Why Is Automation Important in E-Commerce Logistics?
Discover why automation is critical for e-commerce logistics. Learn how automated systems improve efficiency, accuracy, and delivery speed while reducing operat...
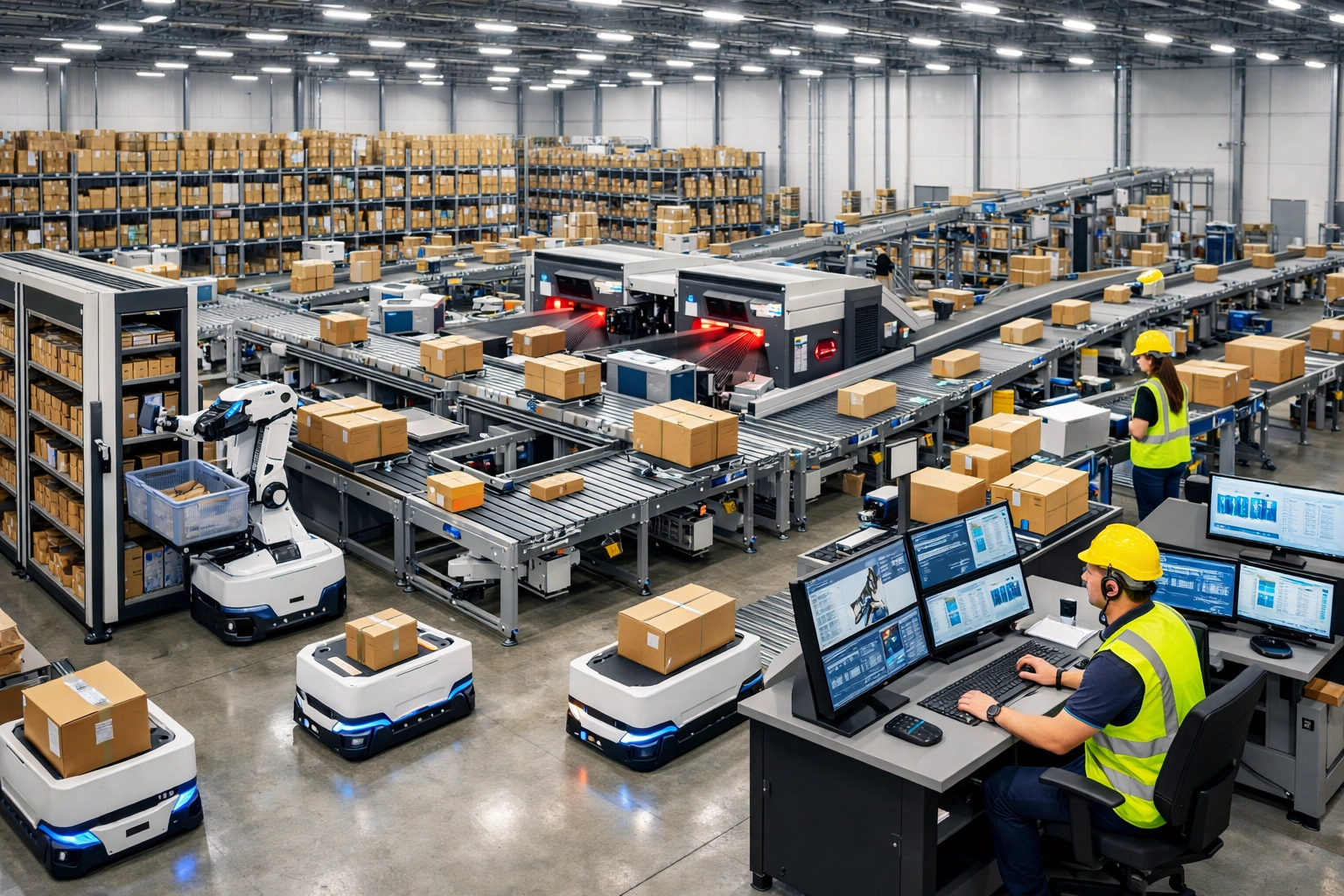

Discover key e-commerce logistics trends for 2026: warehouse automation, AI fulfillment, sustainable delivery, and last-mile innovations.
