requires a thoughtful approach that balances business needs with user privacy and regulatory compliance. Transparency is paramount: websites should clearly disclose what data is being collected, how it’s being used, and which third parties have access to it, typically through comprehensive privacy policies and cookie consent notices. Obtain explicit user consent before implementing any tracking beyond what’s strictly necessary for website functionality, particularly for non-essential analytics and advertising tracking. Implement granular consent management that allows users to accept certain types of tracking while rejecting others, rather than forcing an all-or-nothing choice. Respect user preferences by honoring “Do Not Track” signals and providing easy mechanisms for users to opt out of tracking, even after initial consent. Use server-to-server tracking for critical conversion data whenever possible, as it provides better accuracy and reduces dependence on client-side storage that users can delete. Regular audits of your tracking implementation ensure compliance with evolving regulations and help identify unnecessary data collection that can be eliminated. Document your tracking methods and data flows clearly, as this documentation is often required by privacy regulators and helps demonstrate good-faith compliance efforts.
The evolution from Flash cookies to modern tracking technologies represents a fundamental shift in how the digital marketing industry approaches user data and privacy. Flash cookies were powerful but problematic—they offered sophisticated tracking capabilities but at the cost of user privacy, transparency, and regulatory compliance. The transition to HTML5 Local Storage, server-to-server tracking, and other modern methods has created a more sustainable ecosystem where effective marketing attribution can coexist with genuine user privacy protection. Post Affiliate Pro exemplifies this evolution, providing affiliate marketers with tracking solutions that leverage modern technologies while maintaining the accuracy and reliability necessary for successful affiliate programs. If you’re still relying on outdated tracking methods or struggling with privacy compliance, now is the time to evaluate modern alternatives that can deliver both business results and user trust. Explore how Post Affiliate Pro’s contemporary tracking infrastructure can transform your affiliate program into a privacy-compliant, high-performing marketing channel that respects user data while driving measurable business results.
Flash cookies, also known as Local Shared Objects (LSOs), were stored by Adobe Flash Player and persisted data independently of browser cookies. Unlike regular HTTP cookies that are limited in size and easily deleted, Flash cookies could store larger amounts of data and were much harder for users to clear, making them controversial for tracking purposes. Flash cookies operated outside the browser's standard cookie management system, which made them less transparent to users.
Post Affiliate Pro discontinued Flash cookie support due to Adobe's end-of-life for Flash Player in December 2020 and the industry-wide shift toward modern, transparent tracking methods. Flash technology became increasingly incompatible with modern browsers and devices, particularly mobile platforms that never supported Flash. The move aligns with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, which require more transparent and user-friendly tracking mechanisms.
HTML5 tracking is generally considered more secure and transparent than Flash cookies because it operates within the browser's standard security model and is subject to the same-origin policy. Users have direct control over HTML5 storage through browser settings, and websites must comply with privacy regulations when using these technologies. HTML5 tracking also benefits from modern encryption standards and security protocols that weren't available during the Flash era.
No, Post Affiliate Pro no longer supports Flash cookies as the platform has fully transitioned to HTML5-based tracking methods. Since Adobe discontinued Flash Player support globally, Flash cookies are no longer functional in modern browsers anyway. Post Affiliate Pro's modern tracking approach uses first-party cookies and HTML5 storage, which are more reliable, compliant, and future-proof.
Post Affiliate Pro's HTML5 tracking approach ensures GDPR compliance by implementing transparent consent mechanisms and allowing users to easily manage their tracking preferences. The platform respects user privacy settings and provides clear documentation about what data is collected and how it's used. Post Affiliate Pro also supports cookie-less tracking options and ensures that affiliate tracking data is processed in accordance with GDPR requirements.
First-party cookies are set by the website you're visiting and are generally more reliable and privacy-friendly, while third-party cookies are set by external domains and are increasingly restricted by browsers. Post Affiliate Pro primarily uses first-party cookies for affiliate tracking, which provides better accuracy and respects user privacy more effectively. Third-party cookies face significant limitations in modern browsers, making first-party tracking the preferred approach for affiliate programs.
HTML5 tracking is actually more accurate than Flash cookies because it integrates seamlessly with modern browser APIs and benefits from improved data synchronization. Post Affiliate Pro's HTML5 implementation provides reliable cross-domain tracking while maintaining better compatibility with current web standards and analytics tools. The accuracy is further enhanced by eliminating the technical inconsistencies that sometimes plagued Flash-based tracking systems.
