How to Check Your Website's Loading Time: Complete Guide to Speed Testing Tools
Learn how to check your website's loading time using free and paid tools like Pingdom, Google PageSpeed Insights, and GTmetrix. Discover key metrics, benchmarks...

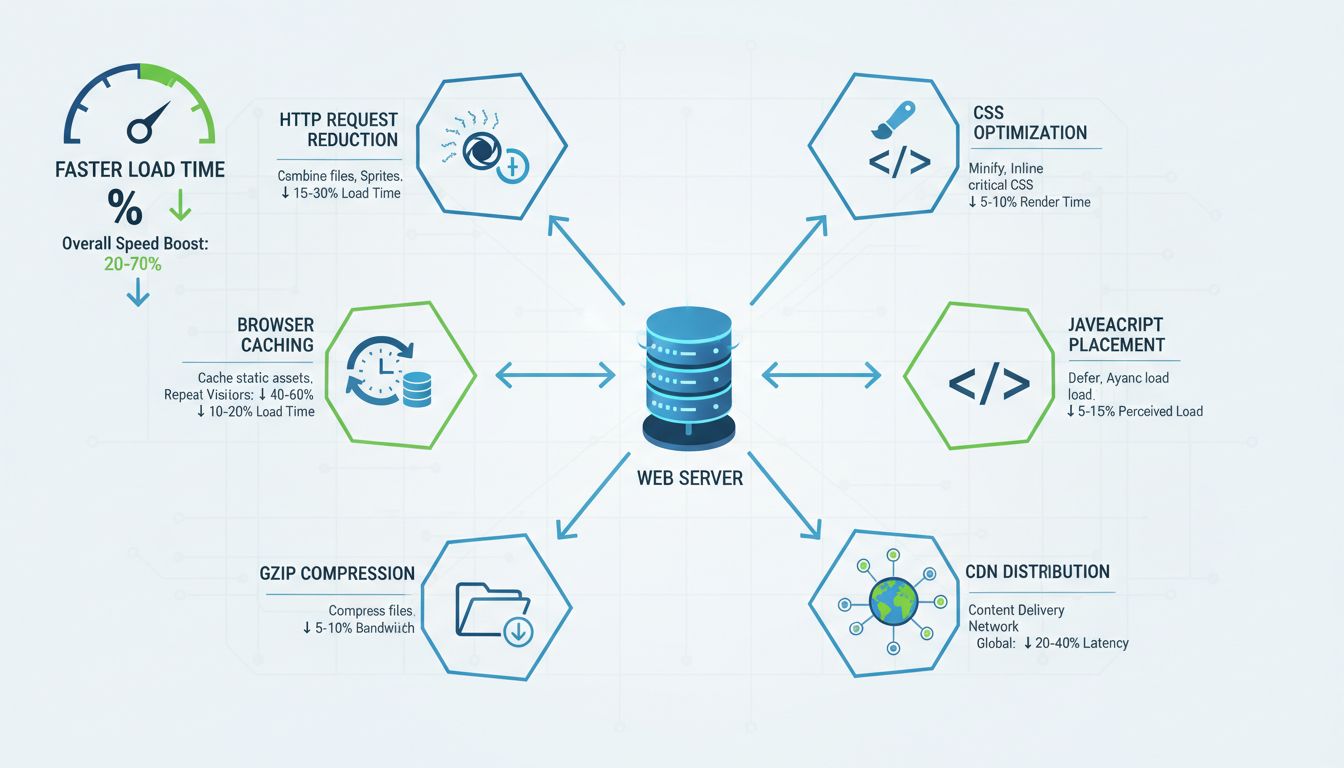
Discover the most effective website speed optimization techniques including HTTP request reduction, image optimization, caching, compression, and CDN strategies to boost performance and conversions.
The top methods to speed up a website include reducing HTTP requests, optimizing images, enabling browser caching, compressing files with Gzip or Brotli, optimizing CSS and JavaScript, improving JavaScript placement, using a Content Delivery Network (CDN), and choosing quality web hosting. These techniques can reduce load times by 50% or more and significantly improve user experience and SEO rankings.
Website speed has become a critical factor in determining online success. Research from Google and industry leaders consistently shows that every additional second of load time results in significant user abandonment rates. The BBC discovered they lost an additional 10% of users for every additional second their site took to load, while Rakuten 24 increased revenue per visitor by 53.37% and conversion rates by 33.13% through Core Web Vitals optimization. PostAffiliatePro recognizes that speed optimization is essential not just for user experience, but for business outcomes including conversion rates, bounce rates, and overall revenue generation.
The relationship between performance and business success is undeniable. When websites load quickly and respond to user input promptly, they engage and retain users significantly better than slow-loading alternatives. Mobile users are particularly demanding, expecting pages to load almost instantly on their devices. Implementing comprehensive speed optimization strategies requires understanding multiple interconnected techniques that work together to reduce load times and improve overall site performance.