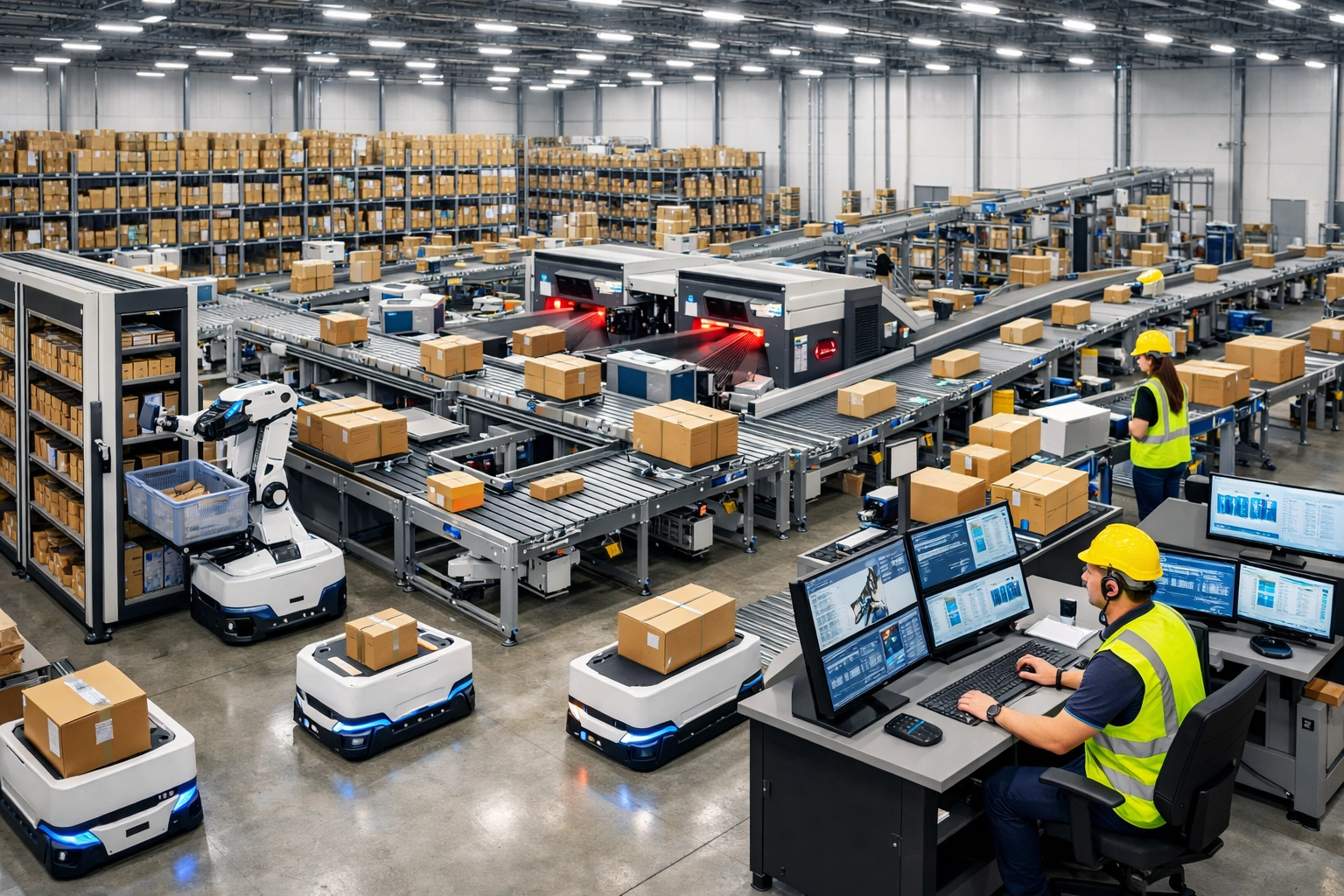

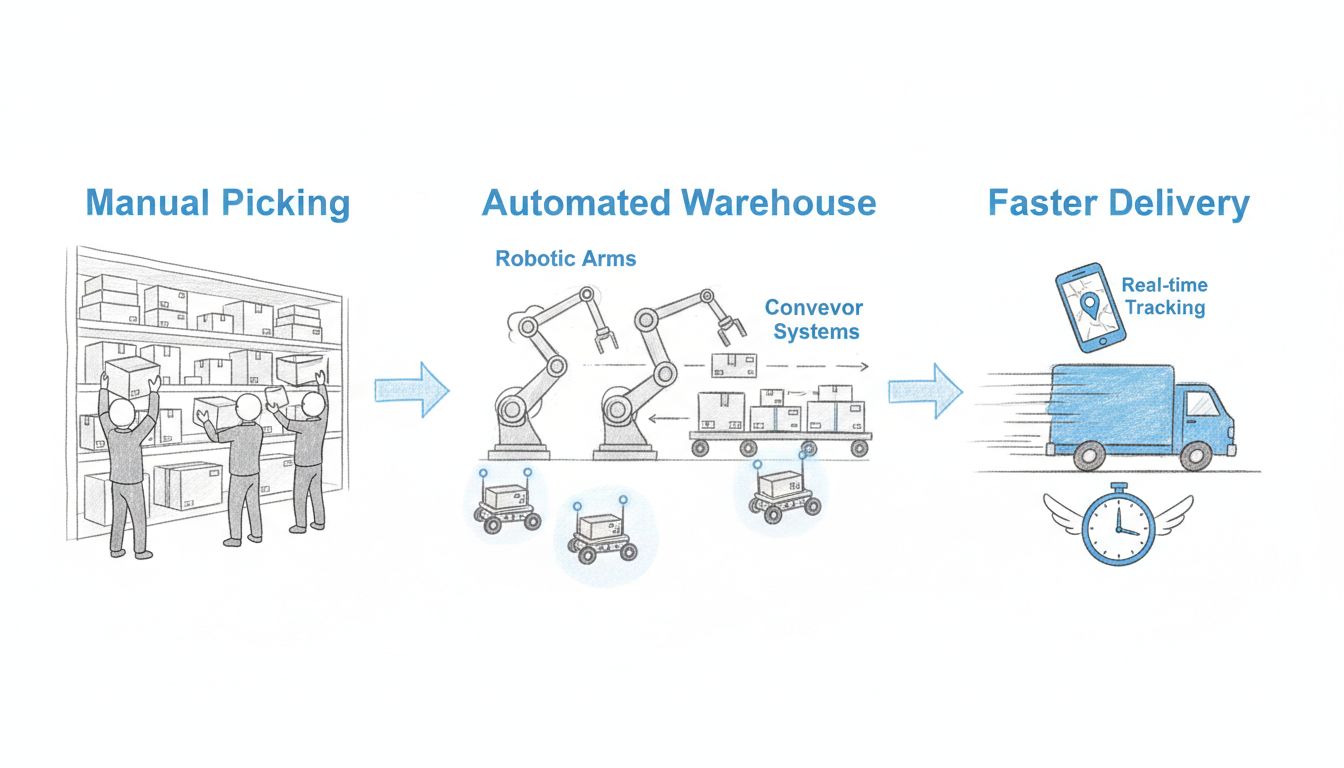
Modern warehouse automation is fundamentally transforming how e-commerce companies handle order fulfillment. High-speed sorting machines equipped with advanced barcode recognition technology can process thousands of packages per hour, while automated conveyor systems route items with precision to their destinations. Collaborative robots (cobots) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) work alongside human employees to pick, pack, and sort items, reducing the time from order placement to shipment readiness. These technologies have enabled companies to achieve 40% efficiency gains in warehouse operations while simultaneously reducing human error and labor costs. Real-time inventory management systems powered by these automated solutions provide instant visibility into stock levels, preventing both stockouts and overstock situations. The integration of these technologies has become essential for e-commerce businesses competing in an increasingly fast-paced market where delivery speed directly impacts customer satisfaction.
