Adware in Marketing: A Basic Overview
Adware is often downloaded when people look for another program and people usually do not realize it. Learn more about this potential threat.

Learn what adware does, how it works, and its security risks. Discover how adware tracks your data, slows your device, and how to protect yourself with PostAffiliatePro’s security solutions.
Adware is a type of software that automatically displays or downloads advertising material when a user accesses the internet. It can track browsing habits, slow down devices, redirect searches, and potentially expose users to malicious content or spyware.
Adware, short for advertising-supported software, is a type of software that automatically displays or downloads advertising material when a user accesses the internet. While some adware is legitimate and transparent about its purpose, malicious adware operates without user consent and can pose serious security and privacy risks. Understanding what adware does is essential for protecting your devices, data, and business operations in today’s digital landscape.
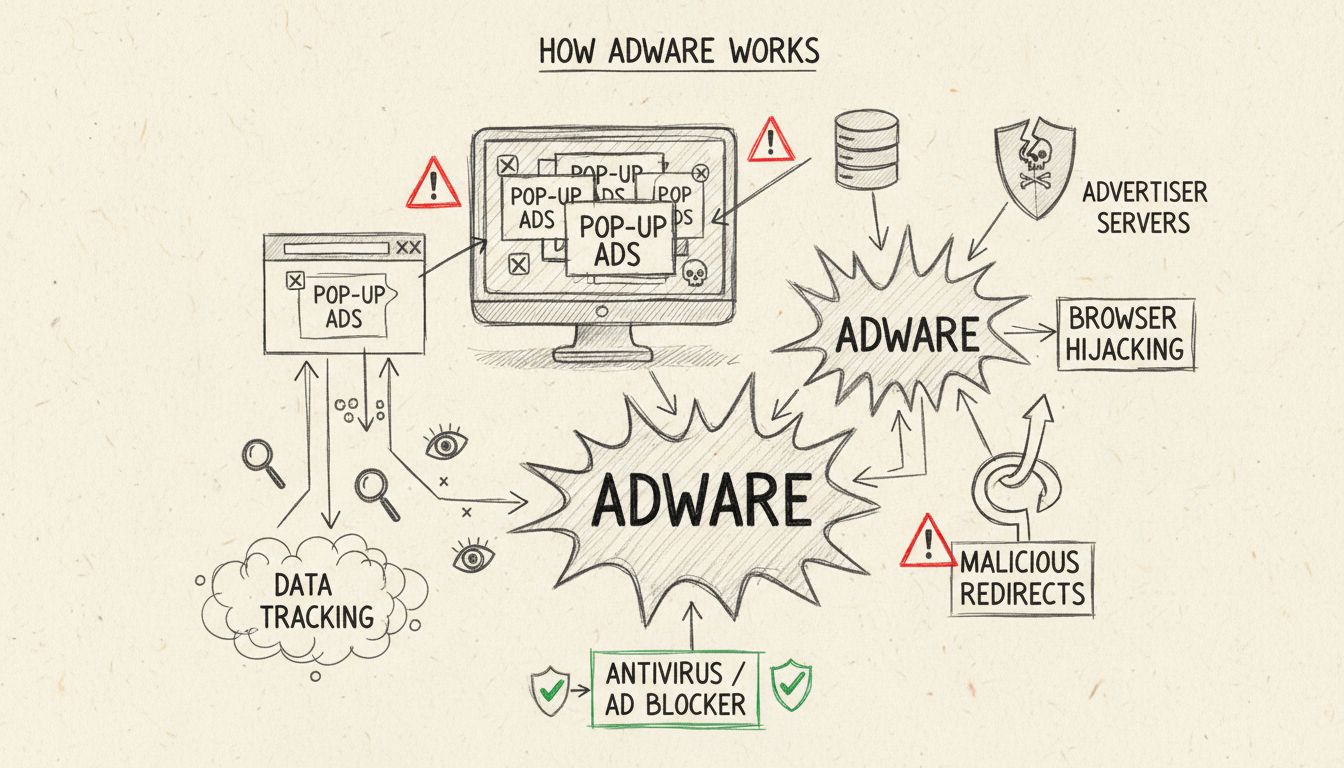
Adware works by installing itself on your device, either through bundled software downloads or by exploiting security vulnerabilities in your operating system or web browser. Once installed, the adware generates revenue for its developers through multiple monetization methods. The primary mechanisms include pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, where developers earn money each time you click on an advertisement, pay-per-view (PPV) where they profit from each ad display, and pay-per-install (PPI) where they receive compensation for each successful installation on a device.