You should migrate to Post Affiliate Pro's modern HTML5 tracking solution immediately, as Flash cookies are no longer functional in any major browser. Post Affiliate Pro provides seamless migration tools and support to help you transition your affiliate tracking without losing historical data or disrupting your program. The platform's modern approach ensures better compliance, improved accuracy, and future-proof tracking for your affiliate operations.
Experience the power of modern, compliant tracking with Post Affiliate Pro. Our HTML5-based tracking methods ensure accuracy, security, and full GDPR/CCPA compliance for your affiliate program.
Cookie is a data or code that is stored in a computer by a website. It stores login information or information about user’s interests. In affiliate marketing, c...

Discover why longer cookie lifetimes don't always benefit affiliates. Learn how purchase cycles, attribution models, and privacy regulations impact cookies.
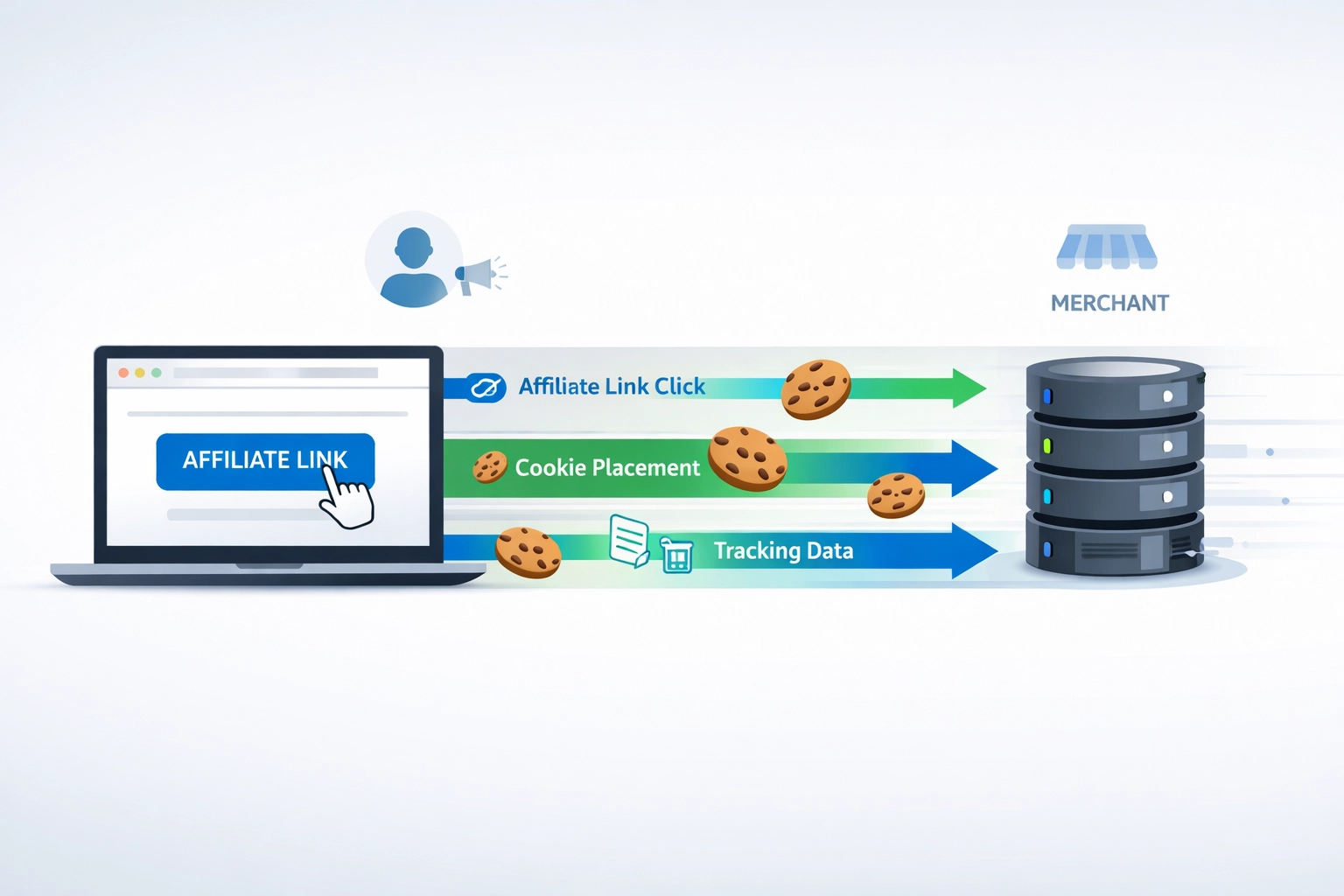
Learn how cookie tracking works in affiliate marketing, including cookie duration, types, compliance, and best practices for accurate attribution.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.