The rise of omnichannel retail has fundamentally changed how businesses approach order fulfillment. Retailers now seamlessly integrate their online and offline operations, allowing customers to purchase online and pick up in-store (BOPIS), or conversely, order in-store for home delivery. This approach not only improves customer convenience but also optimizes inventory utilization by leveraging existing physical store locations as mini-fulfillment centers. Third-party logistics (3PL) providers have responded by developing specialized fulfillment services tailored to different product categories—from perishables requiring temperature control to high-value items needing enhanced security. Fulfillment-as-a-Service (FaaS) platforms enable smaller e-commerce businesses to access enterprise-level logistics infrastructure without massive capital investments, leveling the competitive playing field. Real-time inventory synchronization across all channels ensures customers see accurate stock information regardless of where they shop.
| Aspect | Traditional Fulfillment | Omnichannel Fulfillment | Specialized 3PL Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delivery Speed | 5-7 business days | 1-2 days (same-day options) | 2-4 days (optimized) |
| Operational Costs | High (single channel) | Moderate (shared infrastructure) | Lower (economies of scale) |
| Inventory Management | Manual, siloed | Real-time, synchronized | Automated, predictive |
| Customer Experience | Limited options | Flexible, personalized | Specialized handling |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable | Highly scalable |
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have become indispensable tools for modern logistics operations. These technologies analyze vast amounts of real-time data to optimize every aspect of the supply chain, from demand forecasting to route planning. AI-powered systems can predict customer demand with 85-90% accuracy, enabling businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels and reduce carrying costs. Machine learning algorithms continuously improve route optimization, considering factors like traffic patterns, weather conditions, and delivery priorities to minimize fuel consumption and delivery times. Predictive analytics identify patterns in returns data, helping companies improve product descriptions and packaging to reduce return rates. Automated systems now handle customer service inquiries, order tracking, and even returns processing, freeing human resources for more complex tasks.