The software operates silently in the background, displaying advertisements through pop-up windows, banners, or browser toolbars. More sophisticated adware variants can hijack your browser homepage, redirect your search queries to sponsored pages, and inject advertisements into legitimate websites you visit. This constant barrage of ads not only disrupts your user experience but also consumes system resources, causing noticeable performance degradation on your device.
One of the most concerning aspects of adware is its ability to track and collect user data without explicit consent. Malicious adware can monitor your browsing history, search queries, websites visited, and even your location information. This collected data is then used to build comprehensive behavioral profiles of users, which are sold to third-party marketers and advertisers. The information gathered can include your shopping habits, interests, online preferences, and usage patterns.
This data collection extends beyond simple browsing behavior. Advanced adware variants can track your keystrokes, monitor your email communications, and record your online activities. While some adware developers claim to anonymize this data, there is no guarantee that personally identifiable information won’t be exposed or misused. The collected data becomes a valuable target for cybercriminals who can use it for identity theft, financial fraud, or other malicious purposes. In business environments, this data collection can compromise sensitive company information and violate data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Adware significantly impacts device performance by consuming valuable system resources. The constant downloading and displaying of advertisements requires processing power, memory, and bandwidth. Users often experience noticeable slowdowns in their computer or mobile device performance, with applications taking longer to load and the system becoming increasingly sluggish. In severe cases, adware can cause system crashes, unexpected restarts, and complete system instability.
The bandwidth consumption is particularly problematic for users with limited data plans or slower internet connections. Each advertisement download consumes data, and in some cases, adware can consume gigabytes of data monthly without the user’s knowledge. This leads to higher internet bills, reduced browsing speeds, and degraded network performance for other applications and users on the same network. For businesses, this performance degradation translates to reduced employee productivity, increased IT support costs, and potential revenue loss.
A common tactic employed by malicious adware is browser hijacking, where the software takes control of your web browser settings. Adware can change your homepage to a fake search engine, modify your default search engine to redirect queries through sponsored pages, and inject unwanted toolbars and extensions into your browser. These hijacked search results often display sponsored links and advertisements before legitimate search results, making it difficult to find the information you actually need.
Browser hijacking also includes the installation of malicious browser extensions that monitor your browsing activity and inject advertisements into web pages. Some adware variants prevent users from modifying their browser settings, making it nearly impossible to remove the hijacked homepage or search engine without specialized removal tools. This loss of control over your browser represents a significant violation of user autonomy and can expose you to phishing websites and malicious content.
| Adware Type | Characteristics | Threat Level | Distribution Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legitimate Ad-Supported Software | Transparent, user-consented, minimal tracking | Low | Official app stores, legitimate downloads |
| Potentially Unwanted Programs (PUPs) | Deceptive installation, aggressive ads, moderate tracking | Medium | Bundled with free software, misleading installers |
| Malicious Adware | Hidden installation, extensive tracking, spyware components | High | Exploit kits, malicious websites, compromised downloads |
| Browser Hijackers | Homepage/search engine changes, forced redirects | High | Bundled software, fake updates, drive-by downloads |
| Ad Clicker Malware | Clicks ads without user knowledge, subscribes to services | Critical | Malicious apps, compromised websites, email attachments |
While adware itself may seem like merely an annoyance, it frequently serves as a gateway for more dangerous malware. Malicious adware can contain vulnerabilities that cybercriminals exploit to install additional malware such as spyware, trojans, ransomware, or viruses. The adware essentially opens a door for attackers to compromise your system further. Additionally, adware can be used to carry out “malvertising” attacks, where malicious advertisements are used to distribute malware to unsuspecting users.