HTTP requests represent one of the most impactful factors in page load time. Each element on a webpage—images, stylesheets, JavaScript files, fonts, and other resources—requires a separate HTTP request to the server. The more requests made, the longer the browser must wait to assemble and render the complete page. Modern websites often make 50-100+ HTTP requests, which can significantly slow down load times, especially on slower connections or mobile networks.
To reduce HTTP requests effectively, consider combining multiple CSS files into a single stylesheet and merging JavaScript files where possible. Image sprites combine multiple small images into one larger image file, reducing the number of image requests dramatically. Removing unnecessary elements like unused fonts, outdated JavaScript libraries, and redundant stylesheets can eliminate wasteful requests. Additionally, using inline SVG graphics instead of separate image files for icons and simple graphics reduces request counts. HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 protocols improve this situation by allowing multiplexing—multiple requests over a single connection—but reducing the total number of requests remains fundamental to optimization.
Images typically comprise 50-80% of a webpage’s total file size, making image optimization one of the highest-impact optimization strategies. Unoptimized images can add megabytes to page size, creating significant performance bottlenecks. Modern image optimization involves multiple complementary techniques working together to reduce file sizes without compromising visual quality.
Selecting the appropriate file format is crucial: JPEG works best for photographs and complex images with many colors, PNG is ideal for images requiring transparency or simple graphics, and WebP provides superior compression ratios (25-35% smaller than JPEG) while maintaining quality. Tools like ImageOptim, TinyPNG, and Google’s Squoosh can compress images without visible quality loss. Responsive images using the srcset attribute allow browsers to load appropriately sized images based on device screen size and resolution, preventing unnecessary downloads of oversized images on mobile devices. Lazy loading defers image loading until they enter the user’s viewport, dramatically reducing initial page load time. Modern lazy loading implementations using the loading="lazy" attribute require no JavaScript and provide native browser support across all modern browsers.
| Image Optimization Technique | File Size Reduction | Implementation Complexity | Browser Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| WebP Format | 25-35% | Medium | 95%+ modern browsers |
| Compression (Lossy) | 40-60% | Low | All browsers |
| Responsive Images (srcset) | 30-50% on mobile | Medium | 95%+ modern browsers |
| Lazy Loading | 50-70% initial load | Low | 95%+ modern browsers |
| Image Sprites | 20-40% | High | All browsers |
Browser caching allows visitors’ browsers to store static assets locally, eliminating the need to re-download unchanged resources on subsequent visits. This technique provides dramatic performance improvements for returning visitors, with potential load time reductions of 50% or more. Implementing effective caching requires setting appropriate HTTP headers that instruct browsers how long to cache specific resources.
The Cache-Control header provides granular control over caching behavior, allowing you to specify maximum age values for different resource types. Static assets like images, CSS, and JavaScript files that rarely change should have long cache expiration periods (typically 1 year or more), while HTML files should have shorter expiration times to ensure users receive updated content. The Expires header provides an alternative method using absolute dates. ETags (Entity Tags) enable more sophisticated cache validation by comparing file versions rather than just timestamps, ensuring users receive updated content when files change while still leveraging cached versions when appropriate.
Service workers represent an advanced caching strategy, particularly valuable for progressive web apps. They intercept network requests and serve cached content when available, providing offline functionality and dramatically improved performance. Modern implementations using service workers can reduce load times by 70-80% for returning visitors while providing seamless offline experiences.
Gzip and Brotli compression reduce the size of text-based files—HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—by 50-70%, significantly decreasing bandwidth consumption and transfer times. Gzip has been the standard compression method for years and is supported by virtually all modern browsers and servers. Brotli, developed by Google, provides even better compression ratios (10-20% better than Gzip) and is now supported by 95%+ of modern browsers.
Enabling compression on your server requires minimal configuration. Most modern web servers including Apache, Nginx, and IIS support Gzip compression through simple configuration directives. Brotli support requires slightly more setup but provides superior compression. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix can verify whether compression is properly enabled on your site. The compression process happens transparently—browsers automatically decompress content—making it a zero-effort optimization for users while providing substantial performance benefits.
Unoptimized CSS contributes to bloated file sizes and slow page rendering. CSS optimization involves multiple complementary techniques that reduce file size and improve rendering performance. Minification removes unnecessary whitespace, comments, and redundant code, typically reducing CSS file sizes by 20-30%. Tools like CSSNano and CleanCSS automate this process while maintaining functionality.
Critical CSS optimization identifies and inlines the CSS required for above-the-fold content directly in the HTML <head>, allowing the browser to render visible content immediately without waiting for external stylesheet downloads. This technique can reduce perceived load time by 30-50%. Removing unused CSS using tools like PurgeCSS or UnCSS eliminates dead code that serves no purpose, often reducing CSS file sizes by 40-60%. Modern CSS frameworks like Tailwind CSS are specifically designed to minimize unused CSS through utility-first approaches. Organizing CSS into logical modules and using CSS-in-JS solutions where appropriate can further optimize rendering performance.
JavaScript can block page rendering, preventing the browser from displaying content until scripts finish downloading and executing. This render-blocking behavior significantly impacts perceived load time and user experience. Strategic JavaScript placement and loading techniques dramatically improve performance without sacrificing functionality.