Key AI Applications in E-Commerce Logistics:
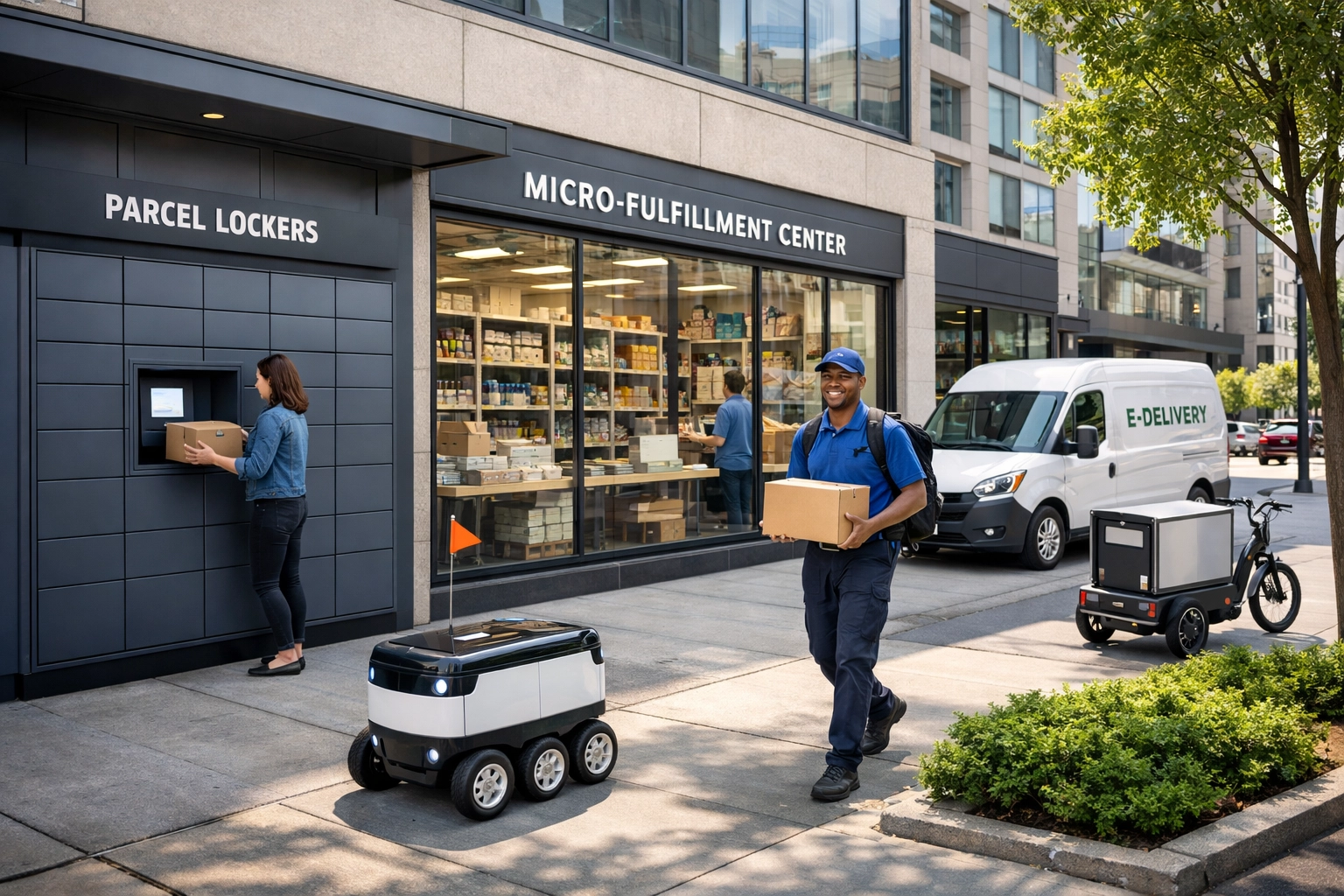

The last mile—the final leg of delivery from distribution center to customer—remains the most expensive and challenging aspect of e-commerce logistics. Micro-fulfillment centers strategically located in urban areas have emerged as a game-changing solution, enabling same-day or next-day delivery by positioning inventory closer to customers. Parcel lockers and PUDO (Pick-Up Drop-Off) networks provide customers with flexible delivery options while reducing failed delivery attempts and associated costs. These self-service solutions have proven particularly effective in dense urban environments where traditional home delivery is inefficient. Autonomous delivery methods, including delivery robots and drones, are being piloted in select markets to further reduce last-mile costs and improve delivery speed. Companies like Amazon and DHL are rapidly expanding their parcel locker networks globally, recognizing that customer convenience directly translates to competitive advantage. The combination of these solutions allows businesses to offer multiple delivery options while maintaining cost efficiency.
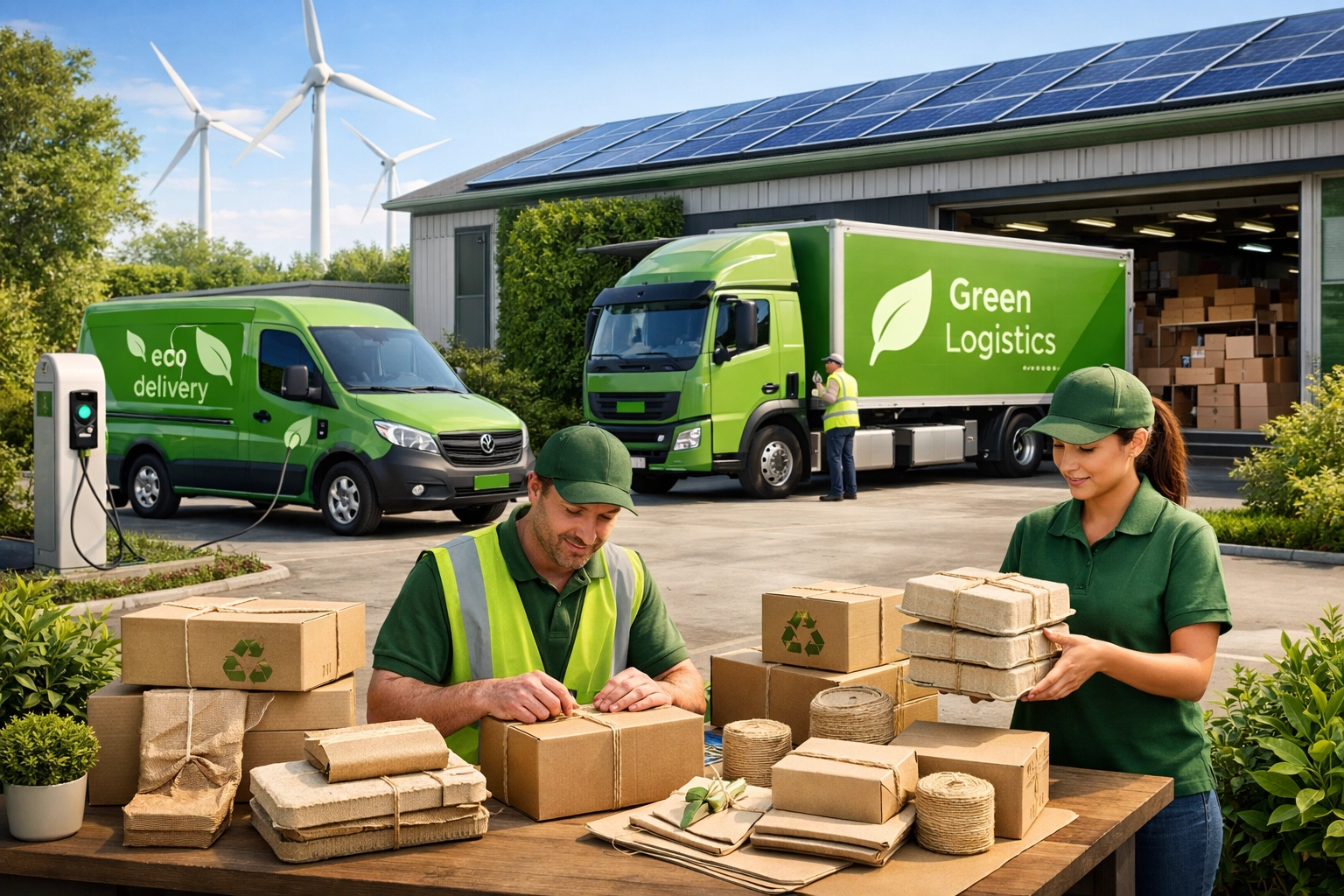

Environmental consciousness is reshaping logistics strategies across the e-commerce industry. Companies are increasingly adopting electric vehicles for last-mile delivery, with some operators reporting 50-70% reductions in carbon emissions compared to traditional diesel-powered fleets. Eco-friendly packaging materials are replacing plastic-heavy solutions, reducing waste while maintaining product protection. Route optimization powered by AI not only improves efficiency but also minimizes fuel consumption and associated emissions. Circular logistics models are gaining traction, where returned products are refurbished, resold, or recycled rather than discarded, creating both environmental and economic benefits. Companies that successfully integrate sustainability into their logistics operations gain competitive advantages through improved brand reputation and customer loyalty. Measuring and reporting carbon footprint metrics has become standard practice, with many businesses setting ambitious targets to achieve carbon neutrality in their logistics operations.