The combination of adware with spyware is particularly dangerous, as it creates a comprehensive surveillance tool that monitors all user activities while displaying advertisements. This dual-purpose malware can steal passwords, financial information, and sensitive personal data. In business environments, this combination can lead to corporate espionage, data breaches, and significant financial losses. The presence of adware on a system should be treated as a warning sign that your device may be compromised and vulnerable to additional attacks.
Mobile devices, particularly Android phones, are increasingly targeted by adware developers. Many free applications available on app stores bundle adware frameworks within their code, often without the developer’s full understanding of the data collection scope. Users download these apps expecting legitimate functionality but instead receive aggressive advertising and extensive tracking. Mobile adware can drain battery life, consume data allowances, and display intrusive notifications that interrupt the user experience.
Android adware is particularly problematic because it can request extensive permissions that allow it to access location data, contacts, photos, and other sensitive information. Some mobile adware variants can even subscribe users to premium services without their knowledge, resulting in unexpected charges on their phone bills. The mobile app ecosystem, while generally safer than downloading from unknown websites, still contains numerous adware-laden applications that pass initial security reviews. Users must carefully review app permissions and read user reviews before installing applications to avoid adware-infected apps.
Recognizing the signs of adware infection is crucial for taking prompt action. Common indicators include an unexpected change in your browser’s homepage or default search engine, the appearance of new toolbars or extensions you didn’t install, and an overwhelming increase in pop-up advertisements even when not actively browsing. Your device may experience significant performance degradation, with applications crashing frequently and the system becoming increasingly unstable. Web pages may display incorrectly or redirect to unfamiliar websites, and you may notice new applications installed that you don’t remember downloading.
On mobile devices, signs of adware infection include apps taking longer to load, rapid battery drain, unexpected data usage spikes, and numerous ad notifications appearing throughout the day. You may also notice apps you don’t remember installing or unexpected charges on your phone bill. Some adware is particularly aggressive and embeds itself deep within the system using rootkit technology, making it extremely difficult to detect and remove without specialized tools. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to take immediate action to scan and clean your device.
Removing adware requires a multi-faceted approach depending on the severity of the infection. For less severe cases, you can attempt manual removal by uninstalling suspicious programs from your system, removing unwanted browser extensions, and resetting your browser settings to default. However, many adware variants are designed to resist manual removal and may reinstall themselves even after deletion. Professional antivirus and anti-malware software is often necessary to completely remove stubborn adware infections.
Prevention is significantly more effective than removal. Keep all software, operating systems, and browsers updated with the latest security patches, as these updates often close vulnerabilities that adware exploits. Download software only from trusted sources such as official websites and legitimate app stores. Read software installation prompts carefully and uncheck any boxes that opt you into installing additional software or adware. Use reputable antivirus software that includes adware detection and removal capabilities. Enable pop-up blockers in your browser and consider using browser extensions that block advertisements and tracking scripts. Finally, practice safe browsing habits by avoiding suspicious websites, not clicking on unknown links, and being cautious with email attachments.
For businesses, adware represents a significant security and operational threat. Infected employee devices can compromise network security, expose sensitive company data, and violate compliance requirements. Adware can redirect employees to malicious websites, expose them to phishing attacks, and potentially install spyware that monitors business communications. The performance degradation caused by adware reduces employee productivity and increases IT support costs. Additionally, if customer-facing systems become infected with adware, it can damage the company’s reputation and customer trust.
Enterprises should implement comprehensive endpoint protection solutions that detect and prevent adware installation. Regular security awareness training for employees can reduce the likelihood of accidental adware installation through social engineering or deceptive downloads. Network monitoring tools can identify suspicious traffic patterns associated with adware activity. Implementing strict software installation policies and using mobile device management solutions can prevent unauthorized applications from being installed on company devices. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments help identify and remediate potential adware threats before they cause significant damage.
PostAffiliatePro provides comprehensive affiliate tracking and fraud detection to protect your business from malicious activities. Secure your affiliate network with advanced monitoring and real-time threat detection.
Adware is often downloaded when people look for another program and people usually do not realize it. Learn more about this potential threat.
Learn how adware harms your PC, including performance degradation, privacy risks, and security vulnerabilities. Discover detection methods and removal strategie...
Learn how to earn money from pay-per-click advertising. Discover PPC strategies, platforms, and proven methods to monetize your website with PostAffiliatePro.