Placing non-critical JavaScript files just before the closing </body> tag allows the browser to render page content before executing scripts. The async attribute downloads JavaScript files in parallel with page rendering and executes them immediately upon completion, suitable for independent scripts like analytics. The defer attribute downloads files in parallel but delays execution until after the HTML document finishes parsing, ideal for scripts that depend on DOM elements. Code splitting breaks large JavaScript bundles into smaller chunks loaded only when needed, reducing initial load time. Minification removes unnecessary characters from JavaScript, typically reducing file sizes by 30-40%.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) distribute website content across geographically dispersed servers worldwide, serving content from locations nearest to users. This dramatically reduces latency and network distance, improving load times for users regardless of their geographic location. CDNs can reduce load times by 50% or more, particularly for users far from your primary server.
CDN providers like Cloudflare, AWS CloudFront, and KeyCDN maintain networks of edge servers that cache your static content. When users request resources, the CDN serves content from the nearest edge server rather than your origin server, reducing round-trip time and bandwidth consumption. Modern CDNs provide additional benefits including DDoS protection, SSL/TLS termination, and automatic image optimization. Implementing a CDN typically requires minimal configuration—often just updating DNS records or configuring your web server to serve static assets through the CDN.
The quality of your web hosting significantly impacts site performance. Shared hosting environments where multiple websites share server resources can result in performance degradation when other sites experience traffic spikes. Upgrading to more powerful hosting solutions like Virtual Private Servers (VPS) or dedicated servers provides dedicated resources and better performance isolation.
Modern hosting providers offer specialized solutions optimized for specific platforms. Managed WordPress hosting includes server-level caching, automatic updates, and WordPress-specific optimizations. Application-specific hosting for platforms like Node.js, Python, or PHP provides runtime environments optimized for those technologies. Server location matters significantly—hosting your site in a data center geographically close to your primary user base reduces latency. Many providers now offer multiple data center locations, allowing you to choose optimal server placement. PostAffiliatePro’s infrastructure is built on high-performance servers designed to handle demanding affiliate tracking and reporting workloads with minimal latency.
Dynamic websites relying on databases require optimization at the database level to maintain performance. Excessive queries, missing indexes, and redundant data can create significant performance bottlenecks. Database optimization involves identifying slow queries, adding appropriate indexes, and implementing caching strategies.
Query optimization ensures database queries execute efficiently by using appropriate indexes, avoiding N+1 query problems, and selecting only necessary data. Database indexing dramatically speeds up query execution—properly indexed tables can execute queries 10-100x faster than unindexed tables. Caching frequently accessed data at the database level using tools like Redis or Memcached reduces database load and improves response times. For WordPress sites, plugins like WP-Optimize clean up unnecessary data including old revisions, spam comments, and transients, improving database performance. Regular database maintenance including optimization and defragmentation ensures consistent performance over time.
Proper performance measurement requires using appropriate tools and understanding their metrics. Google PageSpeed Insights measures performance based on Core Web Vitals including Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). GTmetrix combines Google PageSpeed Insights and YSlow metrics, providing comprehensive analysis. Pingdom offers waterfall analysis showing individual resource load times. WebPageTest provides advanced testing including multi-step transactions and video capture.
Consistent measurement methodology is essential for tracking improvements. Testing from the same geographic location, running tests multiple times to ensure cache population, and using the same tool for ongoing measurements ensures reliable data. Cache headers should show “HIT” status for static assets, indicating content is serving from cache rather than origin servers. Monitoring tools like New Relic provide continuous performance monitoring, alerting you to performance degradation before users notice issues.
Implementing website speed optimization requires a strategic approach prioritizing high-impact techniques. Start by measuring current performance using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to identify the biggest bottlenecks. Image optimization and enabling caching typically provide the highest return on investment with minimal implementation effort. Implementing a CDN provides dramatic improvements for geographically distributed users. Progressive enhancement—implementing optimizations incrementally and measuring results—ensures you focus efforts on techniques providing the greatest benefit.
Testing is critical throughout the optimization process. Run speed tests multiple times to ensure cache population, test from different geographic locations to verify CDN effectiveness, and monitor real user metrics through tools like Google Analytics. Document baseline performance before implementing changes, then measure improvements after each optimization. This data-driven approach ensures optimization efforts produce measurable business results including improved conversion rates, reduced bounce rates, and increased user engagement.
Just like website speed impacts user experience, PostAffiliatePro's high-performance affiliate management platform ensures your commission tracking, payouts, and reporting run at lightning speed. Optimize your entire affiliate program with our proven solution.
Learn how to check your website's loading time using free and paid tools like Pingdom, Google PageSpeed Insights, and GTmetrix. Discover key metrics, benchmarks...
Discover how page load time directly affects affiliate conversions. Learn why fast-loading pages reduce bounce rates, improve user experience, and increase affi...
Google found that 70% of pages took up to 7 seconds to load, causing many businesses to lose revenue. Learn how to speed up your website with 7 effective techni...