The shift from centralized mega-warehouses to distributed networks of smaller fulfillment centers represents a fundamental change in logistics strategy. Hyper-local fulfillment brings inventory closer to customers, enabling delivery within hours rather than days. Micro-fulfillment centers, often located in urban areas or near high-density customer populations, operate with significantly lower overhead than traditional warehouses while delivering superior speed. On-demand warehousing platforms like Stord and Flowspace provide businesses with flexible, scalable storage solutions without long-term lease commitments, allowing companies to adjust capacity based on seasonal demand. Crowdsourced delivery networks leverage gig workers and local couriers to handle final-mile delivery, providing flexibility and cost efficiency. This decentralized approach reduces transit times from days to hours, improves regional demand management, and allows businesses to respond quickly to local market variations. The result is a more agile, responsive supply chain that better serves customer expectations for speed and convenience.
The e-commerce logistics landscape is experiencing significant consolidation as major players expand their capabilities through mergers and acquisitions. Amazon, Walmart, and Alibaba have invested billions in building vertically integrated logistics networks, controlling everything from warehousing to last-mile delivery. This integration enables these giants to offer faster, cheaper delivery while gaining valuable data insights across their entire supply chains. Smaller e-commerce businesses face increasing pressure to either partner with established 3PL providers or invest in their own logistics infrastructure to remain competitive. The consolidation trend has created opportunities for specialized logistics providers to differentiate themselves through superior service, technology, or industry expertise. Companies that successfully navigate this consolidation landscape are those that leverage technology partnerships, focus on niche markets, or develop unique value propositions that larger players cannot easily replicate.
Returns have become a critical strategic issue in e-commerce, with some product categories experiencing return rates exceeding 50%. Efficient returns management directly impacts profitability and customer satisfaction, making it a key differentiator among e-commerce businesses. Automated returns processing systems streamline the entire reverse logistics process, from return authorization to restocking, significantly reducing handling costs and processing time. Data analytics applied to returns patterns reveal valuable insights—high return rates for specific products may indicate issues with product descriptions, sizing information, or packaging quality. Companies are investing in simplified return processes, offering multiple return options (mail-back, in-store, locker drop-off), and providing instant refunds to build customer loyalty. The environmental impact of returns is also gaining attention, with businesses implementing circular logistics models that refurbish or recycle returned items rather than discarding them. Proactive returns management has become a competitive advantage, with leading companies using returns data to continuously improve their products and customer experience.
Modern e-commerce logistics depends on integrated digital platforms that provide end-to-end visibility and control. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) optimize storage, automate picking processes, and provide real-time inventory visibility. Transport Management Systems (TMS) coordinate shipments, optimize routes, and monitor carrier performance across the entire transportation network. Order Management Systems (OMS) centralize order processing, synchronize inventory across multiple sales channels, and ensure accurate fulfillment. These systems work together to create a unified view of the entire supply chain, enabling data-driven decision-making and rapid problem resolution. Blockchain technology is emerging as a tool for enhancing transparency and traceability, particularly for high-value items or products requiring ethical sourcing verification. Real-time tracking capabilities allow both businesses and customers to monitor shipments at every stage, reducing uncertainty and enabling proactive communication. The integration of these digital solutions has become essential for managing the complexity of modern e-commerce logistics while maintaining the speed and accuracy customers expect.
Warehouse automation uses robotics, conveyor systems, and AI-powered management to streamline order fulfillment. It increases efficiency by 40%, reduces errors, and enables faster processing of orders. This technology allows businesses to handle higher order volumes without proportionally increasing labor costs, making it essential for competitive e-commerce operations.
Omnichannel fulfillment integrates online and offline operations, allowing customers to buy online and pick up in-store (BOPIS), or order in-store for home delivery. This flexibility improves convenience, reduces delivery times, and optimizes inventory utilization by leveraging physical store locations as mini-fulfillment centers.
AI and machine learning optimize demand forecasting (85-90% accuracy), route planning, inventory management, and returns processing. These technologies analyze real-time data to reduce costs, improve delivery times, and enable predictive decision-making. AI also powers customer service automation and personalized delivery options.
Parcel lockers (automated pickup boxes) and PUDO (Pick-Up Drop-Off) networks provide customers with flexible delivery options while reducing failed delivery attempts and costs. They're particularly effective in urban areas where traditional home delivery is inefficient, and they improve customer convenience by allowing 24/7 package pickup.
Sustainable logistics includes using electric vehicles for delivery (reducing emissions by 50-70%), adopting eco-friendly packaging, optimizing routes with AI to minimize fuel consumption, and implementing circular logistics models for returns. These practices reduce environmental impact while often lowering operational costs and improving brand reputation.
Hyper-local fulfillment uses distributed networks of micro-fulfillment centers located near customer populations, enabling same-day or next-day delivery. By positioning inventory closer to customers, businesses reduce transit times from days to hours, improve regional demand management, and provide superior customer experience.
Return rates in e-commerce can exceed 50% in some product categories, making returns management crucial for profitability. Efficient reverse logistics reduces costs, improves customer satisfaction, and provides valuable data insights. Automated returns processing and circular logistics models help businesses turn returns into competitive advantages.
Essential systems include WMS (Warehouse Management Systems) for inventory optimization, TMS (Transport Management Systems) for route planning and carrier management, and OMS (Order Management Systems) for order processing. These integrated platforms provide end-to-end visibility, enable data-driven decisions, and improve operational efficiency across the entire supply chain.
Streamline your affiliate program management and logistics coordination with PostAffiliatePro's powerful platform. Track shipments, manage fulfillment partners, and monitor affiliate performance in real-time.

Discover why automation is critical for e-commerce logistics. Learn how automated systems improve efficiency, accuracy, and delivery speed while reducing operat...

Discover which business workflows can be automated with AI in 2025. Learn about daily performance summaries, commission recalculations, affiliate onboarding, an...
Discover how automation streamlines affiliate marketing by leveraging customer success data for better segmentation, personalization, and real-time campaign opt...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.